Method for treating zinc leaching residues
A technology of zinc leaching slag and weight percentage, which is applied in the field of chlorination roasting treatment of zinc leaching slag, can solve the problems of adverse effects of zinc, low iron yield, high zinc content, etc., and achieve the goals of reducing dosage, increasing air-fuel ratio, and reducing dosage Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
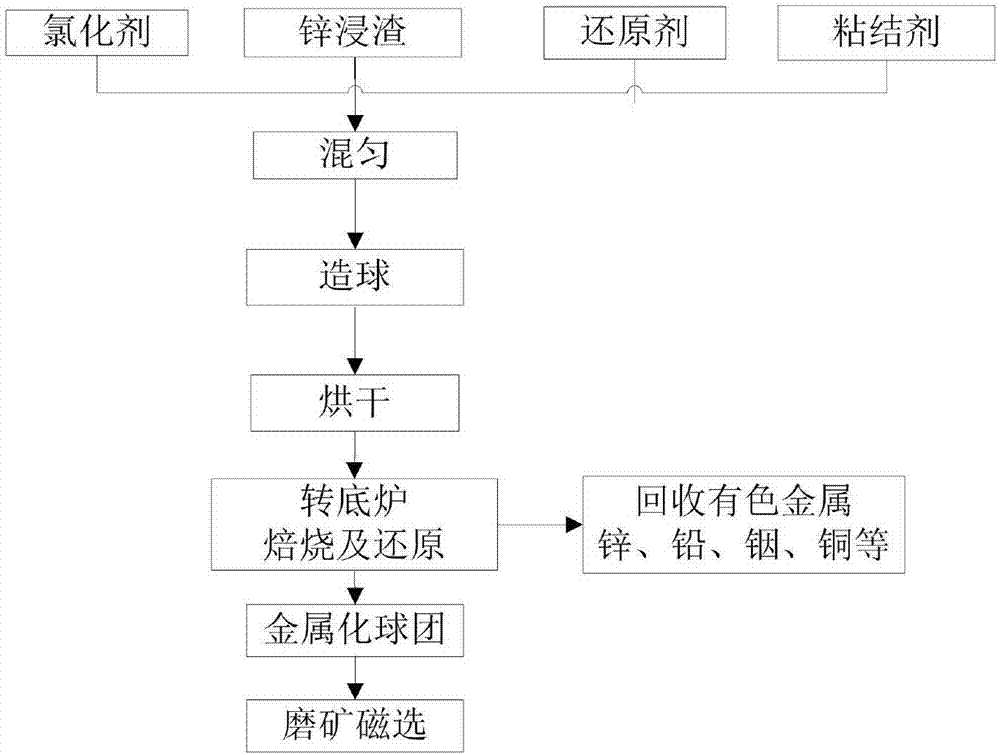
[0050] use figure 1 The process flow of the recovery of lead, zinc, indium, copper and iron in the zinc leaching slag, the composition and content of the zinc leaching slag are: total iron is 32.02wt%, zinc content is 17.52wt%, lead content is 4.23wt%, indium The content is 0.21wt%, the copper content is 1.5wt%, the size is broken to less than 200 mesh accounted for more than 80%, the chlorinating agent used is CaCl 2 , The particle size is between 200 mesh and 100 mesh, the addition amount is 10% of the zinc leaching residue, the reducing agent used is anthracite: fixed carbon 82.56%, volatile matter 6.49%, ash 10.02%, moisture 0.93%, sulfur 0.51%, add The amount is 5% of the zinc leaching slag, the binder used is starch solution, the added amount is 6% of the zinc leaching slag, the four are fully mixed and then pelletized, and then transferred to the rotary hearth furnace to control its chlorination The roasting and reduction process, the chlorination roasting and reduction ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The method for treating zinc leaching slag in this implementation is the same as in Example 1, but the process parameters are different, as follows:
[0053] The composition and content of the zinc leaching slag used are: 35.72wt% of total iron, 16.97wt% of zinc, 3.94wt% of lead, 0.18wt% of indium, 1.8wt% of copper, and crushed particle size below 200 mesh More than 80%, the chlorinating agent used is CaCl 2 , The particle size is between 200 mesh and 100 mesh, the addition amount is 10% of the zinc leaching residue, the reducing agent used is anthracite: fixed carbon 82.56%, volatile matter 6.49%, ash 10.02%, moisture 0.93%, sulfur 0.51%, add The amount is 5% of the zinc leaching slag, the binder used is starch solution, the added amount is 6% of the zinc leaching slag, the four are fully mixed and then pelletized, and then transferred to the rotary hearth furnace to control its chlorination The roasting and reduction process, chlorination roasting and reduction process a...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The method for treating zinc leaching slag in this implementation is the same as in Example 1, but the process parameters are different, as follows:
[0056] The composition and content of the zinc leaching slag used are: total iron is 39.72wt%, zinc content is 19.97wt%, lead content is 4.94wt%, indium content is 0.25wt%, copper content is 2.0wt%, and the particle size is broken to below 200 mesh The chlorinating agent used is NaCl, the particle size is between 200 mesh and 100 mesh, the addition amount is 10% of the zinc leaching residue, and the reducing agent used is anthracite: fixed carbon 82.56%, volatile matter 6.49%, ash content 10.02%, moisture 0.93%, sulfur 0.51%, the addition amount is 15% of the zinc leaching slag, the binder used is starch solution, the addition amount is 6% of the zinc leaching slag, the four are fully mixed and then pelletized, then It is sent to the rotary hearth furnace to control its chlorination roasting and reduction process in sections...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com