Iris lacteal heavy metal ATP enzyme transport protein I1HMA2 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
A technology for transporting proteins and heavy metals, which is applied in the fields of molecular biology and genetic engineering, can solve problems that have not been reported, improve the transport capacity, improve the repair efficiency and practicability, and enhance the tolerance and enrichment of tobacco to cadmium effect of ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The cloning of embodiment 1 Spine heavy metal ATPase transporter gene IlHMA2
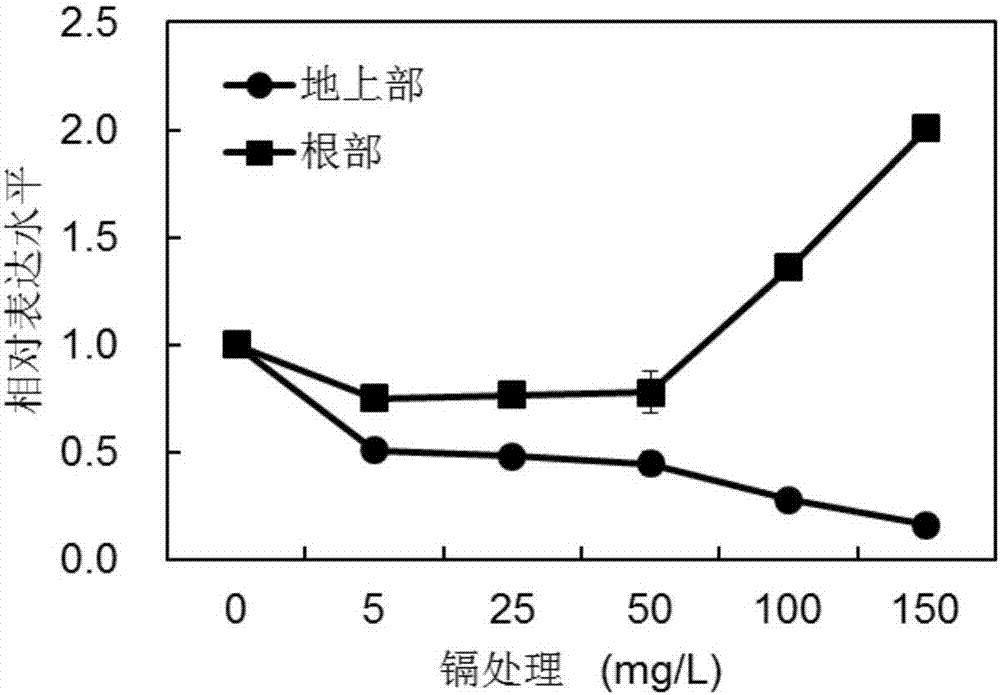
[0028] Cultivate the water cultured to 8 weeks of horseshoe seedlings in 100mg / L CdCl 2 2.5H 2 Stress treatment in the Hoagland nutrient solution of O for 24 hours, cut the roots and wash them with sterile water, put them on sterile filter paper to absorb the water, weigh 100 mg of fresh roots, grind them fully in liquid nitrogen, and follow the TaKaRa MiniBEST Plant RNA Extraction Kit The total RNA was extracted according to the kit instructions, and the concentration was measured by a Quawell5000 nucleic acid protein analyzer, and the integrity of the RNA was detected by 1.2% formaldehyde denaturing gel electrophoresis. Take 1 μg of total RNA, and perform reverse transcription according to the instructions of the TaKaRaPrimeScriptRTase cDNA first-strand synthesis kit. , to synthesize cDNA.
[0029] According to the HMA nucleotide sequence of the plant heavy metal ATPase transporter gene pub...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 The predictive analysis of the structural characteristics of the heavy metal ATPase transporter IlHMA2
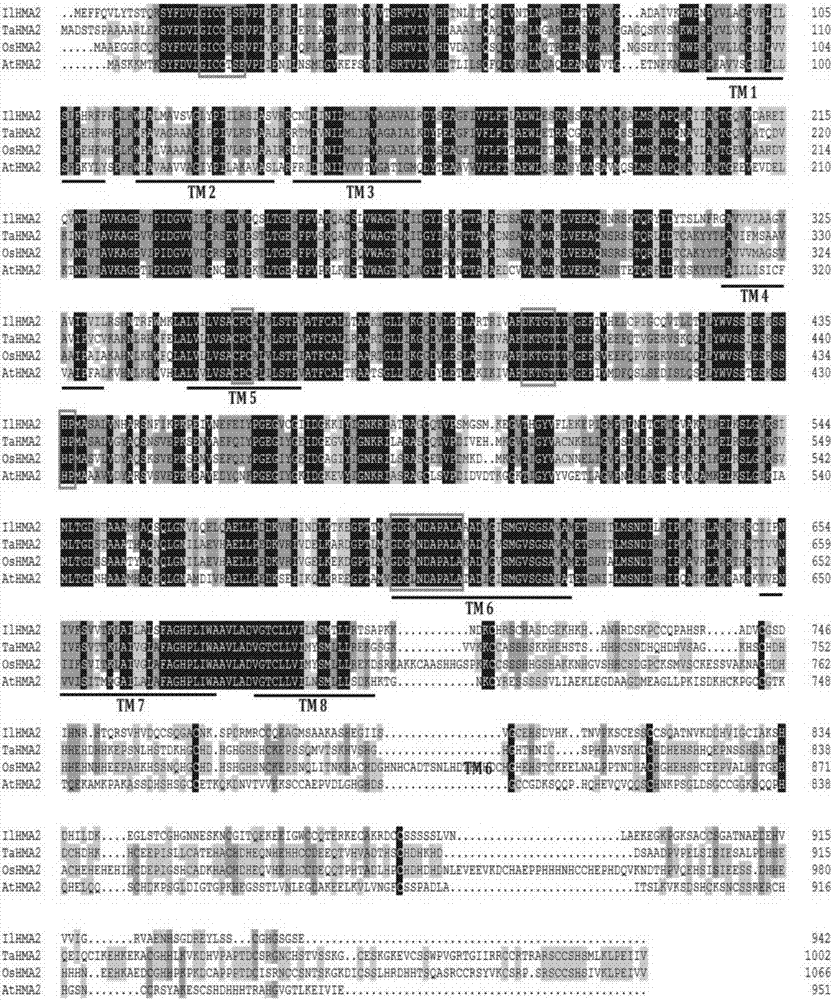
[0044] Using the TMpred program (http: / / www.ch.embnet.org / software / TMPRED_form.html) to predict the transmembrane region of IlHMA2 in S. chinensis, IlHMA2 has 8 transmembrane regions (TM1-TM8). The homology between IlHMA2 and the HMA2 proteins of wheat, rice and Arabidopsis plants was 68%, 66% and 55% respectively through the blast comparison of the NCBI website, and the function prediction of the IlHMA2 protein showed that it contained heavy metal P 1B -ATPase-specific GICCPSE, CPC, DKTGT, HP and GDGMNDAPAL motifs ( figure 1 ). Among them, the motif with metal binding domain contained in the N-terminus is GICCPSE, which belongs to the functional domain of metal-related regulation; the CPC site is responsible for metal ion conduction, and the DKTGT is the phosphorylation binding site for enzyme phosphorylation; the HP site Involved in the translocation of...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Phylogenetic tree analysis of embodiment 3 Malus sinensis heavy metal ATPase transporter gene IlHMA2
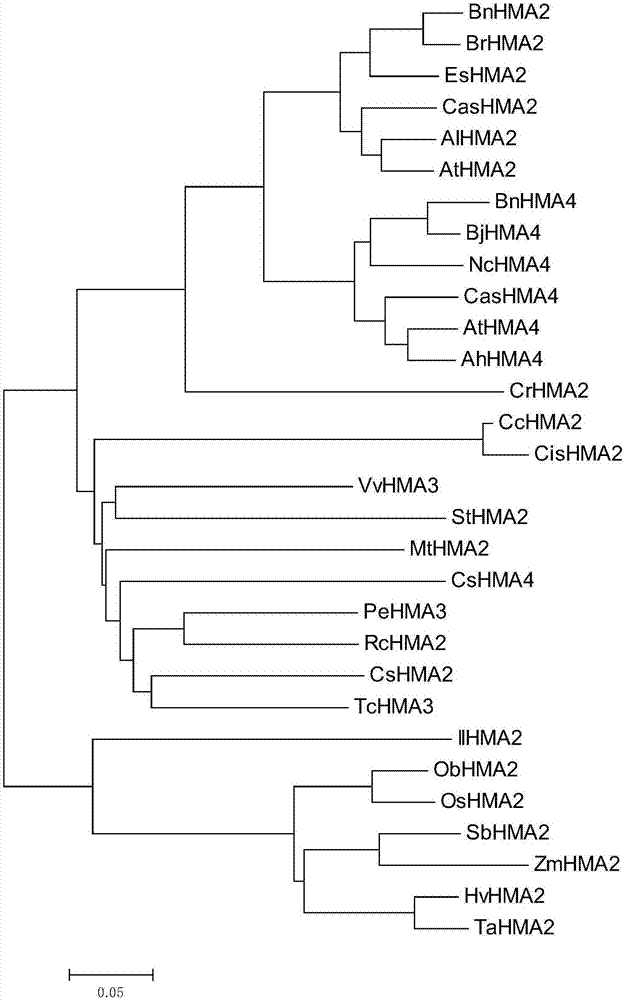
[0046] In order to analyze the phylogenetic relationship between the IlHMA2 gene and other plant HMA genes, using MEGA 6.0 software, other plants (Arabidopsis AhHMA2, Arabidopsis lyre AlHMA2, Arabidopsis AtHMA2 / 4, mustard BjHMA4, turnip BrHMA2, Rapeseed BnHMA2 / 4, Camelina CasHMA2 / 4, Clementine CcHMA2, Orange CisHMA2, Shepherd’s Purse CrHMA2, Cucumber CsHMA2 / 4, Behenia EsHMA2, Barley HvHMA2, IlHMA2 IlHMA2, Medicago truncatula MtHMA2, Celery NcHMA4 Phylogenetic tree analysis of the HMA genes of Oryza sativa, short-anther wild rice ObHMA2, rice OsHMA2, Populus euphratica PeHMA2, castor bean RcHMA2, sorghum SbHMA2, potato StHMA2, wheat TaHMA2, cacao TcHMA3, grape VvHMA3, and maize ZmHMA2). The results showed that IlHMA2 was closely related to monocotyledonous plants such as wheat TaHMA2 gene, rice OsHMA2 gene, and barley HvHMA2 gene, while its genetic relationship with dic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com