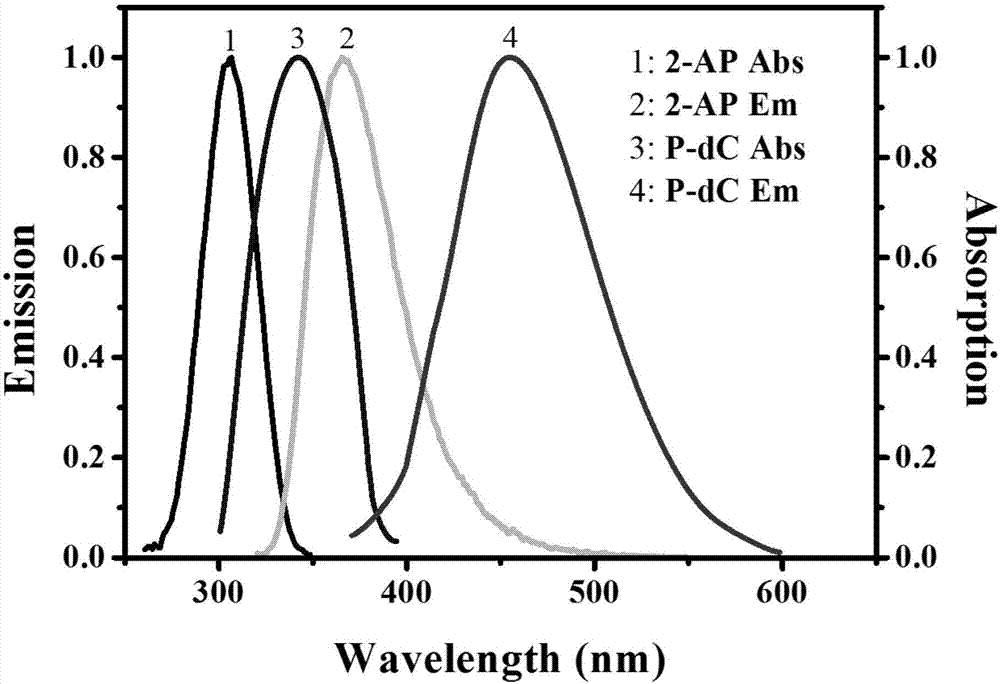
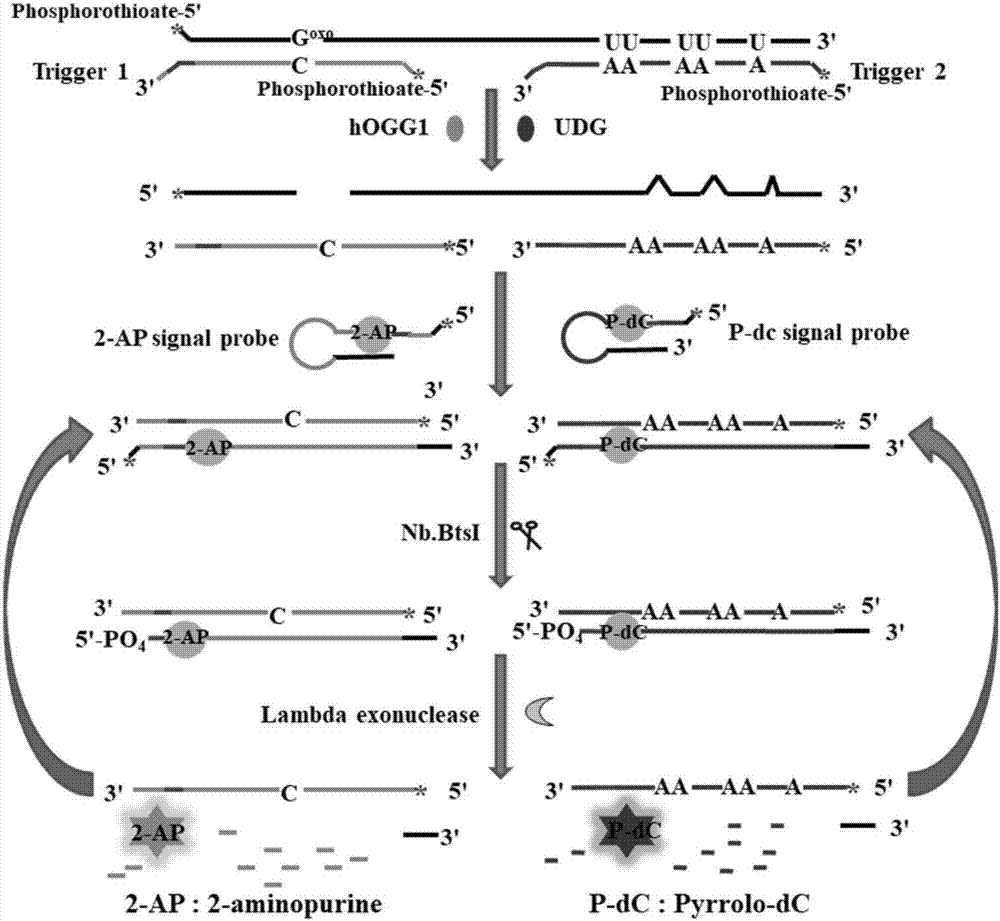
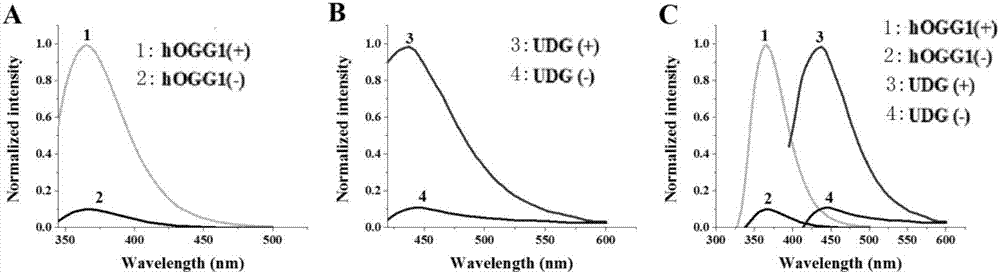
Method for ultra-sensitively simultaneously detecting multiple DNA glycosylases by using intrinsic fluorescent nucleotide
A glycosylase and nucleotide sequence technology, applied in the field of DNA glycosylase detection, can solve the problems of complex design and high cost, and achieve the effects of good specificity, high sensitivity, and long reaction time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Example 1: Detection of HOGG1 and UDG
[0070] (1) Preparation of DNA stock solution: add 10 micromoles per liter of bifunctional DNA probe, 10 micromoles per liter of trigger probe 1 and 10 micromoles per liter of trigger probe 2 into a solution containing 50 millimoles per liter Sodium chloride (NaCl), 10 mmol per liter of Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) and 1 mmol per liter of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) were incubated at 95°C for 5 minutes, then slowly cooled to room temperature to form a sandwich structure. 10 micromoles per liter of the 2-AP signal probe and 10 micromoles per liter of the P-dC signal probe were contained in 1.5 millimoles per liter of magnesium chloride (MgCl 2 ) and 10 millimolar Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) buffer, incubated at 95°C for 5 minutes, and then slowly cooled to room temperature to fold the 2-AP signal probe and the P-dC signal probe to form a hairpin structure . The obtained DNA stock solution was stored at -20°C for future use.
[0071] (2) F...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Embodiment 2: actual sample analysis
[0073] Human cervical cancer cells (HeLa) were used to detect hOGG1 and UDG.
[0074] 1. Test method:
[0075] (1) Cell culture and preparation of cell extracts: human cervical cancer cell line (HeLa) was placed in Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin , at 37°C with 5% CO 2 cultivated in a moist atmosphere. Cell numbers were counted by a Countstar cell counter. Cell extracts were extracted using a nuclear extraction kit (ActiveMotif) according to the instructions.
[0076] (2) The hOGG1 and UDG in the cell extract were detected according to the method in Example 1.
[0077] 2. Test results:
[0078] For hOGG1, the normalized fluorescence intensity increases with the number of HeLa cells, linearly in the range of 5 to 10,000 cells ( Figure 7 A). The regression equation is F=0.3803+0.1473 log 10 N, the correlation coefficient is 0.9855, where F is the...
Embodiment 3
[0079] Example 3: Analysis of DNA Glycosylase Inhibitors
[0080] We chose 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) as the inhibitor for research. Some chemicals such as 5-FU and gentamicin can interact with DNA glycosylase and affect its activity. Among them, 5-FU is the most widely used chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of various tumors.
[0081] Different concentrations of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) were incubated with sandwich hybridization DNA substrate at 25°C for 15 minutes, then hOGG1 and UDG were added and incubated at 37°C for 60 minutes. Subsequent reaction procedures and fluorescence measurements followed the steps described above. According to the formula:
[0082]
[0083] To calculate the relative activity (RA) of DNA glycosylase. where F 0 is the fluorescence intensity in the absence of hOGG1 or UDG, F t is the fluorescence intensity in the presence of 32U per milliliter of hOGG1 or 50U per milliliter of UDG, and F i is the fluorescence intensity in the presence of hO...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com