Indenofluorene-based conjugated polymer laser gain material, method for preparing same and application of indenofluorene-based conjugated polymer laser gain material
A technology of conjugated polymers and laser gain, applied in the direction of luminescent materials, active medium materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient stability and low mobility, and achieve reversible redox characteristics, low laser threshold, The effect of good film-forming properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of compound 1
[0032]
[0033] Step I: Dissolve p-bromoindenofluorenone (1g, 2.27mmol) and phenol (3.84g, 40.82mmol) in 100mL of carbon tetrachloride, slowly add 0.7mL of methanesulfonic acid and phenol, and stir at 80°C 42 hours, remove carbon tetrachloride and phenol, and then with potassium carbonate K 2 CO 3 (3.13g, 22.7mmol), 7-(bromomethyl)-pentadecane (4.16g, 13.62mmol) were mixed, dissolved in 50mL ethanol solution and reacted at 90°C for 14 hours. After the reaction, extracted with dichloromethane and water, collected the organic phase, dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, suction filtered, evaporated The solid obtained from the solvent was purified by column chromatography to obtain compound 1 (3.86 g, yield 98%).
Embodiment 2
[0035] Compound 1 in Example 1 was used to prepare block copolymer A.
[0036]
[0037] Wherein, the synthetic route is as follows respectively:
[0038] Reaction Roadmap:
[0039]
[0040] The synthetic steps of copolymer A are as follows:
[0041] Under the protection of light and nitrogen, compound 1 (168 mg, 0.1 mmol), benzothiadiazole borate (038.9 mg, 0.1 mmol), tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium Pd (PPh 3 ) 4 (11.5mg, 0.01mmol), phase transfer catalyst tetrabutylammonium bromide (25mg, 0.05mmol), toluene solution (4.5mL), 2M K 2 CO 3 The solution (1.5 mL) was added into a 15 mL reaction bottle, and reacted at 95° C. for 72 hours. After the reaction, the copolymer A was obtained through alumina column purification, methanol precipitation, and extraction after the reaction.
[0042] Copolymer A: GPC measured M n = 15445, PDI = 1.76.
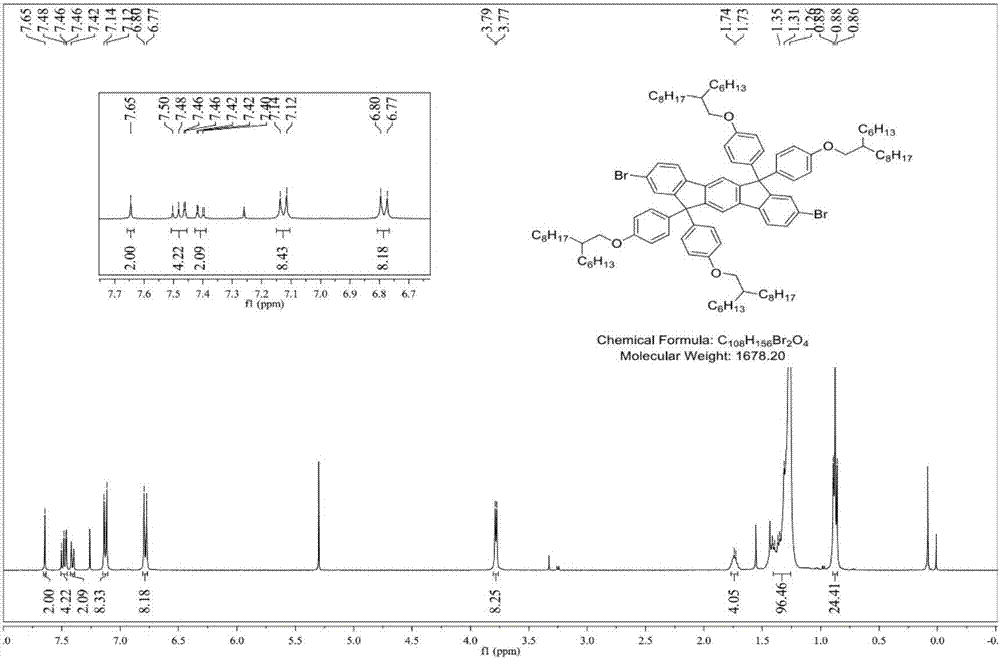
[0043] Compound 1: 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3): δ7.65(s, 2H), 7.49(d, J=8.1Hz, 2H), 7.46(d, J=1.5Hz, 2H), 7.41(d, J=8.1Hz, 2...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Fabrication of Organic Laser Devices
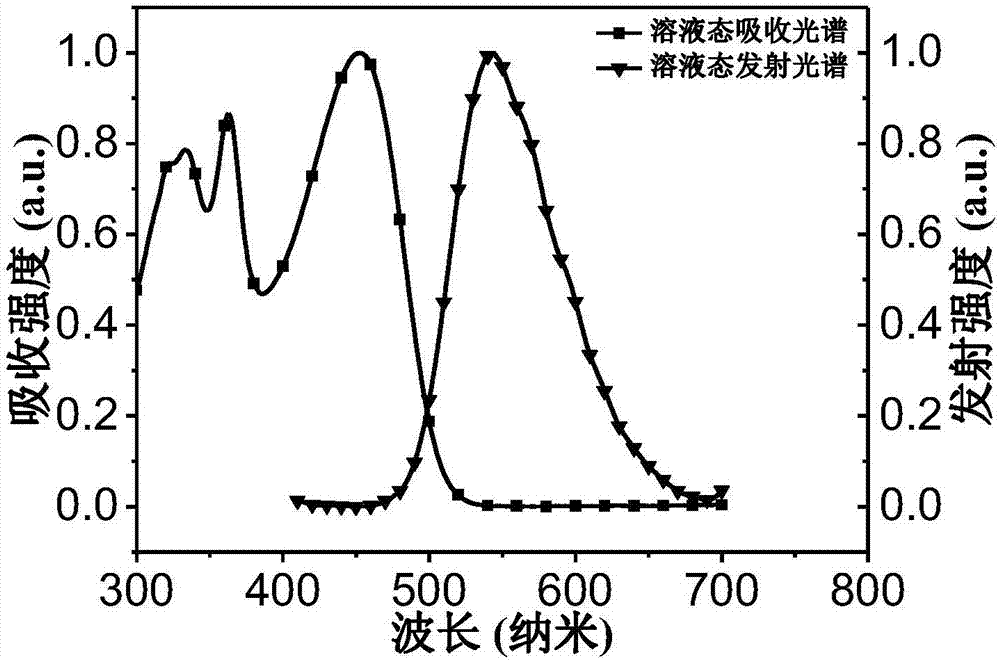
[0046] Using dichlorobenzene as a solvent, the luminescent host is copolymer A, and a 35 mg / mL solution is prepared. The quartz plate was ultrasonically cleaned, and the organic laser device was prepared by a simple spin-coating method, and the spin-coating condition was 1500rpm. Among them, the emission peaks of the PL spectrum of the copolymer A are 545nm, respectively, and are terminated with different acceptors, which is beneficial to the effective transmission of electrons. This type of copolymer A exhibits excellent laser properties, the ASE peaks are at 552nm; the FWHM are 8nm; the ASE threshold is as low as 65.84μJ / cm 2 , the maximum gain factor is 66cm -1 , which is a better result in organic yellow-green laser semiconductors.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com