Preparation and application methods of polyaluminium chloride modified graphene oxide adsorbent
A polyaluminum chloride and oxide stone technology, applied in the field of fatty acids, can solve the problems of difficult solid-liquid separation of purified water, highly dispersed adsorbents, and large electrostatic repulsion, and achieve sustainable economic development, efficient removal, and improved adsorption. The effect of capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
[0046] This case illustrates the preparation method of polyaluminum chloride modified graphene oxide suspension.
[0047] 1) Weighing 1.0 g of aphanitic graphite to prepare graphite oxide, first acid-washing the prepared graphite oxide, then washing with water, and finally centrifuging with a centrifuge.
[0048] 2) drying the centrifuged graphite oxide with a vacuum freeze drying oven for 48 hours, and grinding the dried graphite oxide into powder.
[0049] 3) Use a FLUKO high-shear dispersing mixer to uniformly disperse 0.2 g of graphene oxide powder in 300 mL of water.
[0050] 4) Exfoliate the graphite oxide solution for 9 minutes with a Cole Parmer (750W, 20KHz) ultrasonic cell pulverizer, and control the amplitude at 30%.
[0051] 5) The stripped suspension was centrifuged at 4000r / min for 20 minutes, and the supernatant was the graphene oxide suspension with a concentration of 0.385g / L.
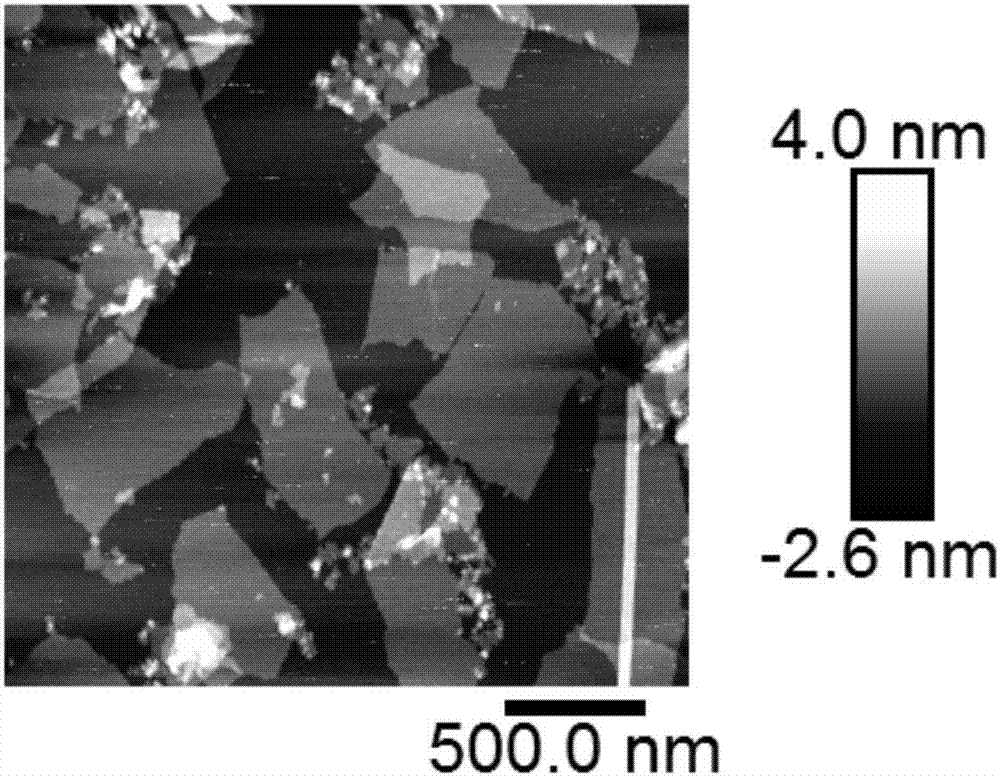
[0052] 6) Graphene oxide thickness detection, the atomic force micrograph of gra...
Embodiment example 2
[0058] This case illustrates the adsorption rate of polyaluminum chloride modified graphene oxide adsorbent on sodium oleate.
[0059] 1) Take the oleic acid wastewater with a concentration of 250mg / L as the object of treatment.
[0060] 2) Mix the polyaluminum chloride-modified graphene oxide suspension (10 mL) prepared in Case 1 with 250 mg / L oleic acid wastewater (40 mL) in a conical flask.
[0061] 3) Put the Erlenmeyer flask on the shaker, at the adsorption reaction temperature of 25°C and the shaking speed of 150rpm, the adsorption and removal times are 0.25h, 1.5h, 3h, 5h, 9h, 11h, 21h and 24h respectively.
[0062] 4) Take out the Erlenmeyer flask after the adsorption reaction is completed from the oscillator, and finally take out the solution in the Erlenmeyer flask and centrifuge it for 15 minutes at a speed of 12000r / min in a centrifuge to realize the solid-liquid separation of the graphene oxide after adsorption, and take out the centrifuge The final supernatant w...
Embodiment example 3
[0066] This case illustrates the effect of solution pH on the adsorption capacity of polyaluminum chloride modified graphene oxide adsorbent.
[0067] 1) Take 40 mL of sodium oleate waste water with a concentration of 250 mg / L and inject it into 7 Erlenmeyer flasks as the object of treatment.
[0068] 2) Mix the graphene oxide suspension (10 mL) prepared in Case 1 with 250 mg / L oleic acid wastewater (40 mL) in a conical flask. And adjust the pH value of the suspension in the Erlenmeyer flask to 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 respectively.
[0069] 3) Put the Erlenmeyer flask on the shaker, at the adsorption reaction temperature of 25° C. and the shaking speed of 150 rpm, the adsorption and removal time is 24 hours.
[0070] 4) Take out the Erlenmeyer flask after the adsorption reaction is completed from the oscillator, and finally take out the solution in the Erlenmeyer flask and centrifuge it for 15 minutes at a speed of 12000r / min in a centrifuge to realize the solid-liquid separatio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com