Preparation method of magnetic-cellulose-microsphere-immobilized lipase catalyst
A technology for immobilizing lipase and cellulose microspheres, which can be used in biochemical equipment and methods, immobilized on/in organic carriers, enzymes, etc., and can solve the problem of restricting the large-scale application of lipase, difficult to recover, separate and purify , lipase inactivation and other problems, to achieve the effect of being conducive to recycling and reuse, low price and high selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
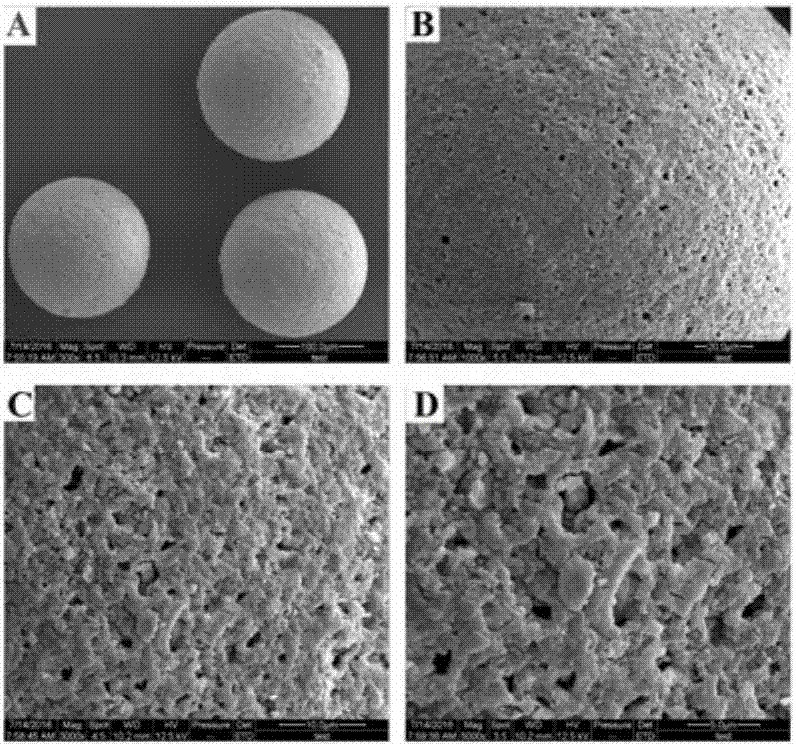
[0019] Preparation of regenerated cellulose microspheres by hot melt adhesive conversion method: Soak absorbent cotton with a certain amount of lye for 2-5 hours, then drain the solution, leave it for aging for 40-50 hours, add appropriate amount of CS 2 Sulfonate at 25-40°C for 6-10 hours, add appropriate amount of lye and CaCO 3 Stir evenly, pour into 400~600mL transformer oil containing 0.05~0.1g potassium oleate, 0.2~0.4g Span 60, stir at room temperature for 0.5~2h, then slowly raise the temperature to 70~90℃, and cure for 1.5~3.5h, Pour out the oil, wash the solid with a large amount of hot water until there is no oil, and obtain cellulose microspheres; add the cellulose microspheres to an appropriate amount of dilute hydrochloric acid solution, shake until there are no bubbles, pour out the liquid, add new dilute hydrochloric acid, and repeat several times , until the liquid becomes acidic, and the porous cellulose microspheres are prepared.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Chemical modification: add porous cellulose microspheres to epichlorohydrin, add an appropriate amount of lye to react, and prepare epoxidized cellulose microspheres; add appropriate amount of epoxidized cellulose balls to 8-12mL In the amine modification reagent, react at 40-60° C. for 8-12 hours to obtain amino-modified cellulose microspheres.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Preparation of magnetic cellulose microspheres by co-precipitation: add amino-modified cellulose microspheres to 100-200mL Fe 3+ and Fe 2+ The mixed liquid is vacuum filtered at 0-25°C for 1 hour, ammonia water is added to adjust the pH of the liquid to 9-11, and coprecipitation is carried out at 50-60°C for 1-3 hours to prepare the magnetic cellulose microsphere matrix.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com