Method for screening sumoylation target protein of Aspergillus flavus based on in vitro reaction system
A reaction system, the technology of Aspergillus flavus, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of limited success rate and accuracy, low homologous comparison scores, protein instability, etc., achieve high success rate and accuracy, and reduce background noise , the effect of increased stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1: Cloning of Aspergillus flavus SUMOylation enzyme system and construction of prokaryotic expression vector
[0067]The inventor searched the The Fungal and Oomycete Genomics Resource database (http: / / fugidb.org / fungidb / ) and used bioinformatics comparative analysis to find the SUMOylation modification with Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Aspergillus nidulans in the genome sequence of Aspergillus flavus Enzyme genes with high homology genes are named as Aspergillus flavus Afsum O , Afaos A , Afuba B , ikB and AfsizA Gene (the nucleic acid sequence and amino acid sequence of its coding region are shown in SEQ ID NO.1-10). The inventor amplified from the cDNA of Aspergillus flavus by RT-PCR technology Afsum O , Afaos A , Afuba B , ikB and AfsizA The coding region fragment is cloned into the expression vector pColdI to prepare for the prokaryotic expression and purification of the protein components of the Aspergillus flavus SUMOylation modificatio...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Embodiment 2: prokaryotic expression of Aspergillus flavus SUMOylation modification enzyme system;
[0082] The prokaryotic expression vector of the Aspergillus flavus SUMOylation enzyme system constructed in Example 1 was transformed into an Escherichia coli expression strain to obtain the prokaryotic expression strain of the Aspergillus flavus SUMOylation enzyme system. The purified recombinant Aspergillus flavus SUMOylated enzymes AfSumO, AfAosA, AfUbaB, AfUbcI and AfSizA were obtained by cold shock-induced expression and Ni column purification.
[0083] The specific steps and conditions are as follows:
[0084] 1. Construction of the prokaryotic expression strain of Aspergillus flavus SUMOylation enzyme system: the above prokaryotic expression vector pCold- Afsum O , pCold- Afaos A , pCold- Afuba B , pCold- ikB and pCold- AfsizA Transform into Escherichia coli C41 (DE3) to obtain the prokaryotic expression strain of the corresponding gene;
[0085] 2. Ind...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Embodiment 3: the in vitro SUMOylation reaction of Aspergillus flavus
[0089] Using the recombinant Aspergillus flavus SUMOylation modified enzyme system components obtained in Example 2, carry out the SUMOylation in vitro reaction, the specific steps and conditions are as follows:
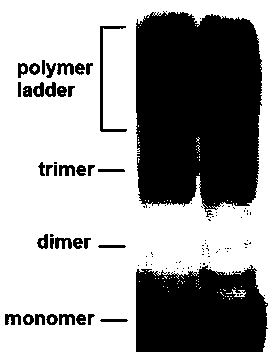
[0090] The solution system is a mixture of the following components: 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.2), 100 mM NaCl, 10 mMMgCl 2 , 0.1 mM dithiothreitol, 10 mM ATP, 50 μg / mL recombinant AfSumO (without His6-tag removal), 10 μg / mL recombinant AfAosA (without His6-tag), 10 μg / mL recombinant AfUbaB (without His6-tag), 10 μg / mL recombinant AfUbcI (without His6-tag) and 10 μg / mL recombinant AfSizA (without His6-tag). React at 30°C for 30 minutes.
[0091] The reaction product was immediately separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a membrane and analyzed by Western blot. The primary and secondary antibodies were respectively used Mouse anti-His6 Monoclonal antibody and HRP-conjugated Goat anti Mouse IgG (H+...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com