Hot metal pretreatment dephosphorization agent and preparation method thereof
A technology of molten iron pretreatment and dephosphorization agent, applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy, can solve the problems of serious erosion of refractory materials, adverse effects on steel hardenability, adverse environmental effects, etc., achieves good fluidity, good economic and social benefits, avoids The effect of F on the pollution of the environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
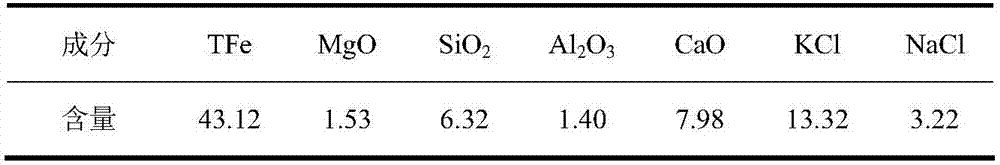
[0027] The composition of the electrostatic precipitator ash of the sintering head is shown in Table 1.
[0028] Table 1 Composition of ESP dust in sintering head (wt,%)
[0029]
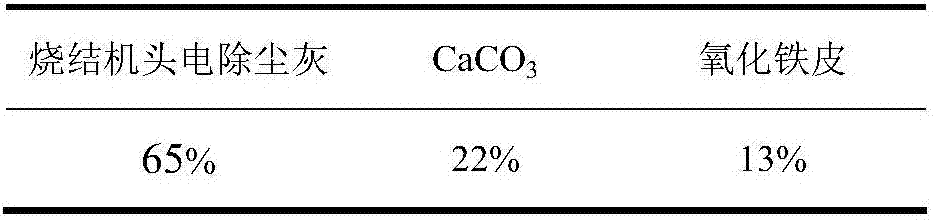
[0030] The ingredient scheme of dephosphorization agent is shown in Table 2, and the composition of conventional dephosphorization agent is shown in Table 3.
[0031] Table 2 Dephosphorization agent batching scheme of the present invention (wt,%)
[0032]
[0033] Table 3 Composition scheme of conventional calcium-based dephosphorization agent (wt,%)
[0034]
[0035] After the above-mentioned dephosphorization agent is dried, it is ground to a thickness of less than 1 mm, and mixed evenly. Then, in a 200kg induction furnace, 100kg molten iron was charged, and 3kg dephosphorization agent was sprayed into the molten iron at 1350° C.
[0036] Table 4: Comparison of dephosphorization effects (%)
[0037]
example 2
[0039] The ash composition of sintering head ESP is shown in Table 5.
[0040] Table 5 Composition of ESP dust in sintering head (wt,%)
[0041]
[0042] The ingredient scheme of dephosphorization agent is shown in Table 6, and the composition of conventional dephosphorization agent is shown in Table 7.
[0043] Table 6 Dephosphorization agent batching scheme of the present invention (wt,%)
[0044]
[0045] Table 7 Composition scheme of conventional calcium-based dephosphorization agent (wt,%)
[0046]
[0047] After the above-mentioned dephosphorization agent is dried, it is ground to a thickness of less than 1 mm, and mixed evenly. Then, in a 200 kg induction furnace, 100 kg of molten iron was charged, and 3 kg of dephosphorization agent was sprayed into the molten iron at 1350° C.
[0048] Table 8: Comparison of dephosphorization effects (%)
[0049]
example 3
[0051] The composition of the electrostatic precipitator ash of the sintering head is shown in Table 9.
[0052]Table 9 Composition of ESP dust in sintering head (wt,%)
[0053]
[0054] The ingredient scheme of dephosphorization agent is shown in Table 10, and the composition of conventional dephosphorization agent is shown in Table 11.
[0055] Table 10 Dephosphorization agent batching scheme of the present invention (wt,%)
[0056]
[0057] Table 11 Conventional calcium-based dephosphorization agent ingredient scheme (wt,%)
[0058]
[0059] After the above-mentioned dephosphorization agent is dried, it is ground to a thickness of less than 1 mm, and mixed evenly. Then, in a 200kg induction furnace, 100kg of molten iron was charged, and 3kg of dephosphorization agent was sprayed into the molten iron at 1350°C. The dephosphorization effects of the molten iron dephosphorization agent in Example 3 of the present invention and conventional dephosphorization agents ar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com