Application of Glibenclamide in Preparation of Drugs for Protecting Radiation-induced Lung Injury
A radiation-induced lung injury and drug technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as the preventive effect of glibenclamide that has not been reported in the literature, and achieve the effects of reducing toxic damage, small toxic and side effects, and clear pharmacological effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
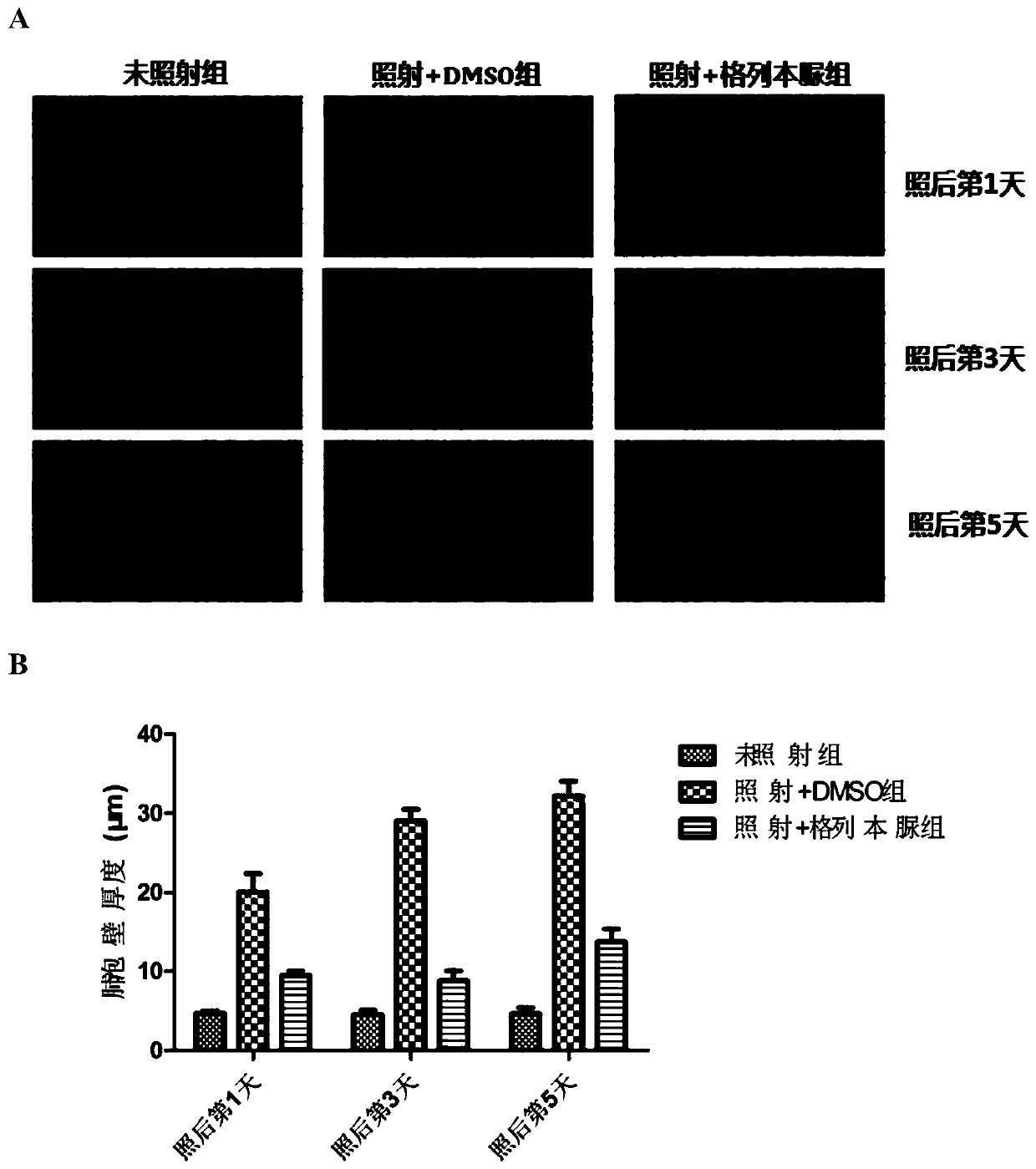
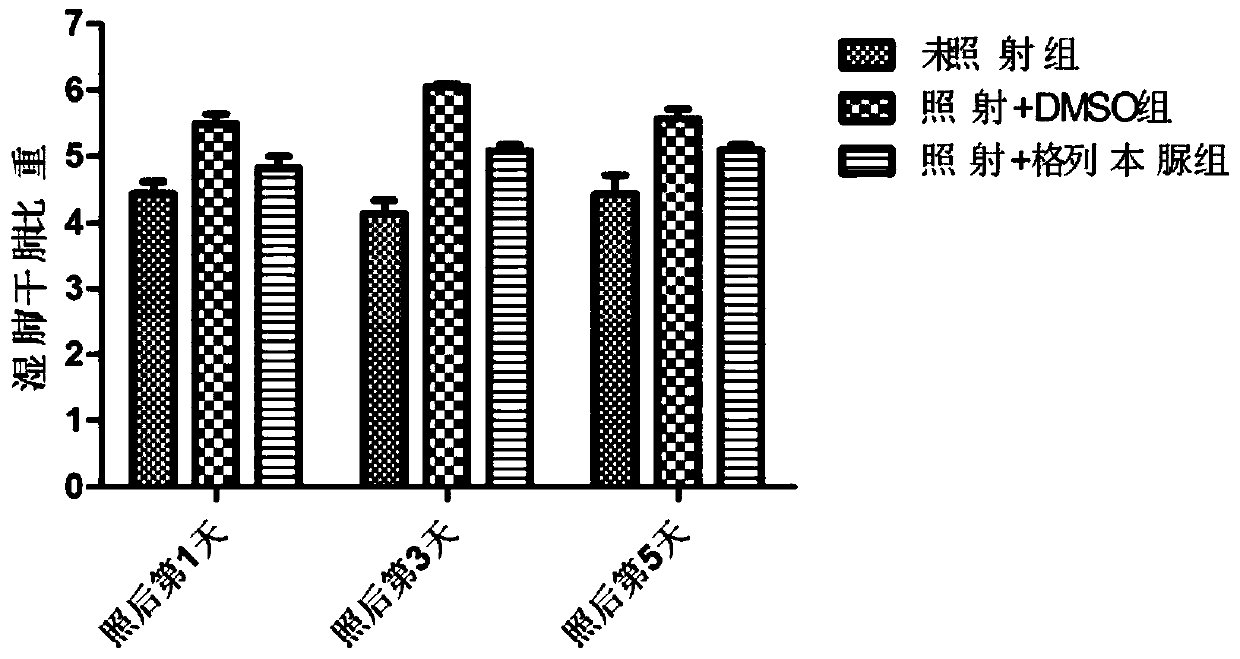
[0028] Example 1: Glibenclamide can reduce lung injury and pulmonary hemorrhage in mice after irradiation
[0029] 1. Experimental method
[0030] C57 / BL6, 7-week-old male mice were selected for the experiment, and the mice were divided into three groups: unirradiated group, glibenclamide group and control group. The non-irradiated group was neither injected nor irradiated. The glibenclamide group was intraperitoneally injected with glibenclamide (10 mg / kg) 1 hour before irradiation, and the inglibenclamide was treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). ) dissolved, so the mice in the control group were intraperitoneally injected with the same dose of DMSO solution.
[0031] The mice in the glibenclamide group and the control group were irradiated by a single dose of local chest irradiation, the dose was 30Gy, the dose rate was 1Gy / min, and the irradiation source was 60Coγ-rays. During irradiation, the lungs are exposed to the irradiation field, and the rest is covered with lea...
Embodiment 2
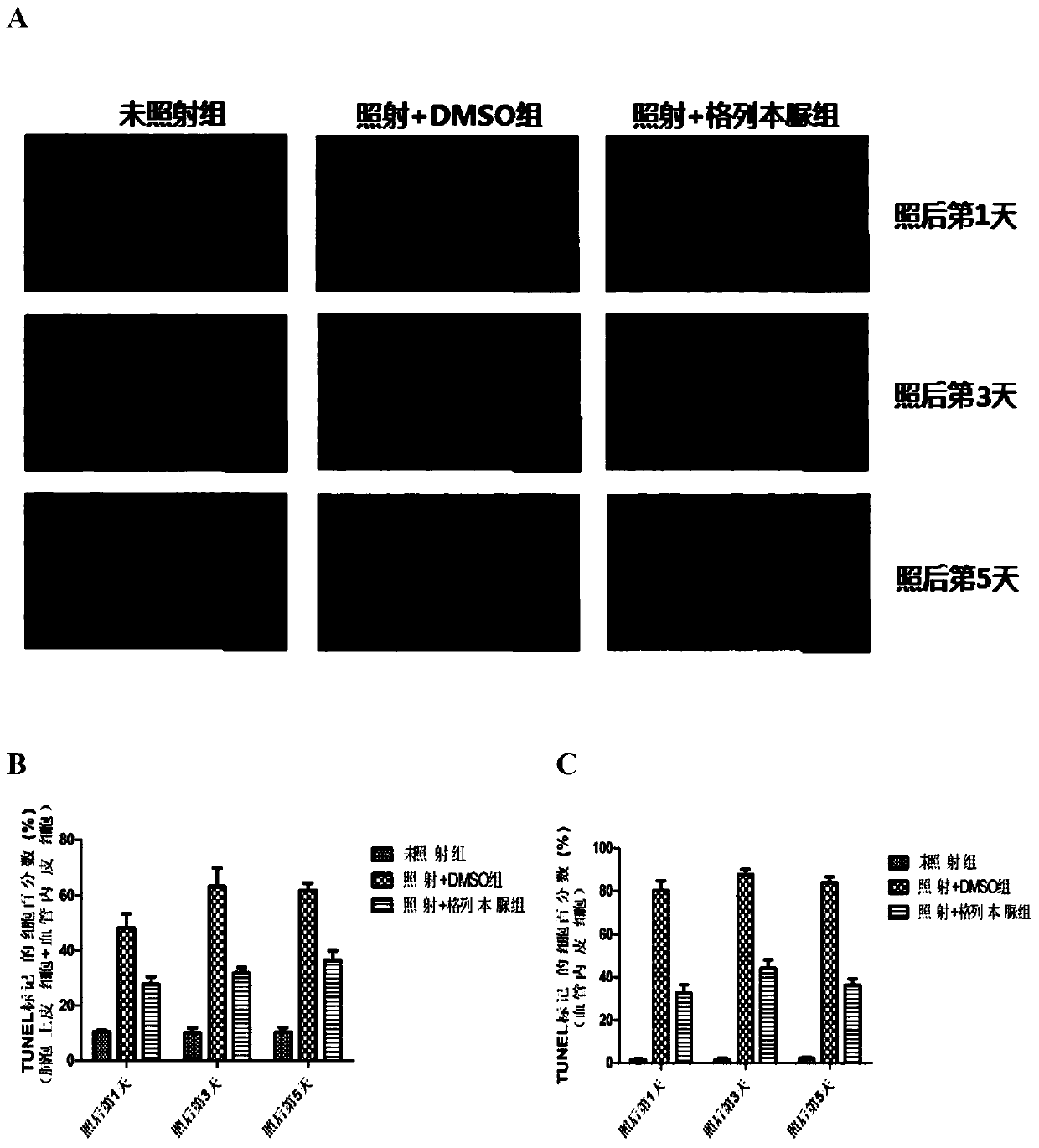
[0037] Example 2: Glibenclamide reduces apoptosis of vascular endothelial cell line HUVEC after irradiation
[0038] 1. Experimental method:
[0039] In order to verify the effect of glibenclamide on cell apoptosis after irradiation, apoptosis detection was performed on the vascular endothelial cell line HUVEC after irradiation.
[0040] Apoptosis was detected by AnnexinV / PI double-staining (purchased from Invitrogen) flow cytometry method, the principle of which is: apoptosis is a process of programmed initiation, which can be divided into two processes: early apoptosis and late apoptosis. During early apoptosis, phosphatidylserine (PS) can change from the original state inside the cell phospholipid membrane to outward. At this time, Annexin V can combine with the everted PS as a detection mark of early apoptosis. In the late stage of apoptosis, the permeability of the cell membrane increases. At this time, propidium iodide (PI), as a nucleic acid dye, can enter the interior...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3: Glibenclamide alleviates the proliferation inhibitory effect of irradiation on the vascular endothelial cell line HUVEC
[0045] 1. Experimental method:
[0046] The detection of cell proliferation ability adopts clone formation experiment. The principle is: a single cell will form a cell cluster of about 50 cells after more than 6 passages, which is called a clone. The number and size of clones can reflect the cell proliferation ability.
[0047] After the cells are irradiated, there are two forms of proliferative death and interphase death, so the clonogenic test can better reflect the proliferation ability of the cells. The specific operation steps are as follows: 24 hours before irradiation, plate the HUEVC cells, try to form a single cell, the cells will form colonies when they proliferate, and the staining points (blue) can be observed after staining. The more vigorous the cell proliferation, the more the number of staining points The more, the larger ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com