Pretreatment method for detecting aminoglycoside antibiotic residues in milk
A technology of aminoglycosides and antibiotics, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of lack of target molecule selectivity, time-consuming, etc., and achieve the effects of rapid extraction and enrichment, overcoming weak selectivity, and uniform pore size distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
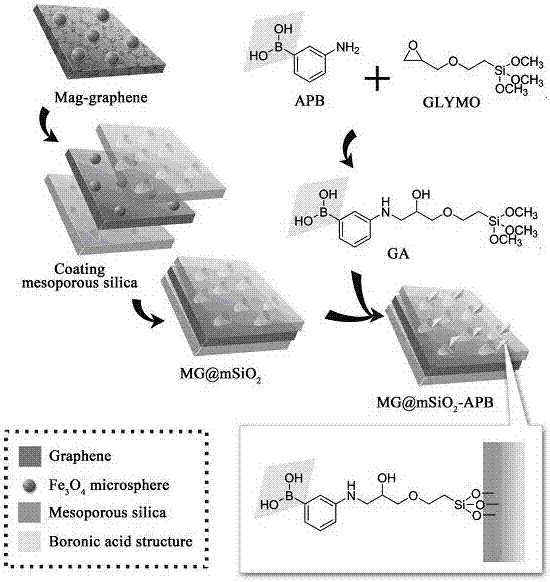
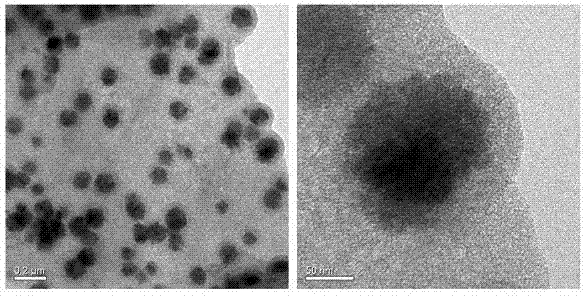
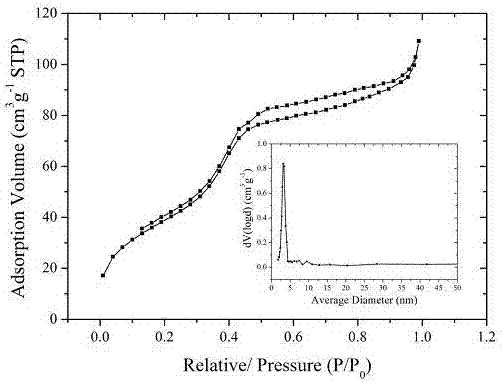
[0027] Example 1. Using boric acid to modify mesoporous magnetic graphene composite material is applied to streptomycin and dihydrostreptomycin in enriched milk:
[0028] (1) Synthesis of boric acid-modified mesoporous magnetic graphene composites:
[0029] 1) Disperse 0.30 g graphene flakes in 120 mL concentrated nitric acid, 60 o C under stirring for 7 hours, the treated graphene was cleaned with deionized water until the pH was neutral, 50 o Collect after C vacuum drying;
[0030] 2) Add 150 mg acidified graphene, 1.8 g anhydrous sodium acetate, 1.0 g PEG-20000, 150 mg trisodium citrate, 150 mg ferric chloride hexahydrate, 40 mL ethylene dichloride into a 100 mL reaction kettle Alcohol, sonicated for 2 hours, reacted at 200 °C for 12 hours, washed 5 times with absolute ethanol, 50 o Collect after C vacuum drying;
[0031] 3) Add 75 mg magnetic graphene, 750 mg cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, 75 mL deionized water to a 1 L round-bottomed flask, sonicate for 30 min, then ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com