Photovoltaic assembly
A technology of photovoltaic modules and laminates, applied in photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of module attenuation, weak resistance to hidden cracks, accidents, etc., achieve reduced thickness or strength requirements, and excellent water vapor barrier performance , reduce thickness and weight effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
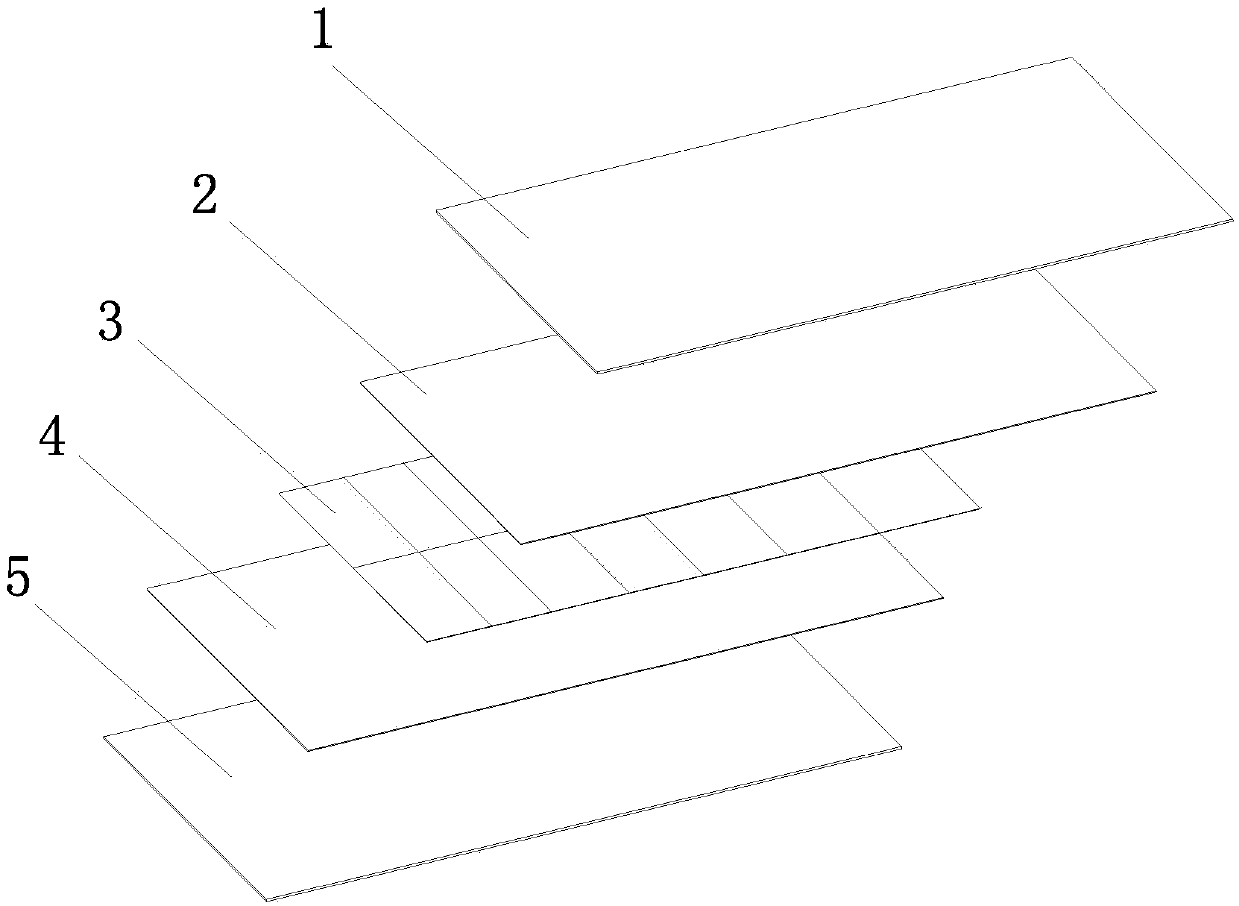
[0046] see figure 1 , a photovoltaic module of this embodiment, comprising a laminate and a frame covering the sides of the laminate, the laminate sequentially includes a front plate 1, a front packaging material 2, a battery layer 3, and a rear packaging material from top to bottom 4 and a back plate 5, the back plate 5 is a metal plate or an inorganic material plate.
[0047] Metal plate 5 can be iron plate, steel plate or aluminum plate. The surface of the metal plate 5 is coated with insulating varnish and / or color paint. The thickness of the metal plate 5 is 0.1-0.5mm, which is much thinner than that of conventional 2.5mm or 2.0mm glass.
[0048] In this embodiment, the rear plate is a metal plate 5 and is a steel plate 5 . Although the packaging material is an insulating material, which can play a certain insulating role, the packaging material will be squeezed during the lamination process of the laminate, causing the battery layer 3 to still be in contact with the m...
Embodiment 2
[0053] A photovoltaic module in this implementation is basically the same as the first embodiment, the difference is that the steel plate 5 in this embodiment is not only coated with insulating varnish, but also coated with colored paint, and the color of the paint can be selected according to the requirements of customers , so that it is both beautiful and can form a protection for the metal plate, thereby increasing the service life of the photovoltaic module.
Embodiment 3
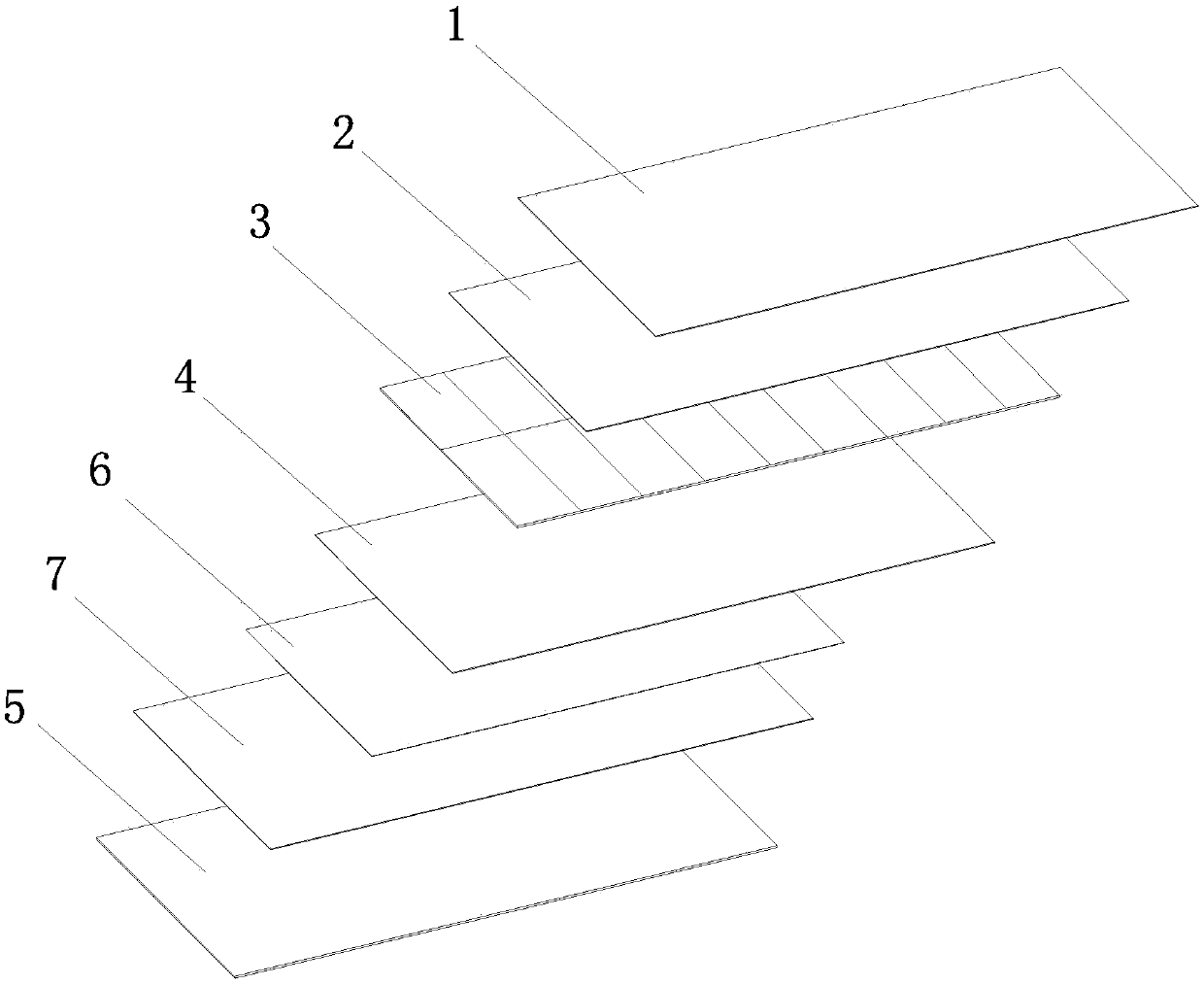
[0055] see figure 2 , a photovoltaic module in this implementation is basically the same as the first embodiment, the difference is that the insulation treatment between the metal plate 5 and the battery layer 3 in this embodiment is that the side of the metal plate 5 close to the battery layer 3 has an insulating layer 6 In order to achieve better insulation effect. The insulating layer 6 is made of PET, glass fiber board, soft ceramic, flexible stone or asbestos board.
[0056] There is an adhesive layer between the insulating layer 6 and the metal plate 5 . The material of the adhesive layer is a conventional packaging material such as EVA, POE, PVB, and the like. Among them, EVA is ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, POE is polyolefin elastomer, and PVB is polyvinyl butyral.
[0057] In this embodiment, the surface anti-corrosion treatment is also carried out on the metal plate 5 to achieve a longer service life. erosion.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com