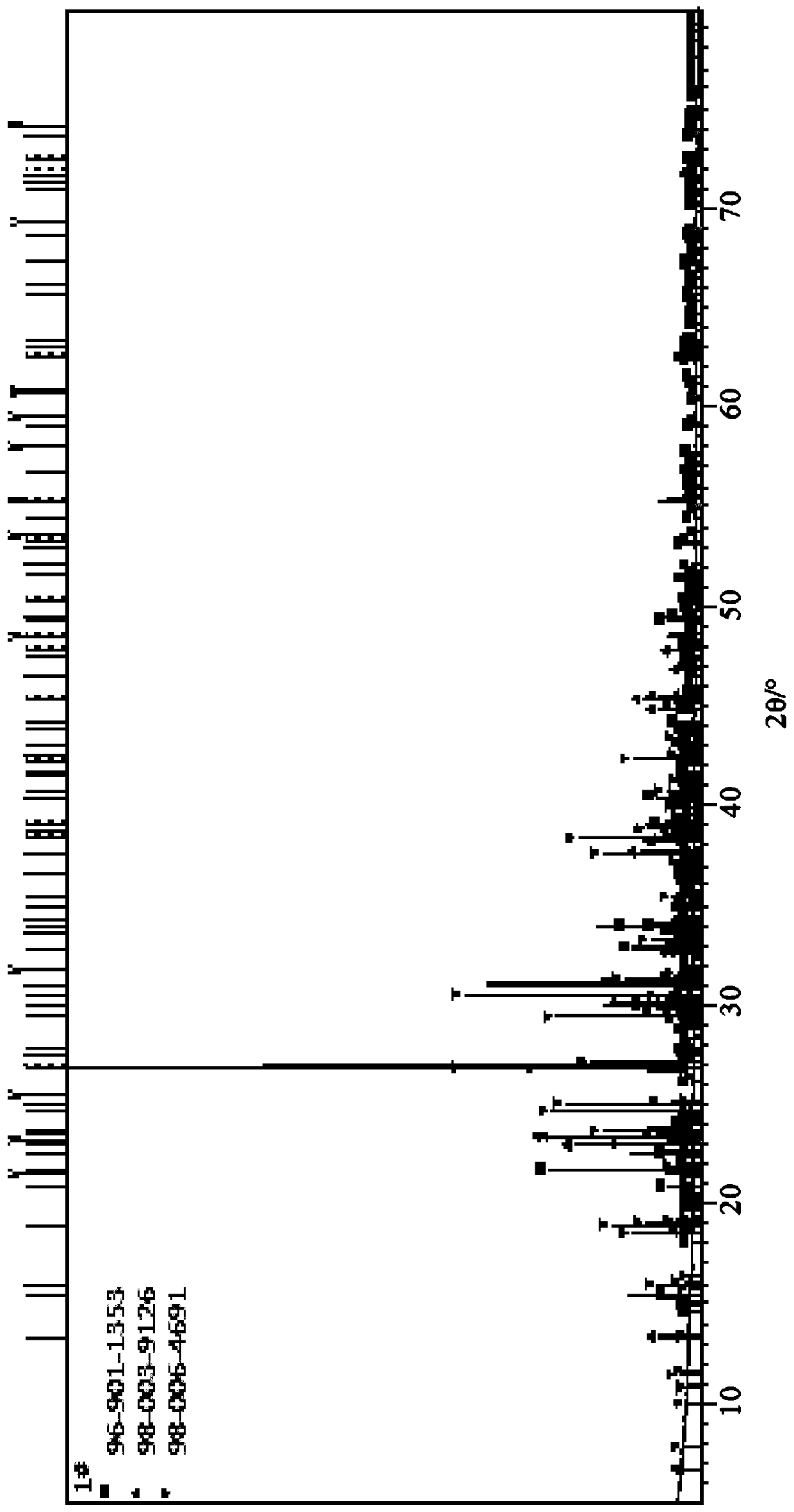
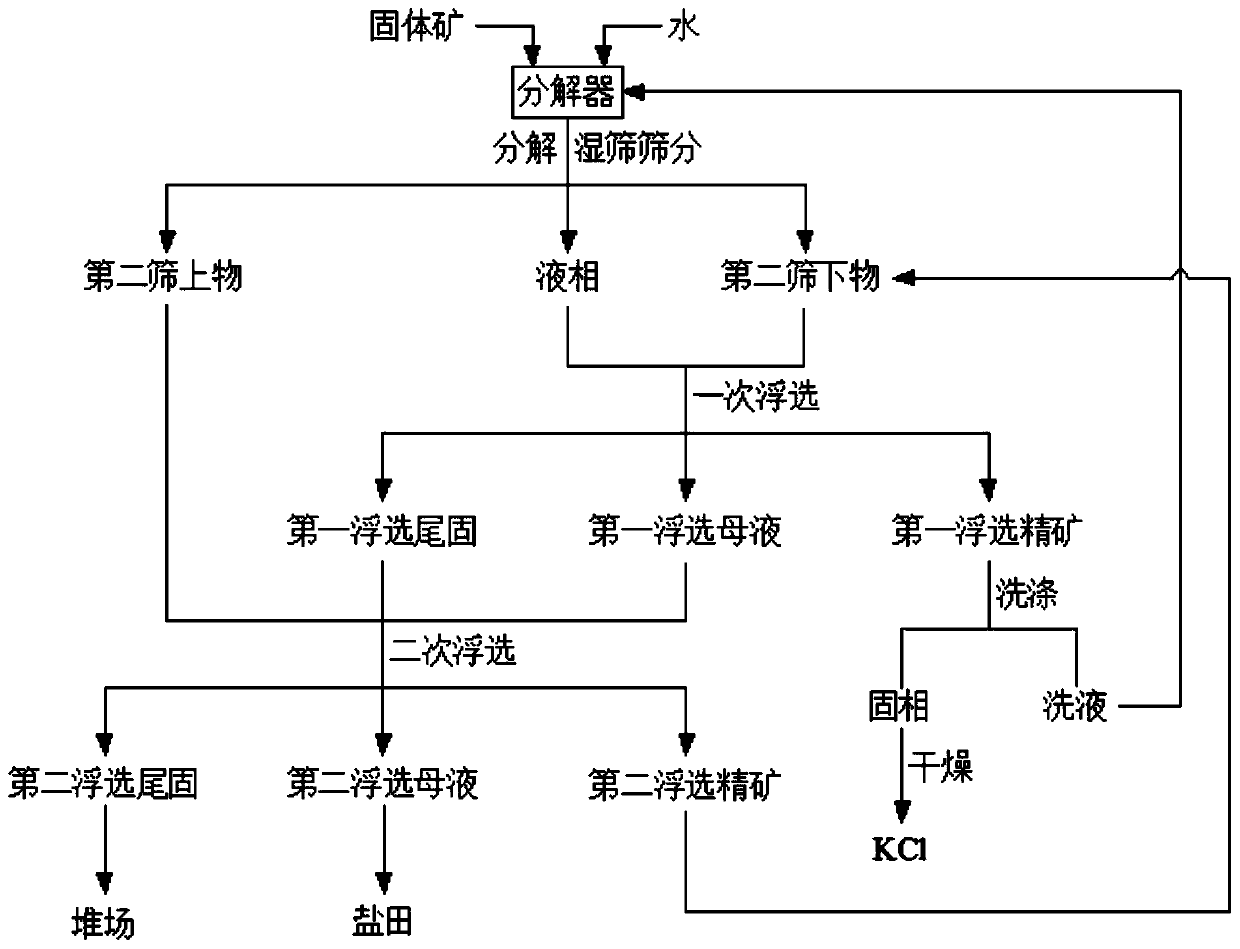
A kind of method for preparing potassium chloride from solid ore containing potassium ammonium magnesium
A solid ore, potassium chloride technology, applied in the direction of alkali metal chloride and the like, can solve problems such as unsuitable application, and achieve the effects of low cost, simple process and improved resource utilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The method for preparing potassium chloride from the solid ore containing potassium ammonium magnesium of the present embodiment may further comprise the steps:
[0041] In step S1, the solid ore is crushed and passed through a 40-mesh sieve, and the first sieve is taken for later use.
[0042] In step S2, the first undersize and fresh water are mixed according to the mass ratio of 2:1, and stirred at 0°C for 4 hours to fully decompose, and then wet sieved through a 40-mesh sieve for solid-liquid separation to obtain the The second oversize with a potassium ion content of 11%, the second undersize with a potassium ion content of 33%, and the liquid phase; the potassium ion yield is 65%.
[0043] In step S3, the second undersize and the liquid phase are mixed for a flotation. The conditions of the first flotation are that the solid-liquid ratio is 1:3, the dosage of the flotation agent is 7mL, the mixing is 5 minutes, and the flotation is 1 minute. The obtained first Th...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The method for preparing potassium chloride from the solid ore containing potassium ammonium magnesium of the present embodiment may further comprise the steps:
[0047] In step S1, the solid ore is crushed and passed through a 40-mesh sieve, and the first sieve is taken for later use.
[0048] In step S2, the first undersize and fresh water are mixed according to the mass ratio of 10:7, and stirred at 25°C for 16 hours to fully decompose, and then wet sieved through an 80-mesh sieve for solid-liquid separation to obtain the The potassium ion yield of the second oversize material with a potassium ion content of 10%, the second undersize material with a potassium ion content of 37% and the liquid phase is 63%.
[0049] In step S3, the second undersize and the liquid phase are mixed for a flotation. The conditions of the first flotation are that the solid-liquid ratio is 1:6, the dosage of the flotation agent is 7mL, the mixing is 10 minutes, and the flotation is 3 minute...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The method for preparing potassium chloride from the solid ore containing potassium ammonium magnesium of the present embodiment may further comprise the steps:
[0053] In step S1, the solid ore is crushed and passed through a 40-mesh sieve, and the first sieve is taken for later use.
[0054] In step S2, the first undersize and fresh water were mixed according to a mass ratio of 5:3, and stirred at 20°C for 8 hours to fully decompose, and then wet sieved through a 60-mesh sieve and separated from solid and liquid to obtain the The second oversize with a potassium ion content of 10%, the second undersize with a potassium ion content of 36% and the liquid phase; the yield of potassium ions is 64%.
[0055] In step S3, the second undersize is mixed with the liquid phase to carry out a flotation. The conditions of the first flotation are that the solid-liquid ratio is 1:9, the dosage of the flotation agent is 8mL, the mixing is 8 minutes, and the flotation is 2 minutes. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com