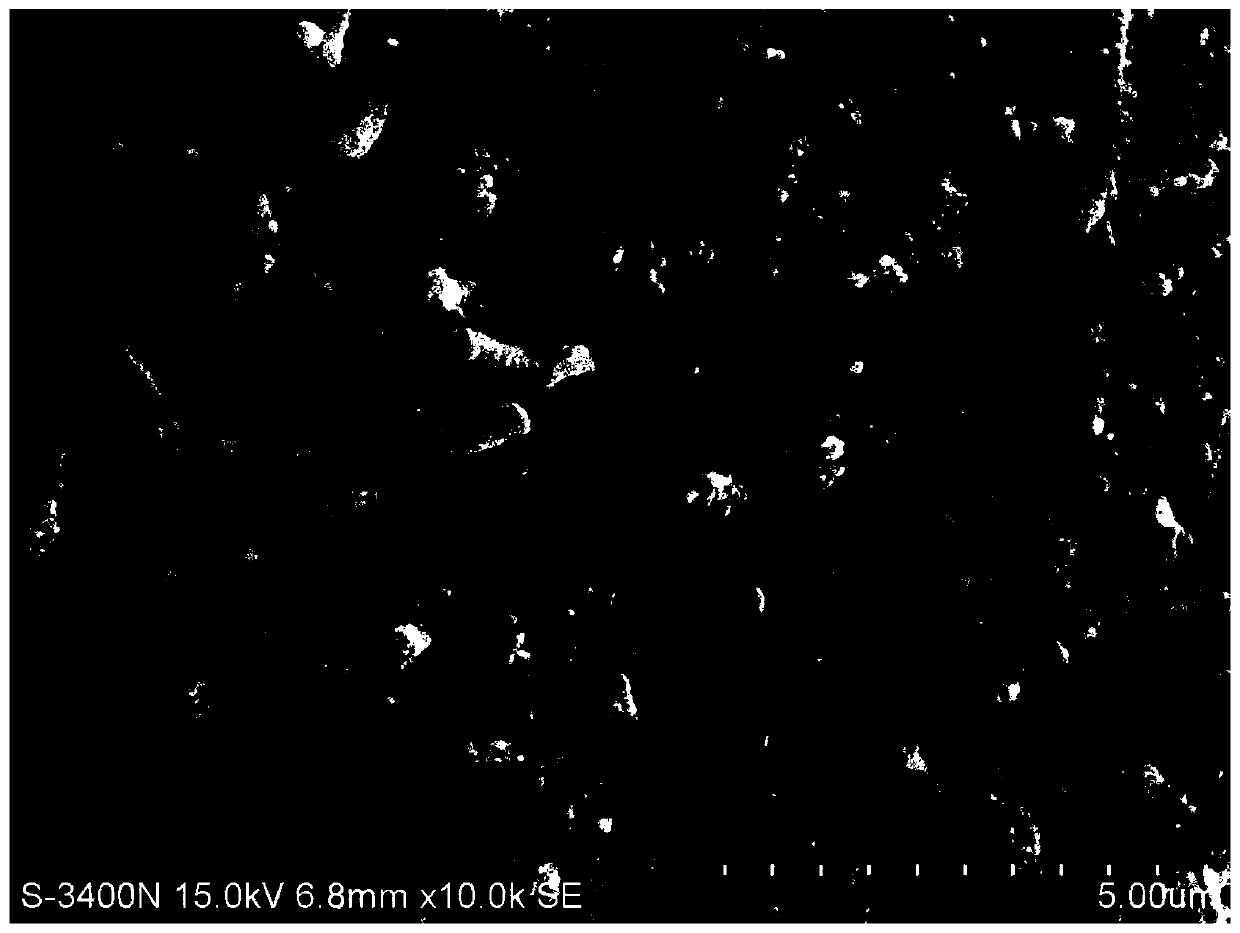
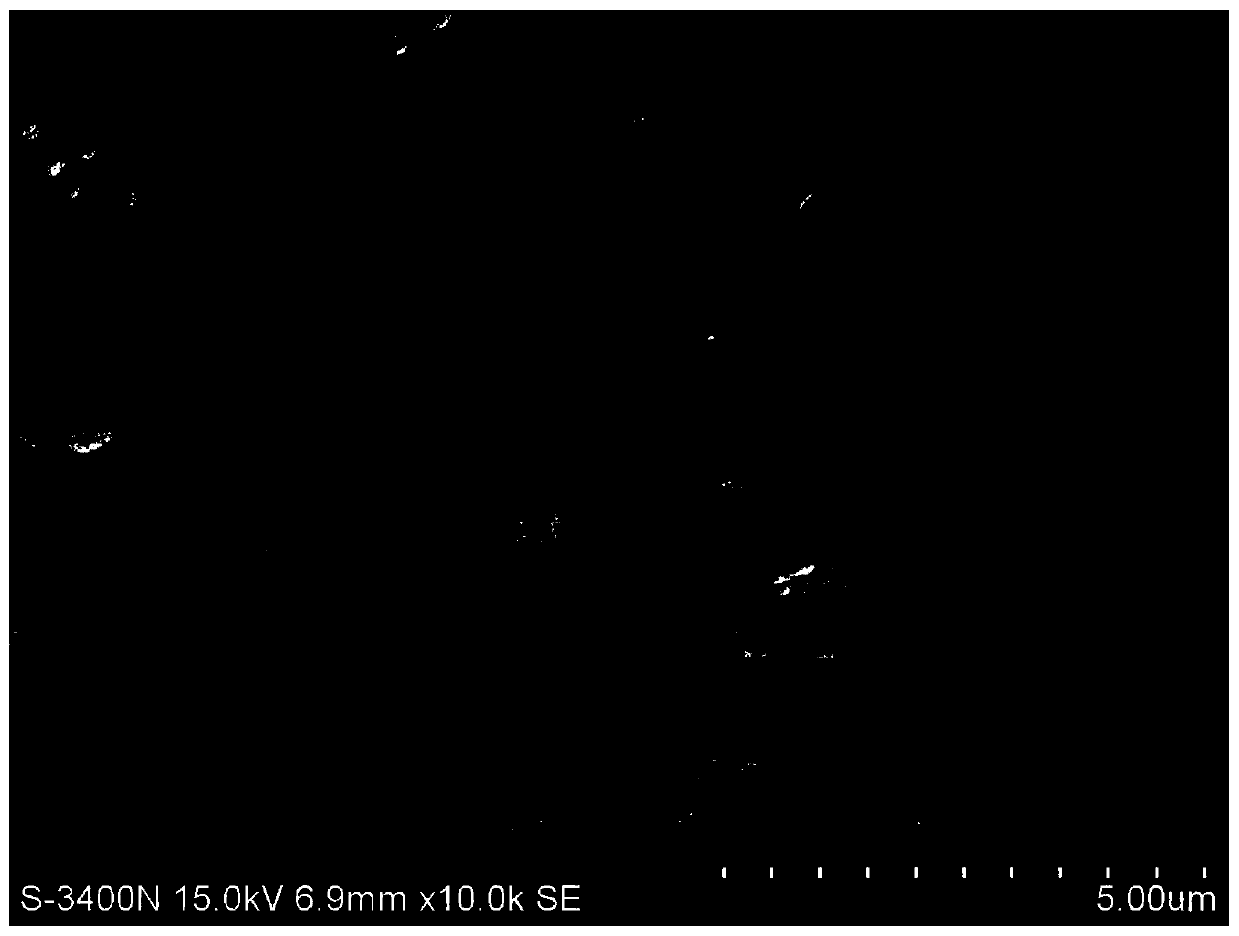
A method for basic n regulation of metal valence in carbide metal organic frameworks
A technology of metal-organic framework and metal carbide, which is applied in the field of material chemistry and catalytic reaction, can solve the problems of precious metal catalysts, such as easy agglomeration, price, inability to be widely used in large quantities, and high cost, to achieve good reaction rate and catalytic activity, and improve activity and efficiency , good modification effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] A method for regulating the valence state of a metal in a metal organic framework material by basic N, comprising the following steps,
[0043] (1) Preparation of metal-organic framework material MOF: Dissolve 0.5448g of anhydrous copper acetate in 24ml of water, and then dissolve 0.6300g of trimesic acid (the mass ratio of copper acetate and trimesic acid is 1:1.16) solution one by one Add dropwise into the anhydrous copper acetate solution, stir at 1000rpm until the mutual solubility is uniform, and the metal organic framework material MOF can be obtained; then the MOF is soaked in the ethanol solution, filtered and placed in a vacuum oven at 100°C for vacuum drying. Degree <100Pa;
[0044] (2) Carbonization of MOF: 0.3g of MOF was placed in a tube furnace under N 2 Carbonization in the atmosphere, the specific parameters of carbonization: N 2 The flow rate is 80mL / min, the heating rate is 10°C / min, the carbonization temperature is 600°C, and the carbonization time ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] A method for regulating the valence state of a metal in a metal organic framework material by basic N, comprising the following steps,
[0047] (1) Preparation of basic N-modified metal-organic framework N-MOF-1: Add 0.05874g (5wt.%) dopamine (alkalinity coefficient pKb is around 3) to 24mL, 0.5448g of anhydrous copper acetate aqueous solution In the process, stir at 1000 rpm for 0.5h, then irradiate and react under a 500W ultrasonic field for 0.5h; then add 0.6300g of trimesic acid (the mass ratio of copper acetate and trimesic acid is 1:1.16) solution one by one Add it dropwise, and continue to stir until it dissolves evenly to obtain a basic nitrogen-modified metal-organic framework material N-MOF-1; soak N-MOF-1 in ethanol solution, filter and place it in a vacuum oven at 120°C Carry out vacuum drying, vacuum degree <100Pa;
[0048] (2) Carbonization of N-MOF-1: 0.3g of N-MOF-1 was placed in a tube furnace, 2 Carbonization in the atmosphere, the specific parameter...
Embodiment 3
[0050] A method for regulating the valence state of a metal in a metal organic framework material by basic N, comprising the following steps,
[0051] (1) Preparation of basic N-modified metal-organic framework N-MOF-2: 0.3695g (10wt.%) melamine (alkalinity coefficient pKb around 9) was added to 24mL of 0.5448g anhydrous copper acetate aqueous solution , stirred at 1000 rpm for 1 h, then irradiated and reacted for 1 h under a 1000 W ultrasonic field; then 3.1500 g of trimesic acid (the mass ratio of copper acetate and trimesic acid is 1:5.78) solution was added dropwise , continue to stir until the mutual dissolution is uniform, and obtain the nitrogen-modified metal-organic framework material N-MOF-2 material; soak the N-MOF-2 in an ethanol solution, filter it, and place it in a vacuum drying oven at 120°C for vacuum drying. Vacuum <100Pa;
[0052] (2) Carbonization of N-MOF-2: put 0.3g of N-MOF-2 in a tube furnace, 2 Carbonization in the atmosphere, the specific parameters...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com