Plasmid vector and method for building plant population by using plasmid vector
A plasmid vector, plant technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors, which can solve the problems of low coverage of whole genome coding genes, complicated operation and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
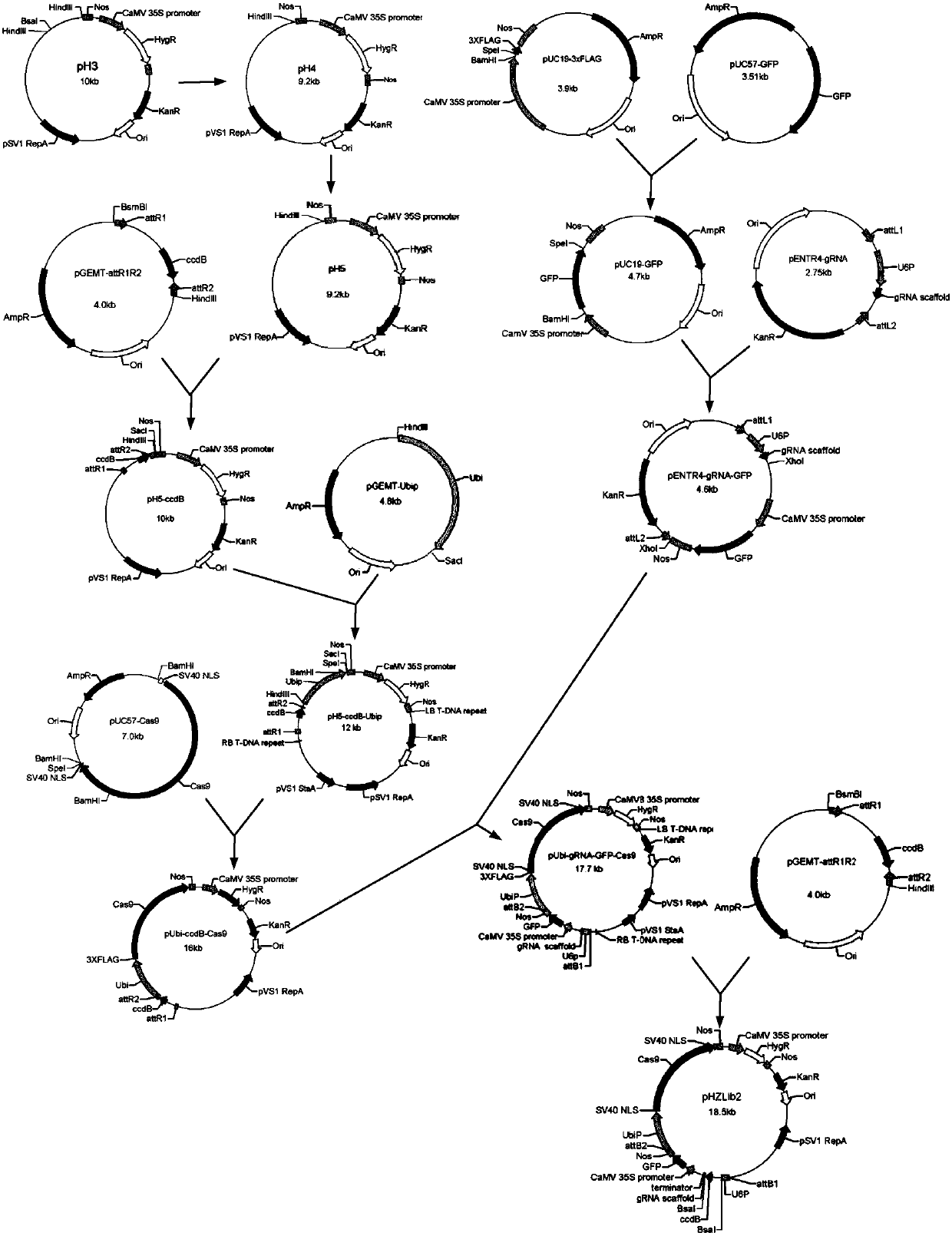
[0083] Embodiment 1: Construction of recombinant plasmid
[0084] The technical route for constructing the carrier is as follows:
[0085] 1. Construction of pUbi-ccdB-Cas9 recombinant plasmid
[0086] Hind III digestion was performed on the binary vector pH3 owned by our laboratory, and the 8.8kb vector backbone was recovered, which was named pH4 after self-ligation with T4DNA Ligase (Takara). The elements included in pH4 are: CaMV35S promoter, hygromycin gene, NOS terminator, pVS1RepA, pVS1 origin of replication. Use BsaI and Hind III to perform double enzyme digestion on pH4, and recover a 5.5kb large fragment, which includes the main elements: CaMV35S promoter, hygromycin gene, and NOS terminator. At the same time, using pH4 as a template, H3-F (SEQ ID No.8, introducing a restriction endonuclease BsaI site) and H3-R (SEQ ID No.9) as primers, using the high-fidelity enzyme I- 5 TM 2 × High-Fidelity Master Mix (purchased from Cloning (Beijing) Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) a...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2: Using pHZLib2 system to construct a plasmid library of rice endogenous MPK gene family and rice transformation
[0093] 1. Construction of pHZLib2-OsMPKs plasmid library
[0094] Synthetic oligonucleotide sequence OsMPK1-oligo-1 (SEQ ID No.16: CCCGCGCGCTGTCGCTTGTGTG TCATCCAGTACAACATCTT GTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAAATAAG, the underline is the target nucleotide sequence of OsMPK1), OsMPK2-oligo-1 (SEQ ID No.17: CCCGCGCGCTGTCGCTTGTGTG ATGGCCATCACGGTGGCATGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAAATAAG, the underline is the target nucleotide sequence of OsMPK2), OsMPK3-oligo-1 (SEQ ID No.18: CCCGCGCGCTGTCGCTTGTGT GAAGTATTACTACTCGATG GTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAAATAAG, the underline is the target nucleotide sequence of OsMPK3), OsMPK4-oligo-1 (SEQ ID No.19: CCCGCGCGCTGTCGCTTGTGTG CTAATGGCATGGGAAACCA GTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAAATAAG, the underline is the target nucleotide sequence of OsMPK4), OsMPK5-oligo-1 (SEQ ID No.20: CCCGCGCGCTGTCGCTTGTGTG TCAGGCC GACGATGACGCA GTTTTAG...
Embodiment 3
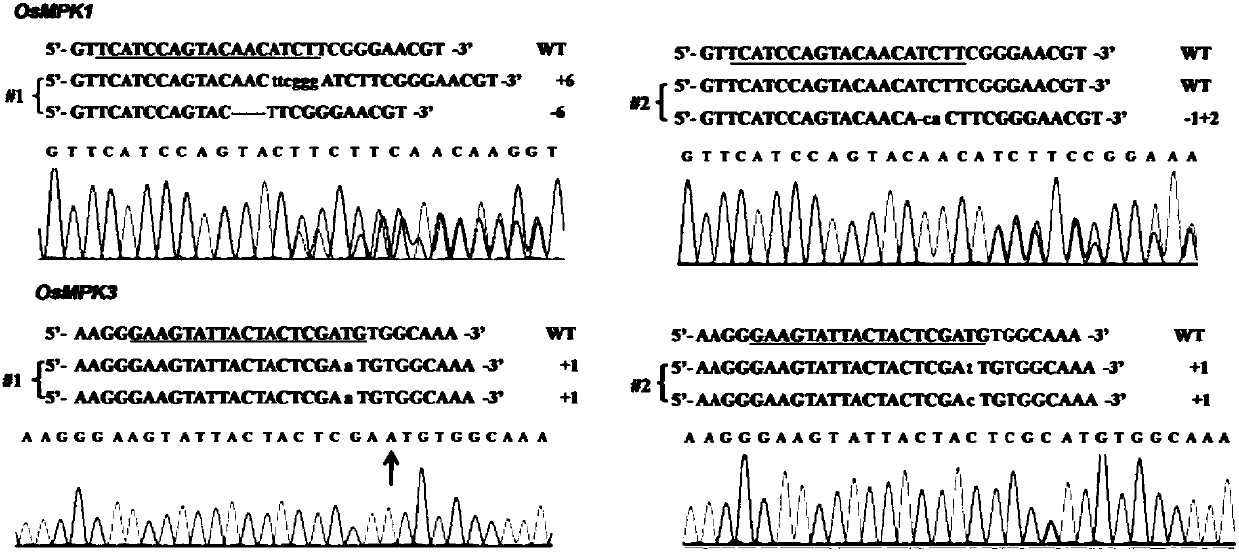
[0106] Example 3: Detection of OsMPKs rice mutant populations
[0107] 1) Extraction of genomic DNA
[0108] About 0.1 g of the leaves of the T0 generation plants were cut and ground with a grinder after quick freezing in liquid nitrogen; 600 μl of 2×CTAB DNA extract (containing 1 / 1000 β-mercaptoethanol) was added, shaken and mixed, and then lysed at 65°C for 45 minutes. Add 500 μl of chloroform and shake vigorously to form an emulsion, and centrifuge at 14000 rpm for 10 min. After centrifugation, transfer the supernatant to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of isopropanol, invert and mix well, centrifuge at 14000rpm for 10min, discard the supernatant, add 700μl 70% ethanol to wash the white precipitate, centrifuge at 14000rpm for 5min, discard the supernatant Place the centrifuge tubes in a fume hood to air dry for 10 min. Add 30 μl ddH 2 O dissolves DNA. The DNA solution was stored at -20°C for later use.
[0109] 2) PCR amplification and sequencing detection...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com