Process for recovering magnesium and manganese elements in industrial waste water
An industrial waste water and process technology, applied in magnesium chloride, magnesium halide, manganese halide and other directions, can solve the problems of not being able to obtain pure manganese products, high concentration of divalent magnesium ions, large amount of bicarbonate, etc., and achieve accurate results and precipitation. The effect of high rate and short response time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
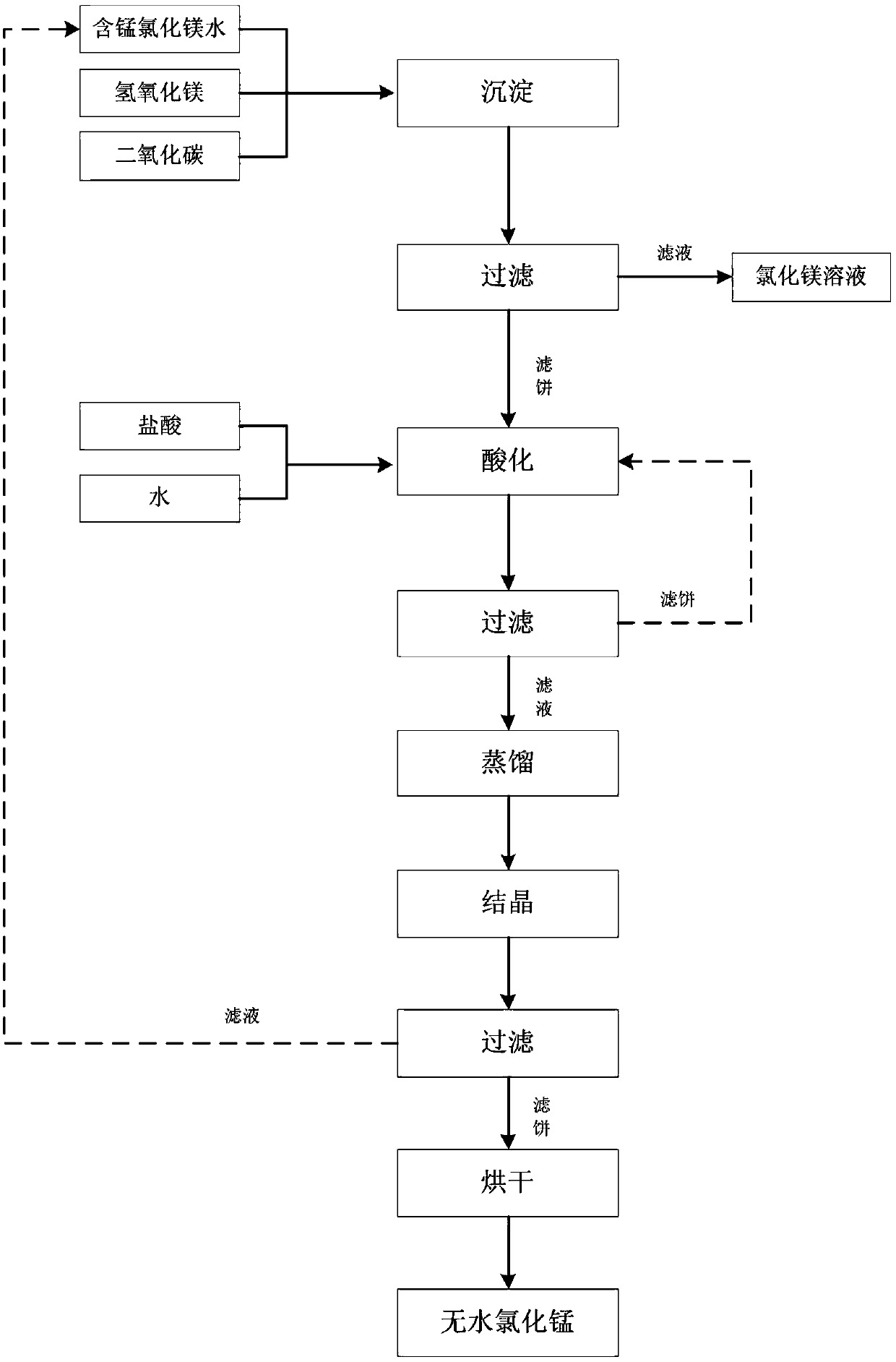
[0037] A process for recovering magnesium and manganese elements from industrial wastewater includes the following steps:
[0038] S1 Wastewater element determination: Collect 500kg of process waste water from the coupling reaction using Grignard reagent to determine the moles of magnesium chloride and manganese chloride in the waste water. The moles of magnesium chloride are 134.4mol and the moles of manganese chloride are 160.5mol;
[0039] S2 precipitation of manganese chloride: add 166.92 mol of magnesium hydroxide to the wastewater, stir in a high-pressure reactor and heat up to 75-85°C, introduce carbon dioxide gas to react, centrifuge, filter, and wash to obtain filtrate I and filter cake;
[0040] S3 acidification and salt precipitation: add 192.6mol of water to the filter cake in step S2 for beating, add hydrochloric acid dropwise at 20°C, and filter to obtain filtrate II;
[0041] S4 distillation crystallization: the filtrate II in step S3 is subjected to vacuum distillation,...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A process for recovering magnesium and manganese elements from industrial wastewater includes the following steps:
[0053] S1 Wastewater element determination: Collect 500kg of process wastewater from the coupling reaction using the Grignard reagent to determine the molar amount of magnesium chloride and manganese chloride in the wastewater, where the molar number of magnesium chloride is 135.6mol, and the molar number of manganese chloride is 160.9mol;
[0054] S2 precipitation of manganese chloride: add 168.9 mol of magnesium hydroxide to the wastewater, stir in a high-pressure reactor and heat up to 75-85°C, introduce carbon dioxide gas to react, centrifuge, filter, and wash to obtain filtrate I and filter cake;
[0055] S3 acidification and salt precipitation: add 197.9mol of water to the filter cake in step S2 for beating, add hydrochloric acid dropwise at 25°C, and filter to obtain filtrate II;
[0056] S4 distillation crystallization: the filtrate II in step S3 is subjec...
Embodiment 3
[0067] A process for recovering magnesium and manganese elements from industrial wastewater includes the following steps:
[0068] S1 Wastewater element determination: Collect 500kg of process waste water from the coupling reaction using Grignard reagent to determine the moles of magnesium chloride and manganese chloride in the waste water, where the moles of magnesium chloride are 134.2mol and the moles of manganese chloride are 163.5mol;
[0069] S2 precipitation of manganese chloride: add 174.9mol of magnesium hydroxide to the wastewater, stir in a high-pressure reactor and heat up to 75-85°C, introduce carbon dioxide gas to react, centrifuge, filter, and wash to obtain filtrate I and filter cake;
[0070] S3 acidification and salt precipitation: add 204.4mol of water to the filter cake in step S2 for beating, add hydrochloric acid dropwise at 30°C, and filter to obtain filtrate II;
[0071] S4 distillation crystallization: the filtrate II in step S3 is subjected to vacuum distillat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com