Antimicrobial, insecticidal and acaricidal system
A system and carrier particle technology, used in the fields of antibacterial, acaricidal compounds, and insecticides, it can solve problems such as poor taste, reduced pest efficacy, and not always achieved, achieve enhanced chemical and thermal stability, reduced minimum concentration, Long-lasting effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
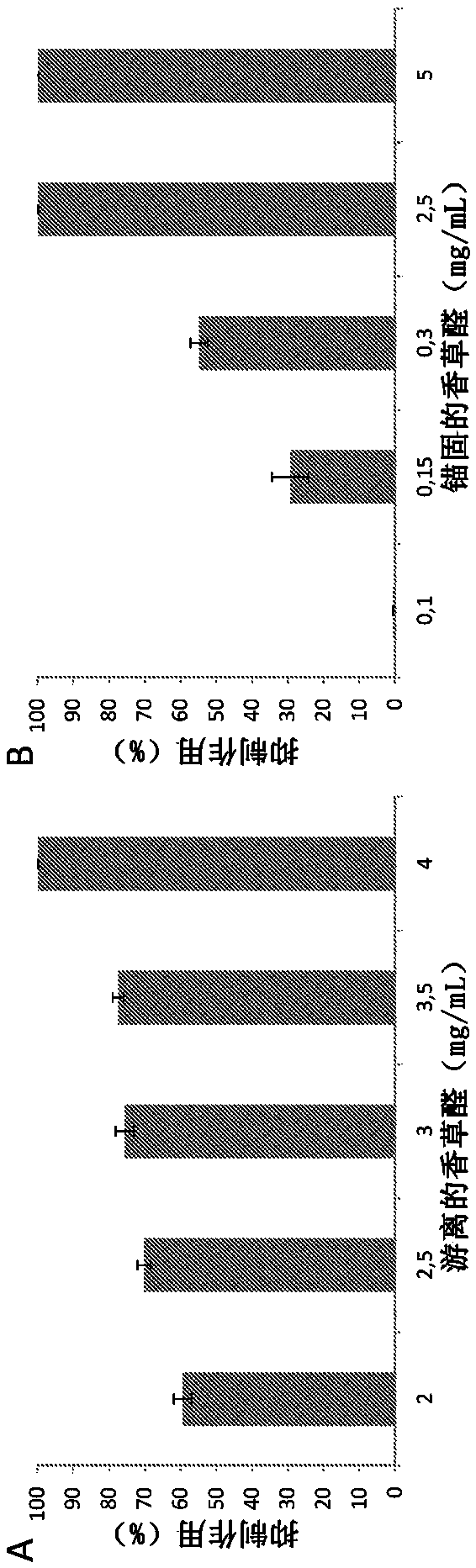
[0055] The first study was the functionalization of vanillin on MCM-41 mesoporous particles and its antibacterial activity.
[0056] To this end, an in vitro assay was performed to determine the effect of L. innocaria ( Listeria innocua ) of bacterial viability. In the absence of pellets or active compound (positive control), microbial survival was determined as 100% of the population to calculate survival in treated samples.
[0057] For this purpose, different suspensions of granules or free vanillin in broth medium (tryptone soy broth) were prepared and added with microbial inoculum to obtain about 10 6 Initial population of CFU / ml. The suspension was incubated for 2 hours at 37°C with orbital agitation (150 rpm). Then, serial dilutions were inoculated in selective medium for 48 hours, followed by counting colony forming units (CFU) and calculating percent inhibition.
[0058] attached figure 1 Shown is the effect of different concentrations of free vanillin (left pa...
example 2
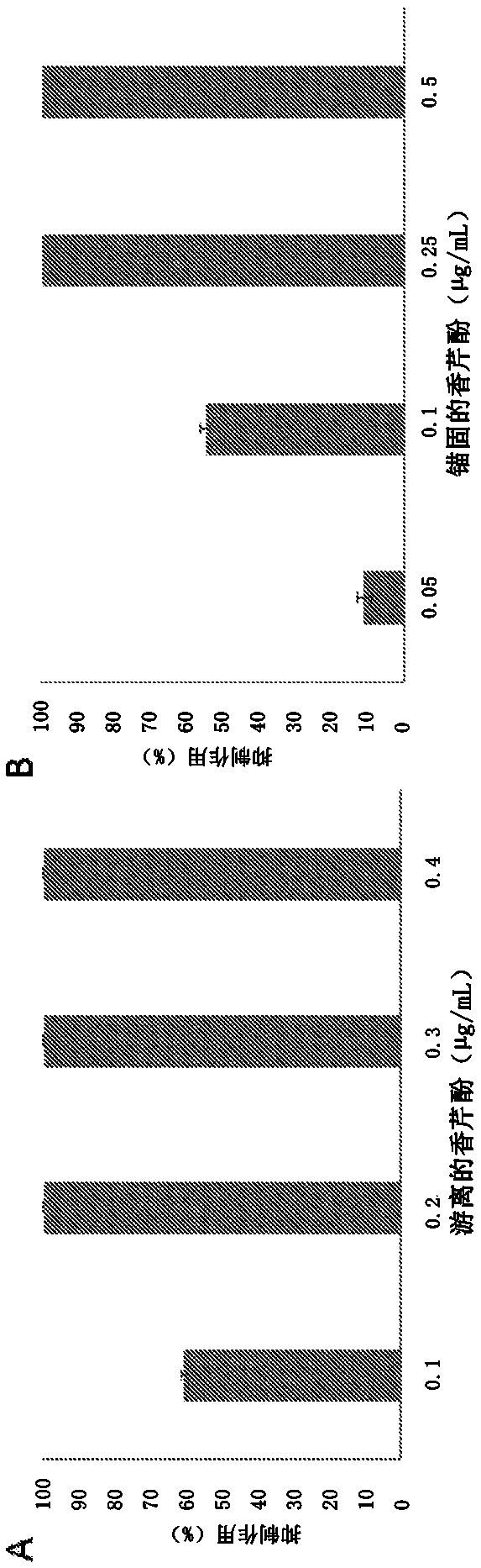
[0063] A study similar to that described in Example 1 was performed to determine the antibacterial activity of carvacrol functionalized on MCM-41 microparticles compared to free carvacrol.
[0064] attached figure 2 Shown are the anti-L. innocuae ( Listeria innocua ) percent inhibition of cultures.
[0065] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that after carvacrol is anchored on the silica microparticles in the same manner as the previous example, its antibacterial activity is maintained.
[0066] Results similar to those described in Examples 1 and 2 above were also obtained using different sized carrier particles (data not shown).
example 3
[0068] The possible mechanism of action of the antibacterial compounds functionalized on the carrier particles was investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). image 3 shows Listeria innocua ( L. innocua ) Morphological changes after treatment with functionalized MCM-41 particles.
[0069] It can be observed that the treated cells exhibit severe morphological damage, rupture of membranes and cell walls, and loss of intracellular components. These results confirm that active compounds functionalized on carrier particles are identical to their free forms and primarily target the outer cell envelope.
[0070] Example 4 (comparative example):
[0071] The anchoring of octanoic acid on mesoporous MCM-41 particles was studied. Caprylic acid is a medium-chain fatty acid that has been shown to have antimicrobial activity against a variety of microorganisms, but its use is limited due to its strong rancid odor. Therefore, anchoring of caprylic acid on MCM-41 micropar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com