Enteric nano-microparticles loaded with insulin as well as preparation method and applications of enteric nano-microparticles
An insulin and enteric technology, which is applied in the field of insulin-loaded enteric nanoparticles and their preparation, can solve problems such as low oral bioavailability, and achieve high oral bioavailability, simple and convenient administration, and relief of diabetes symptoms. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1 Synthesis of quaternized chitosan (HTCC)
[0057] Chitosan (2g) was dissolved in 100mL aqueous solution containing 2wt% acetic acid, then heated to 80 o After C, 5 mL glycidyltrimethylammonium chloride (GTMAC) aqueous solution was slowly added dropwise to the solution for further reaction for 24 hours. After cooling, the resulting solution was precipitated in 10 times the volume of acetone for 3 times, then dialyzed against water for 3 days, and freeze-dried. , to obtain the final product HTCC. The degree of quaternization of HTCC is 43%.
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2 Preparation of Enteric Nanoparticles Loaded with Insulin
[0059] Fast nanocomposite (FNC) technology is a method for rapidly mixing polyelectrolyte aqueous solution with a multi-channel vortex mixer to prepare drug-loaded particles in an efficient, continuous and controllable way (recorded in the inventor's previous patent application number PCT / US2017 / 014080 middle). The nanoparticles prepared by this method have the advantages of small particle size, uniform size distribution, and high batch reproducibility, and the preparation process does not involve the use of organic solvents, which is very suitable for the nano-formulation of biological agents such as proteins, polypeptides, and nucleic acids. The multi-channel vortex mixer device diagram is shown in figure 1 A and 1B, figure 1 A is the overall structural diagram of the device, which is composed of three identical cylindrical metal bodies; figure 1 B is the top view of the structure of three identic...
Embodiment 3
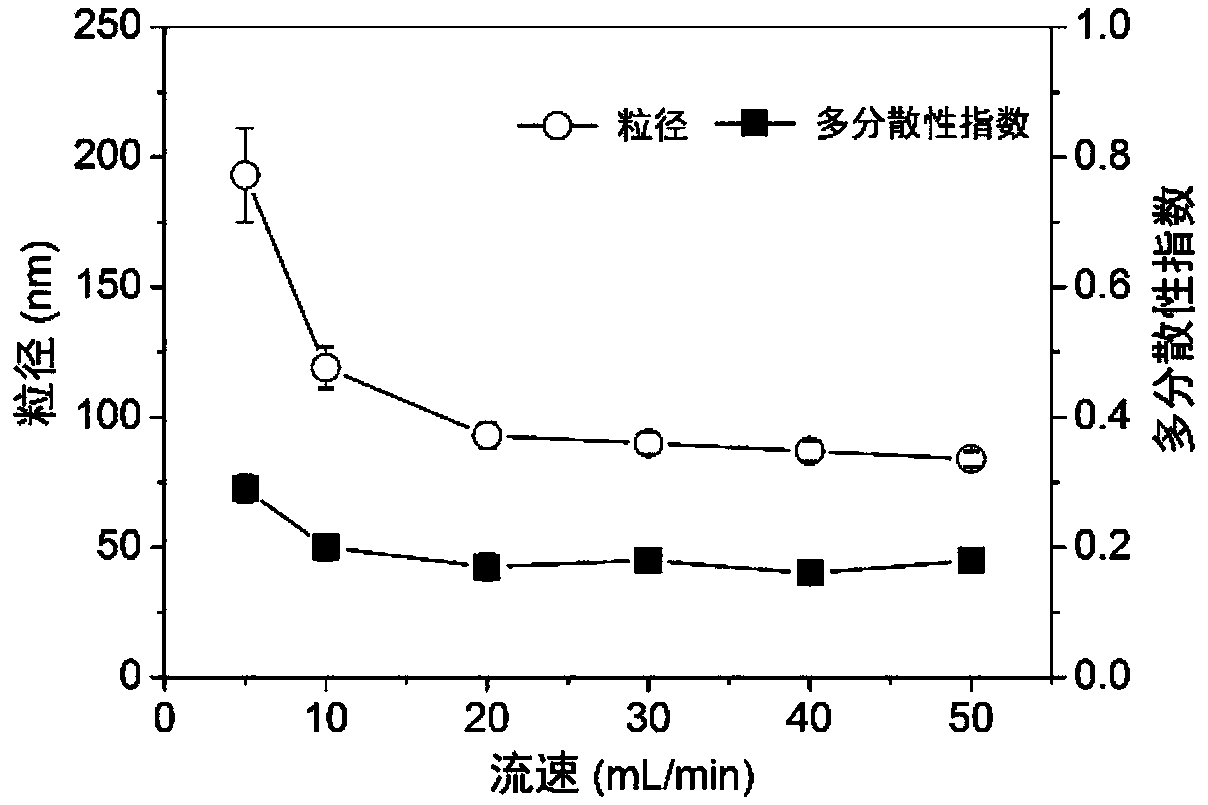
[0078] Example 3 Particle size, potential and morphology characterization
[0079] The particle size, polydispersity index and surface potential of the particle samples in Example 2 were measured by a Malvern particle sizer, and the structure and morphology of various particles were characterized by a transmission electron microscope.
[0080] Figure 11 TEM images of composite nanoparticles (particle-a), enteric particles (particle-b1, particle-b2, particle-b3) are shown. From the electron microscope images, it can be seen that the sizes of particles-a, particles-b1, particles-b2, and particles-b3 are consistent with the particle size results measured by the Malvern particle sizer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com