A device and method for synergistically degrading nitrate based on nanometer zero-valent iron conductive composite resin as catalyst
A nano-zero-valent iron and composite resin technology is applied in the field of water treatment, which can solve the problems of inconvenient engineering application and incomplete removal, and achieve the effect of high-efficiency electrocatalysis, high selectivity, and improved removal efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
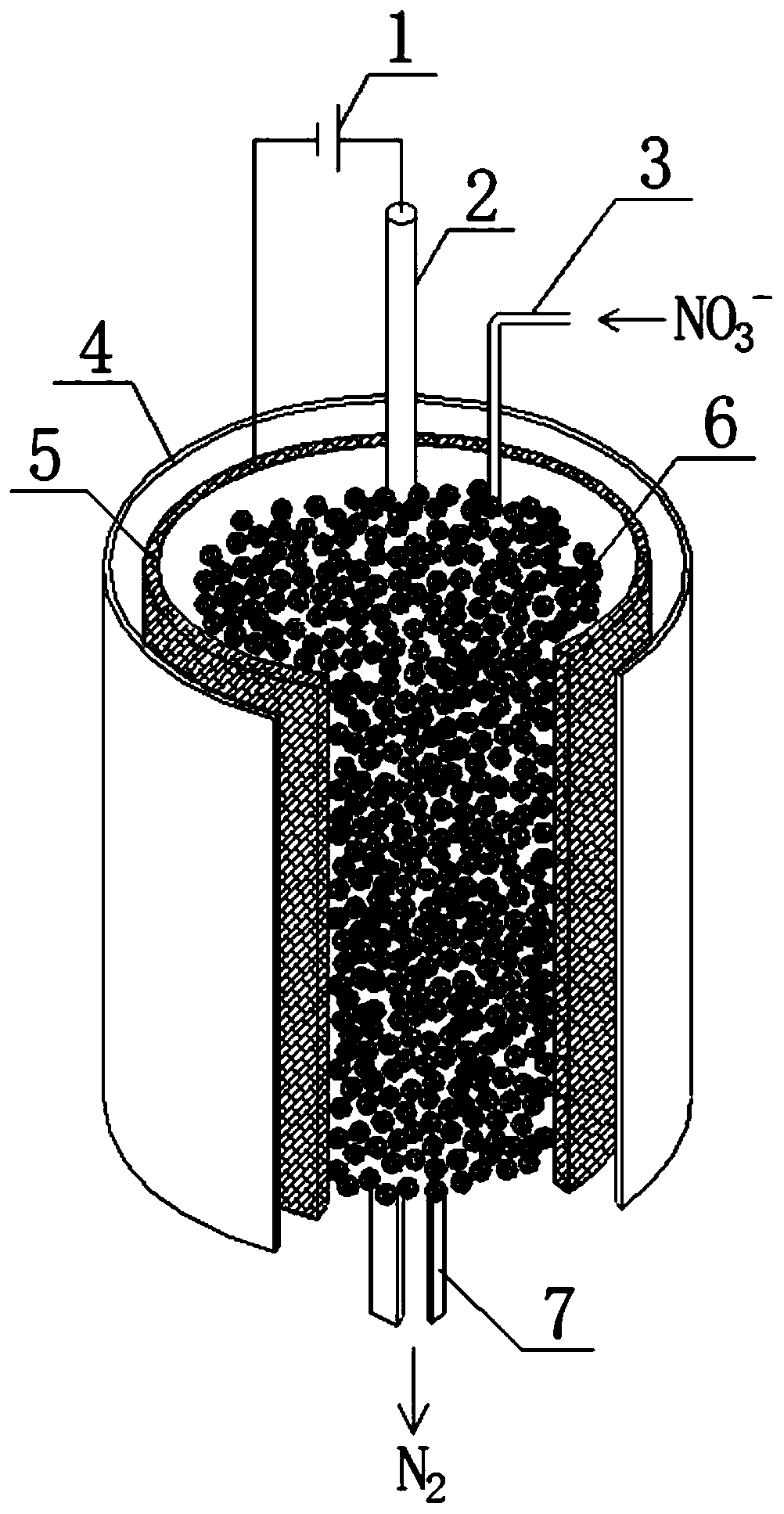
[0044] This embodiment is a device based on a nanometer zero-valent iron conductive composite resin as a catalyst for the synergistic degradation of nitrate between the anode and cathode, such as figure 2 As shown, the device of the present invention is an electrochemical reaction device, including an anode 2, a water inlet pipe 3, a cathode 5, a nanometer-loaded zero-valent iron conductive composite resin 6 and an outlet pipe 7, the cathode 5 is a hollow cylinder, and the The conductive composite resin 6 loaded with nanometer zero-valent iron is evenly filled into the inner space of the cathode 5, and the cathode 5 and the conductive composite resin 6 loaded with nanometer zerovalent iron form a resin column; the anode 2 is inserted into the inner space of the resin column , the water inlet pipe 3 leads to the front end of the resin column, and the water outlet pipe 7 leads out from the rear end of the resin column.
[0045] The device also includes a resin column protection...
Embodiment 2
[0054] This example is an example of using a polystyrene-based resin as a carrier material to prepare a nano-sized zero-valent iron-loaded conductive composite resin for synergistic degradation of nitrate between the cathode and anode.
[0055] The device of the present embodiment is the same as in embodiment 1, and the method comprises the following steps:
[0056] (1) Using methyl acrylate as a monomer and divinylbenzene as a crosslinking agent, adding carbon nanotubes under the action of porogens, initiators and dispersants to obtain a conductive resin containing carboxyl groups; the carbon nanotubes Added to make the resin have conductive function.
[0057] (2) Mix the conductive resin containing carboxyl groups and sodium hydroxide solution in step (1) to react evenly, add the reacted resin to ferric chloride solution for reaction, and finally add sodium borohydride solution for ultrasonic reduction, and finally convert the nano The solid load of zero-valent iron is fixe...
Embodiment 3
[0066] This example is an example of using a polystyrene-based resin as a carrier material to prepare a nano-sized zero-valent iron-loaded conductive composite resin for synergistic degradation of nitrate between the cathode and anode.
[0067] The device of the present embodiment is the same as in embodiment 1, and the method comprises the following steps:
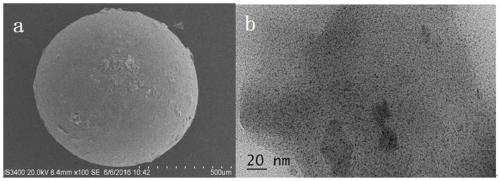
[0068] (1) First, synthesize a conductive composite resin loaded with nano-zero-valent iron. The mass of the resin prepared in this example is 0.5 g, the content of nano-zero-valent iron is 70 mg, and the particle size of the nano-zero-valent iron particles is 5-200 nm ; Pack the resin into a specific conductive resin column.
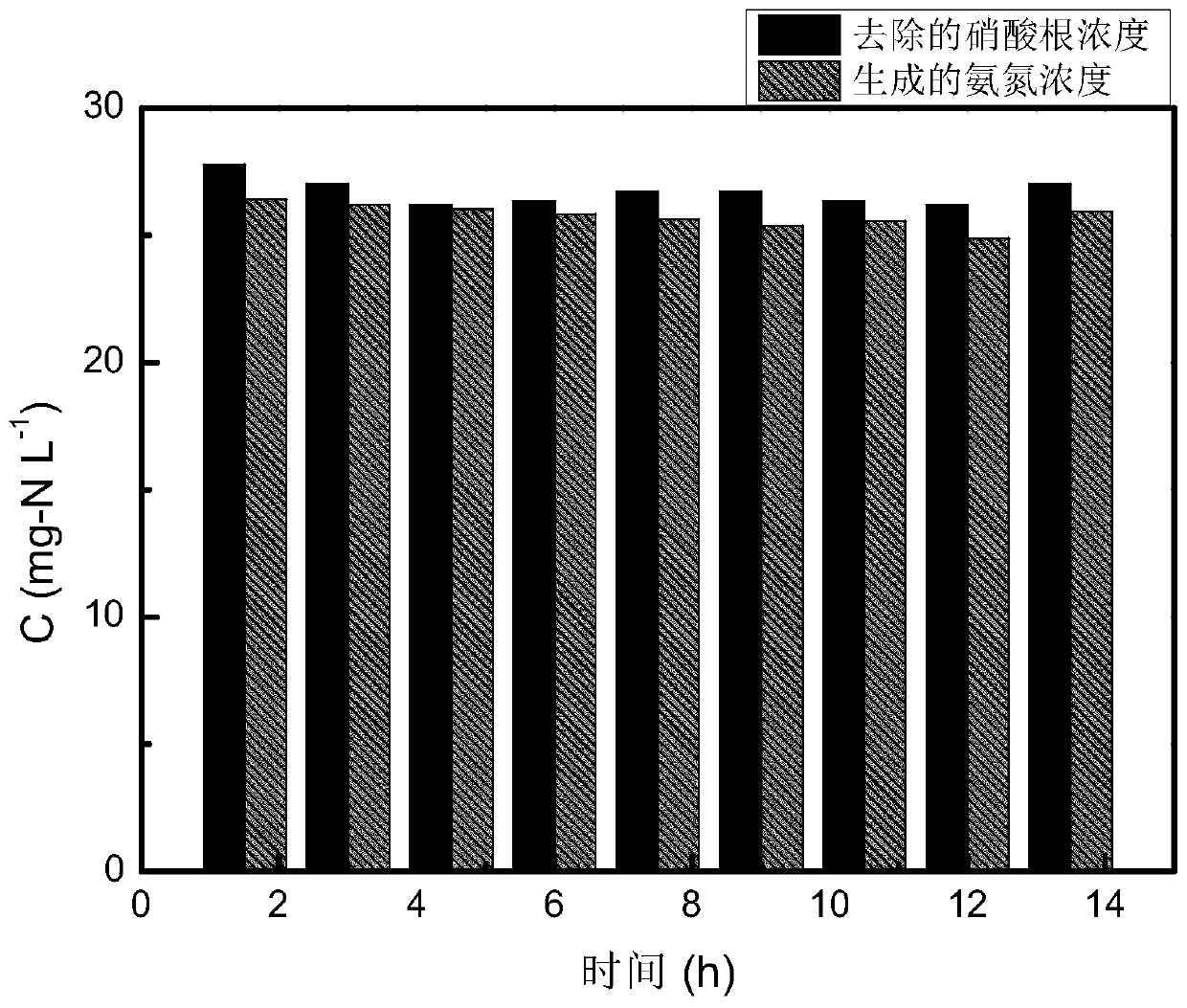
[0069] (2) With 100 mg / L NO 3 - The -N solution is the simulated pollutant, the electrolyte is 2 mol / L sodium chloride solution, and the water output from the resin column is controlled by a peristaltic pump at a speed of 0.15 mL / min.
[0070] (3) When the power is turned on, when the voltage is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com