Construction of a non-aflatoxin-producing strain and method for preventing and controlling Aspergillus flavus contamination
A technology of aflatoxin and Aspergillus flavus strains, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of unknown and pathogenicity of Aspergillus flavus, and achieve the effects of cost reduction, huge economic and social benefits, and pollution control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Embodiment 1, in Aspergillus flavus Aflrum1 gene knockout
[0050] Aspergillus flavus Aflrum1 Gene function in Aspergillus flavus morphogenesis and virulence expression, first knockout in Aspergillus flavus Aflrum1 Gene.
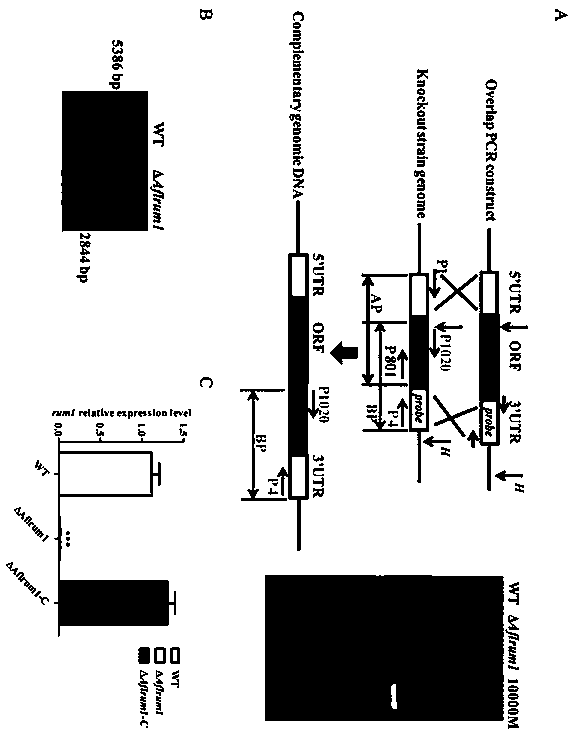
[0051] figure 1 A shows the gene knockout strategy and restriction map. in vitro construction Aflrum1 Gene knockout fragments, through the method of homologous recombination, the chromosome Aflrum1 The 3.5 kb DNA fragment in the gene was used pyrG replacement, thereby knocking out the chromosomal Aflrum1 Gene.
[0052] The specific method is as follows:
[0053] Using the 5' primer GGCACGAGCTATTAGTGATATTAGTCGAGTCCGA (SEQ ID NO: 3); and the 3' primer CAAGTGAGCCGACCGATTGAGGGAAGTAGT (SEQ ID NO: 4); the upstream fragment of about 1.2 kb was amplified by PCR from the genomic DNA of Aspergillus flavus CA14 strain;
[0054] Using the 5' primer ACTACTTCCCTCAATCGGTCGGCTCACTT GGCCTCAAACAATGCTCTTCACCC (SEQ ID NO: 5); and the 3' primer GAACCCATG...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2, Aflrum1 The Effect of Gene Knockout on Sporulation of Aspergillus flavus
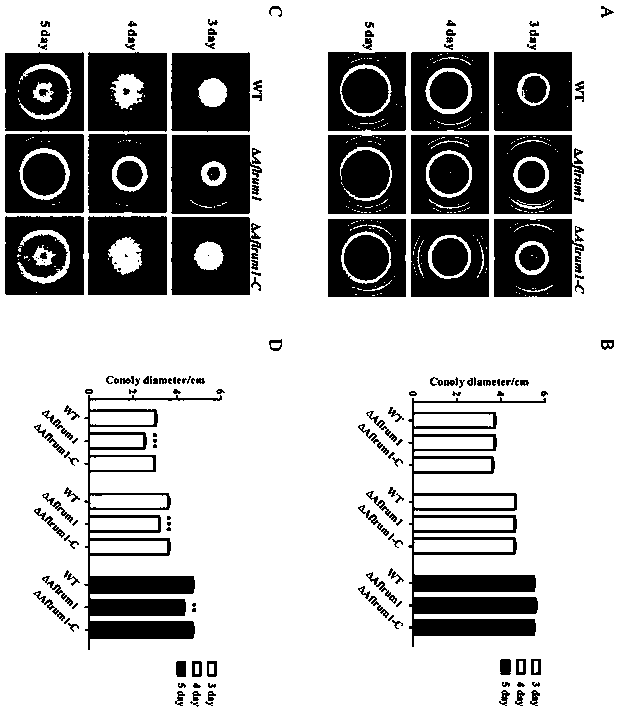
[0058] Knockout in Aspergillus flavus by homologous recombination Aflrum1 Gene, Southern blot analysis confirmed that the knockout was successful. to detect Aflrum1 Whether the deletion of the gene will affect the spore production of Aspergillus flavus, the inoculation concentration on the PDA medium is 10 6 1 μl of spore solution per ml, and placed at 37°C ( figure 2 A, 2B), 29°C ( figure 2 C, 2D) Cultivate under dark conditions for 5 days, and observe the sporulation of the following strains. The wild-type strain WT produced a large number of green spores, while Aflrum1 The number of green spores produced by the deletion strain was much higher than that of the WT, and the statistical analysis of the data also showed this point.
[0059] This result shows that, Aflrum1 Gene deletion affects sporulation in Aspergillus flavus.
Embodiment 3
[0060]Embodiment 3, Aflrum1 Effect of gene knockout on toxin production of Aspergillus flavus
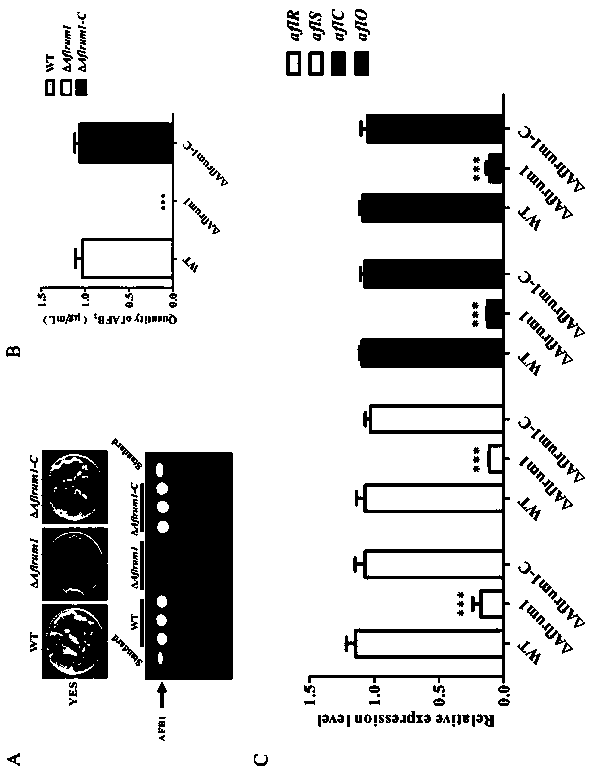
[0061] to detect Aflrum1 Whether the deletion of the gene will affect the toxin production of Aspergillus flavus, inoculate the spores in the YES liquid medium to a final concentration of 10 6 cells / ml, cultured statically for 6 days under continuous dark conditions at 29°C, extracted the toxin, and analyzed the toxin production of each strain by TLC. The results showed that the WT strain produced a large amount of aflatoxins AFB1 and AFB2, while ⊿ Aflrum1 AFB1 and AFB2 are obviously not produced, and the statistical analysis of the data also shows this ( image 3 A, 3B).
[0062] Simultaneous detection of aflatoxin biosynthesis pathway regulatory genes by qRT-PCR wxya and wxya , and some structural genes wxya and wxya the transcription level of actin As an internal control for transcriptional analysis. Compared with the WT strain, ⊿ Aflrum1 The transcription lev...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com