Preparation method of porous zinc support material for composite ZnO nanorod
A scaffold material and nanorod technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of porous zinc scaffold materials, can solve problems such as unsuitability, high energy consumption, complicated process, etc., and achieve the effect of saving time and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The first step is to prepare porous zinc scaffold material:
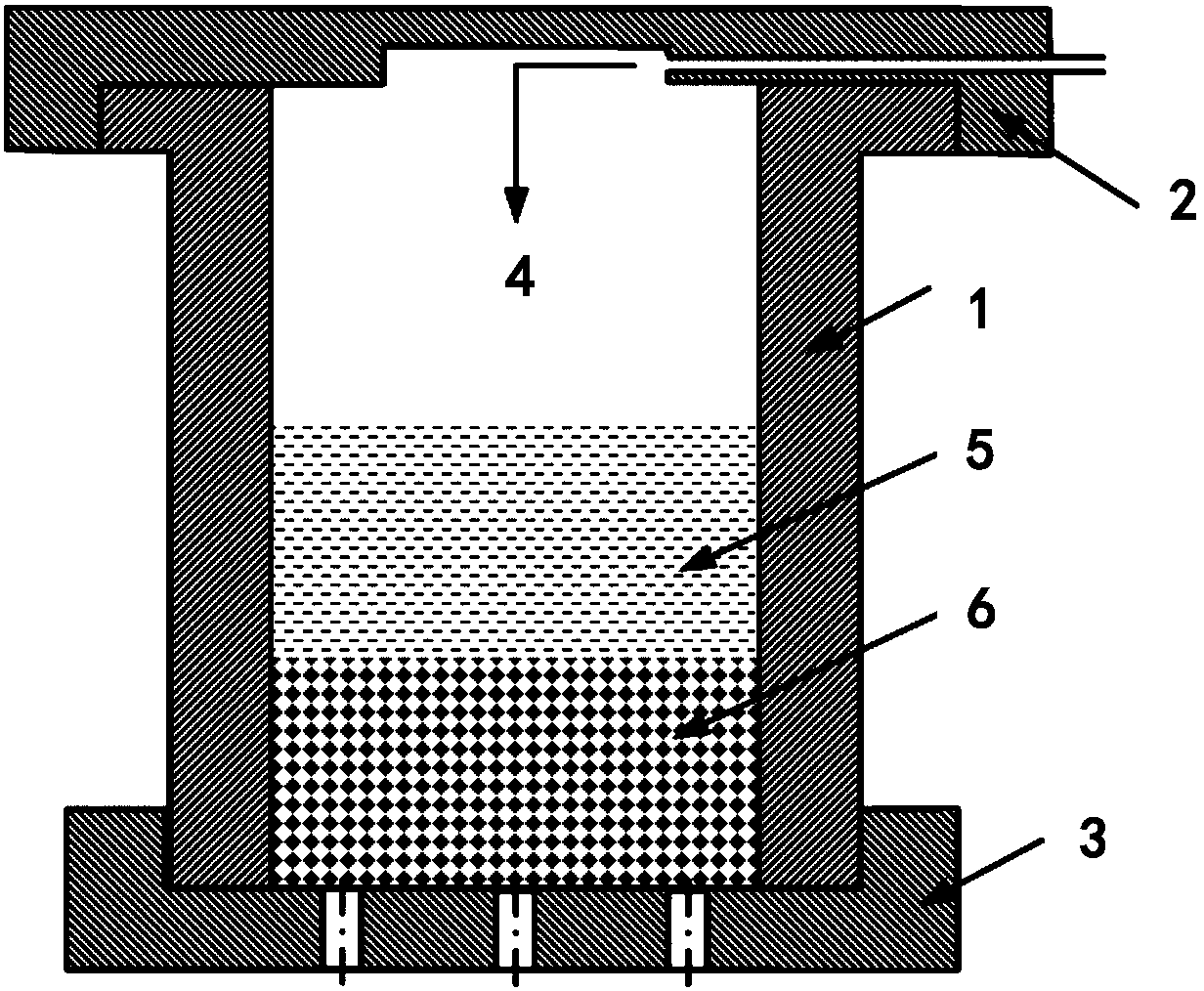
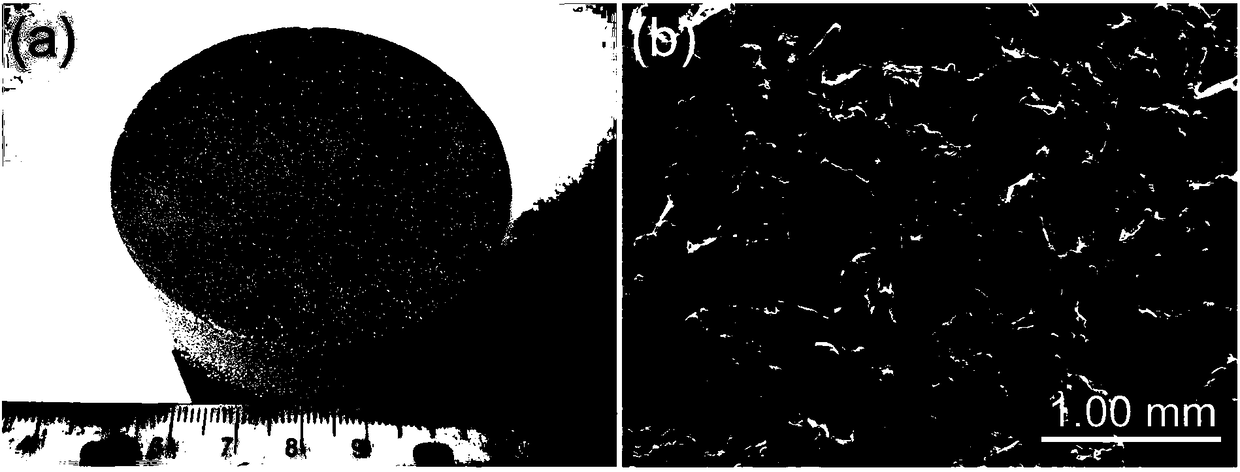
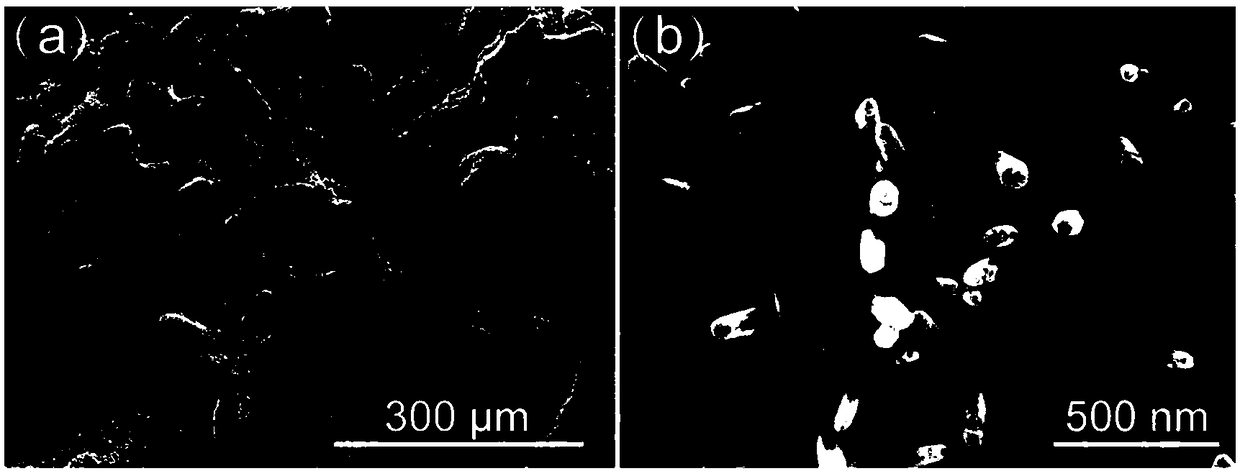
[0037] (1.1) Weigh 755.2g of commercial cast pure zinc ingot and put it into a high-purity graphite crucible, put the graphite crucible into a crucible resistance furnace and heat it to 500°C. Put 230g of ~300μm sodium chloride particles into a steel mold with a height of 200mm and a diameter of φ60mm, put the steel mold into another electric resistance furnace without covering it, heat it to 345°C, and keep it warm for 50min , after the above-mentioned two heat preservation finishes, take out the steel mold from the resistance furnace, pour the zinc melt in the above-mentioned graphite crucible into the above-mentioned steel mold with sodium chloride particles immediately and cover the mold immediately. The upper cover of the steel mold is then filled with compressed air into the steel mold to keep the gas pressure in the inner cavity of the steel mold at 4 MPa, and the pressure holding time is 4 minutes. T...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The first step is to prepare porous zinc scaffold material:
[0050](1.1) Weigh 656.1g of commercial cast pure zinc ingot and put it into a high-purity graphite crucible, put the graphite crucible into a crucible resistance furnace and heat it to 490°C. Put 191.6g of sodium chloride particles ~215μm into a steel mold with a height of 200mm and a diameter of φ60mm, put the steel mold into another electric resistance furnace without the lid on it, heat it to 325°C, and keep it warm 40min, after the heat preservation of the above two is finished, the steel mold is taken out from the resistance furnace, and the zinc melt in the above-mentioned graphite crucible is poured into the above-mentioned steel mold with sodium chloride particles and immediately covered The upper cover of the steel mold immediately fills the steel mold with compressed air to keep the gas pressure in the inner cavity of the steel mold at 3 MPa, and the pressure holding time is 4 minutes. Seepage occur...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The first step is to prepare porous zinc scaffold material:
[0058] (1.1) Weigh 800g of commercial cast pure zinc ingot and put it into a high-purity graphite crucible, put the graphite crucible into a crucible resistance furnace and heat it to 520°C, keep it warm for 60min after the zinc ingot is melted, and weigh the particle size to be 375~ Put 365g of 600μm sodium chloride particles into a steel mold with a height of 200mm and a diameter of φ60mm, put the steel mold into another electric resistance furnace without covering it, heat it to 360°C, and keep it warm for 60min. After the heat preservation of the above two is finished, the steel mold is taken out from the resistance furnace, and the zinc melt in the above-mentioned graphite crucible is immediately poured into the above-mentioned steel mold with sodium chloride particles and the steel mold is immediately covered. Make the upper cover of the mold, and then fill the steel mold with compressed air to keep the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com