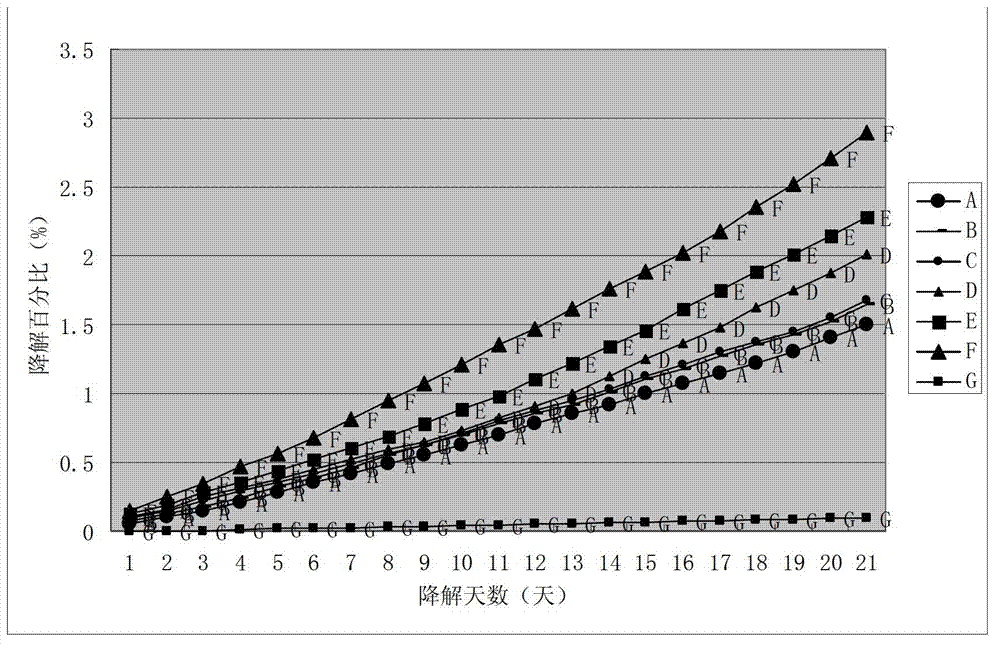
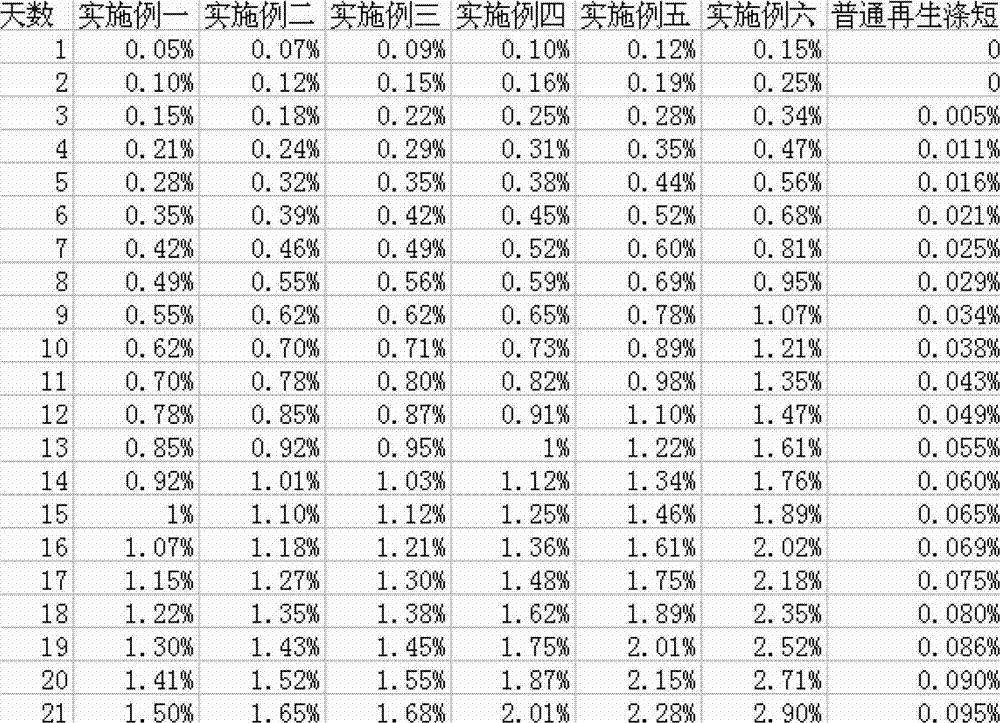
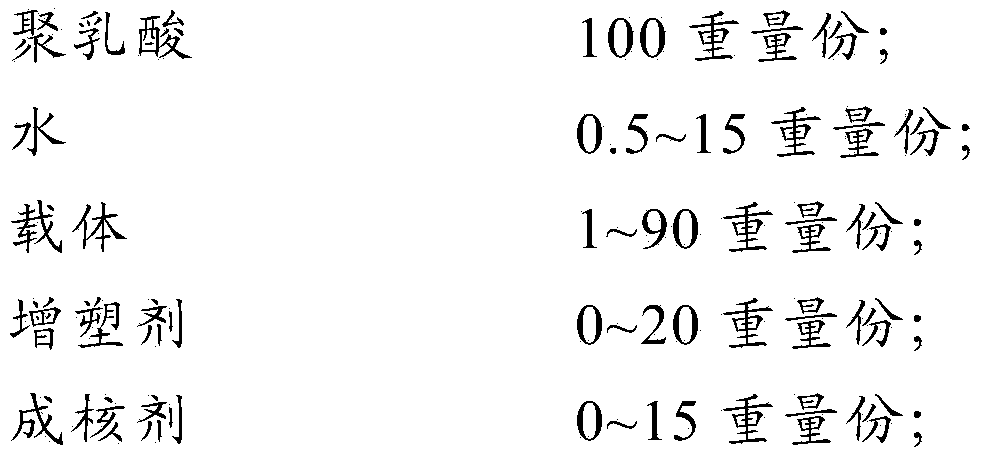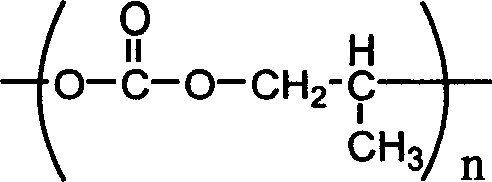Patents
Literature
96results about How to "Achieve biodegradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
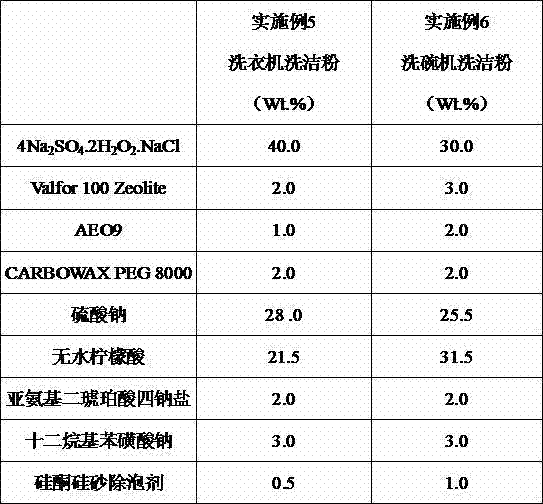
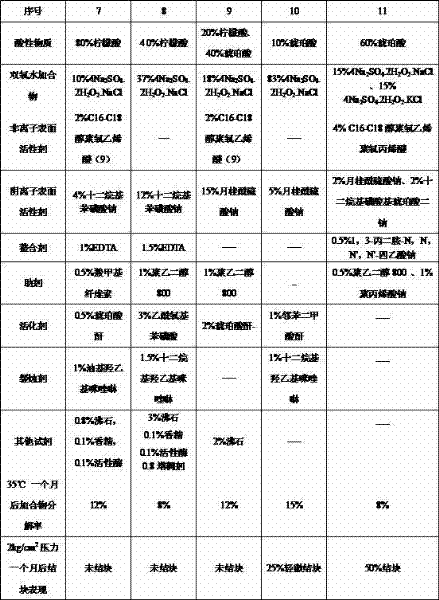
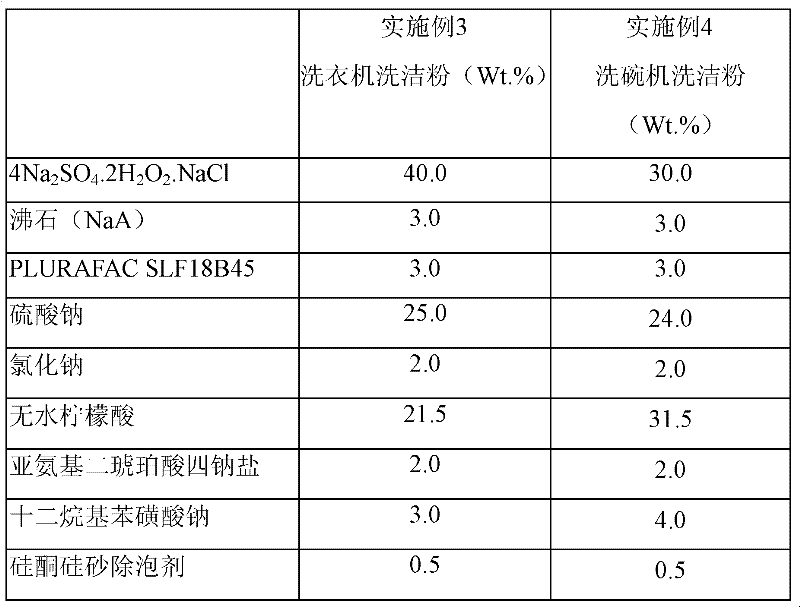
Acidic cleaning composition
InactiveCN102559399ALong term storageImproved bleaching and disinfection functionNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOrganic/inorganic per-compounds compounding agentsLaundry washing machineActive agent
The invention discloses an acidic cleaning composition. The acidic cleaning composition is characterized in that the composition comprises the following components by weight percent: 10-90% of hydrogen peroxide adduct which is stable under the acidic condition, 10-90% of acidic material, 0-50% of anionic surfactant, 0-20% of nonionic surfactant, 0-10% of chelating reagent, 0-90% of additive, 0-40% of activator, 0-10% of corrosion inhibitor and 0-15% of other reagents. The acidic cleaning composition disclosed by the invention has multiple functions of bleaching, descaling, disinfecting, removing the biofilm and the like; and the composition is mainly used as the surface cleaning agent, and can be dispersed in water to wash the inside of the washing machine and the inside of the dish-washing machine or used to clean and disinfect the common hard surface, etc.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG RENDER CHEM
Polylactic acid foam material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103642185AGood biodegradabilityThe preparation process is safe and environmentally friendlyPlasticizerPolylactic acid
The invention provides a polylactic acid foam material, which is obtained by foaming of a mixture. The mixture comprises by weight 100 parts of polylactic acid, 0.5-15 parts of water, 1-90 parts of a carrier, 0-20 parts of a plasticizer, 0-15 parts of a nucleating agent, 0-3 parts of an anti-hydrolysis agent and 0-5 parts of a chain extender. The polylactic acid foam material in the application uses water as a foaming agent rather than an organic foaming agent, so that the foaming of polylactic acid is safe and environment-friendly. The application uses polylactic acid as a matrix for the foam material to endow the foam material with good biodegradability, thus realizing biodegradation of the polylactic acid foam material. The application also provides a reparation method of the polylactic acid foam material.
Owner:天津佰盛环保科技有限公司
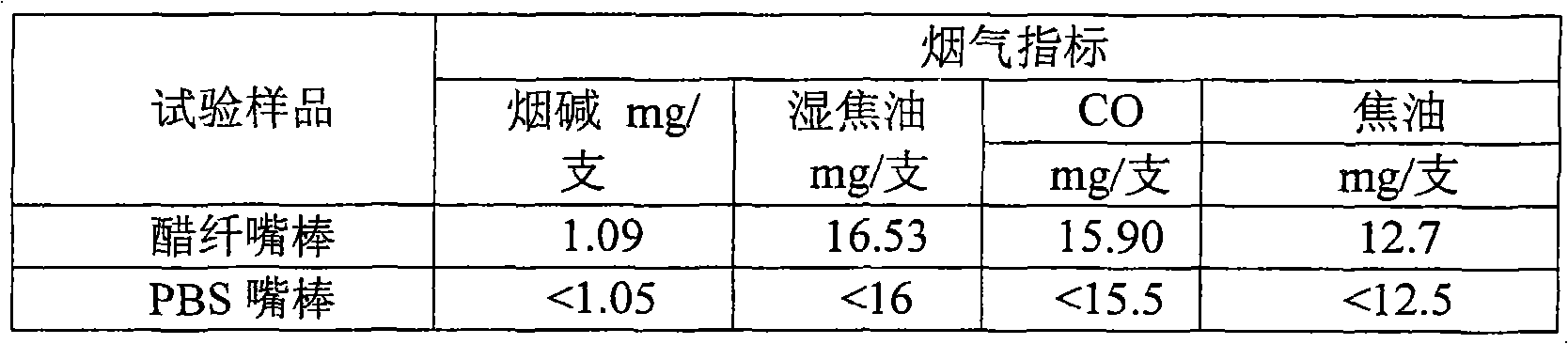
Biodegradable cigarette fiber material and cigarette filter
ActiveCN102080275APromote degradationDegradation meetsTobacco smoke filtersFilament/thread formingFiberPolymer science
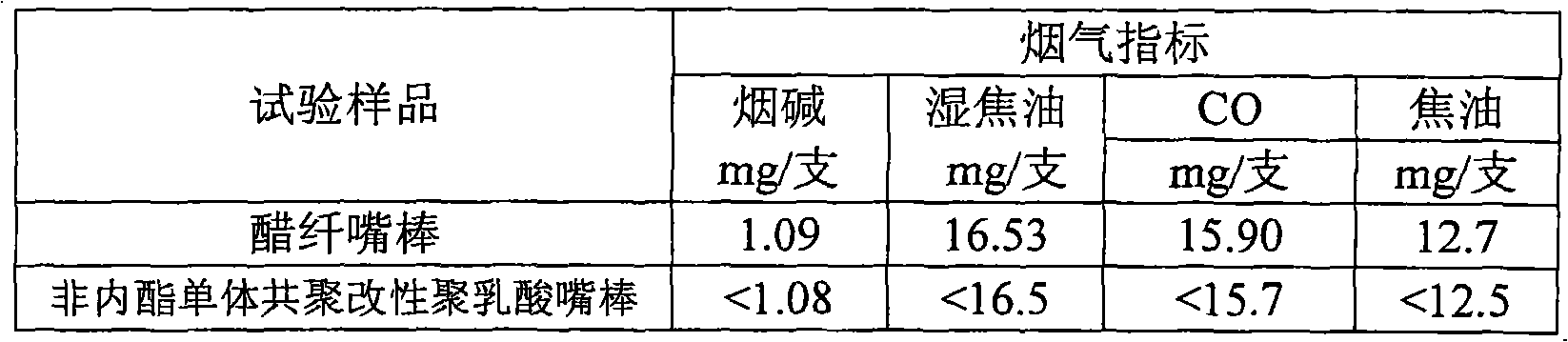
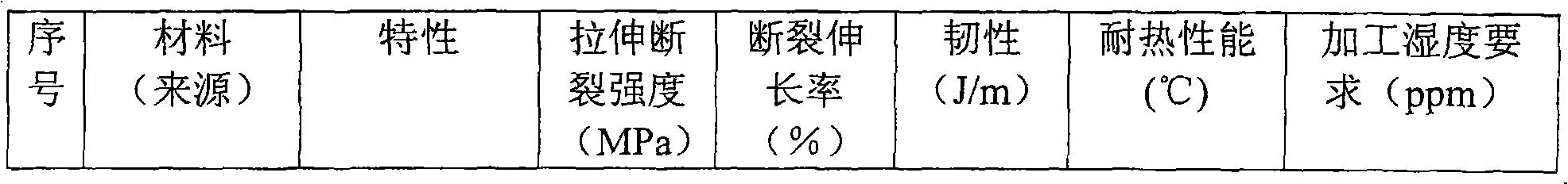
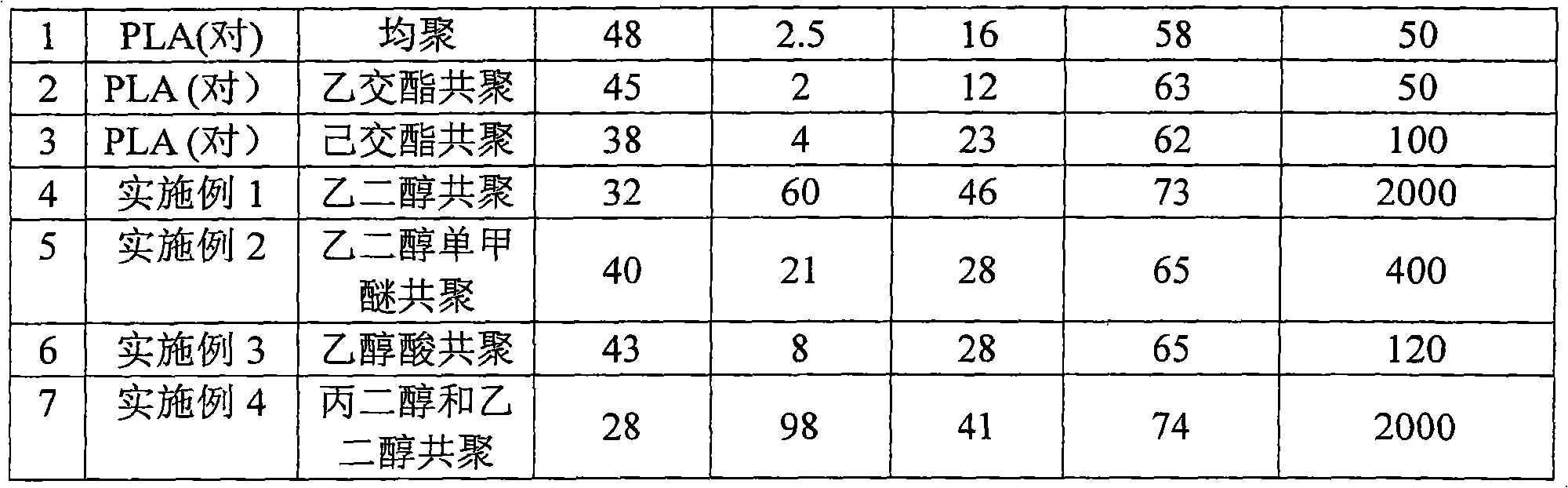
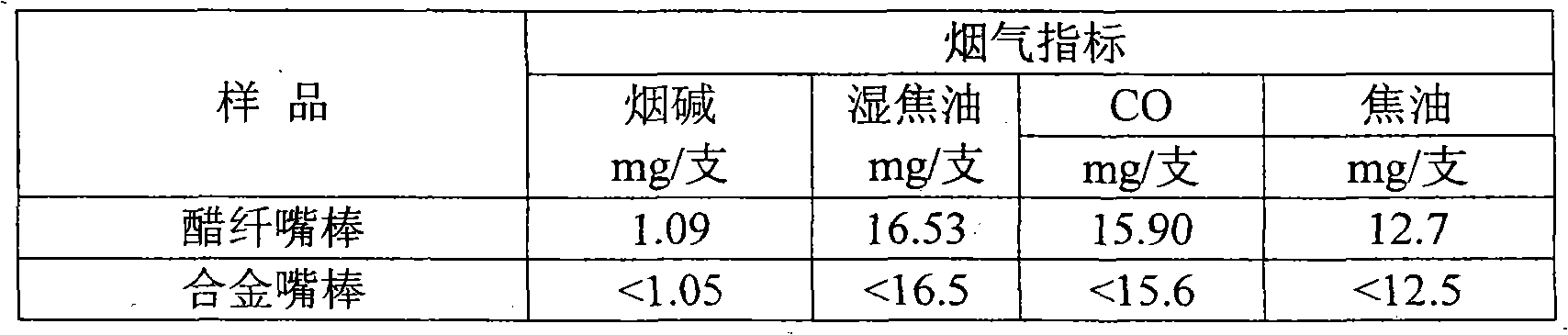
The invention provides a biodegradable cigarette fiber material and a cigarette filter. The biodegradable cigarette fiber material comprises the following raw materials of 90-100 percent of polylactic acid modified by a non-lactone monomer through copolymerization and 0-10 percent of stabilizing agent as well as the balance of high polymer of the polylactic acid chain segments, wherein the polylactic acid modified by the non-lactone monomer through copolymerization is a non-lactone monomer chain segment in a molecular chain containing 1-30 percent of the total quantity of the chain segments, the weight-average molecular weight of the high polymer is 0.5-3.5 millions and the dispersion index of the high polymer is 1.2-3.0. The biodegradable cigarette fiber material is prepared from the raw materials through using a melting spinning process. The invention also provides a biodegradable cigarette filter rod prepared from the cigarette fibre material through sizing processing, and a cigarette product. The processing and using properties of the raw materials are remarkably improved. The provided cigarette filter has a property equivalent to the property of the traditional general cigarette filter, a cigarette end discarded by a smoker can be decomposed within shorter time in the natural environment, and the pollution of the cigarette waste to the environment is avoided at present while the requirement of cigarette production is met.
Owner:海南海福新材料有限公司
Biodegradable cigarette fiber material and cigarette filter
ActiveCN102080278ABiodegradableImprove adsorption capacityTobacco smoke filtersMelt spinning methodsFiberPolymer science
The invention provides a biodegradable cigarette fiber material and a cigarette filter. The biodegradable cigarette fiber material comprises the following raw materials of 1-99wt percent of poly(butylene succinate) polymer, 1-99wt percent of polylactic acid polymer and 0-3wt percent of stabilizing agent, and the cigarette fiber material is prepared by processing the raw materials with a melting spinning process. The poly(butylene succinate) polymer and the polylactic acid polymer can be respective homopolymers of the two polymers per se and can also be copolymers containing other monomer materials, which do not exceed 30 percent of the total quantity of respective molecular chain segments of the two polymers. The invention also provides a biodegradable cigarette filter rod prepared from the cigarette fibre material through sizing processing, and a cigarette product. The provided cigarette filter has a property equivalent to the property of the traditional general cigarette filter, a cigarette end discarded by a smoker can be decomposed within shorter time in the natural environment, and the pollution of the cigarette waste to the environment is avoided at present while the requirement of cigarette production is met.
Owner:海南海福新材料有限公司
Biodegradable cigarette fiber material and cigarette filter tip
ActiveCN102080276APromote degradationDegradation meetsTobacco smoke filtersFilament/thread formingFiberPolymer science
The invention provides a biodegradable cigarette fiber material and a cigarette filter tip. The biodegradable cigarette fiber material comprises the following components: 90-100% of poly (butanediol succinate) polymer and 0-10% of stabilizing agent, wherein the poly (butanediol succinate) polymer is a high molecular polymer of which the chain link of butanediol succinate in the molecular chain accounts for no less than 70% of the total chain link, the weight-average molecular weight is from fifty thousand to three hundred and fifty thousand, and the dispersancy index being 1.2-3.0. The cigarette fiber material is prepared by performing the melting spinning process on the raw materials. The invention further comprises a biodegradable cigarette filter tip rod prepared by shaping the biodegradable cigarette fiber material and cigarette products. The properties of the cigarette filter tip provided by the invention are equivalent to the properties of the universally used cigarette filter tip in the current market. The butt discarded by a smoker can be decomposed in a short time in natural environment. The cigarette production is met while the problem that the traditional discarded butt pollutes the environment is solved.
Owner:海南海福新材料有限公司
Method for desizing, boiling and bleaching cotton fabric by enzyme only
InactiveCN1944785ANo damageImprove wettabilityBiochemical fibre treatmentDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesChemical treatmentAlpha-amylase
The present invention relates to re-compounding and application in cotton fabric treatment of enzyme preparation, and is especially enzyme process for desizing, boiling off and bleaching cotton fabric. Different enzyme preparation is first re-compounded with alpha-amylase, PVA degrading enzyme, lipase, proteinase, alkaline pectase, xylanase, cellulase, sugar oxidase, etc based on different fabric pre-treating requirements; and then used in desizing, boiling off and bleaching cotton fabric to replace traditional concentrated alkali solution and high temperature chemical process. The present invention has low power consumption and environment friendship.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
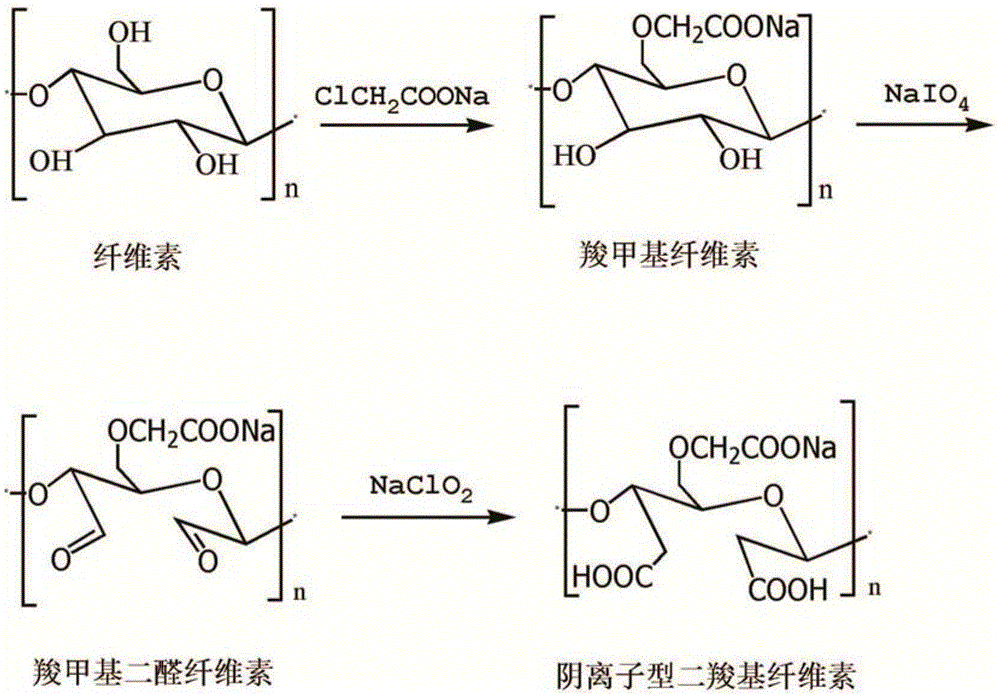
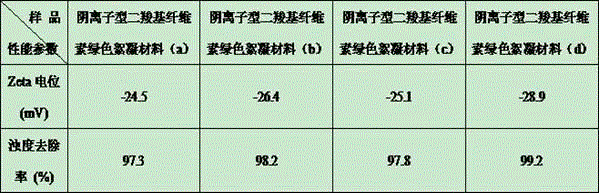
Preparation method for anionic dicarboxy cellulose green flocculation material
InactiveCN105111318AIncreased aldehyde contentEnhanced electronegativityWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationCarboxycelluloseMunicipal sewage
The invention discloses a preparation method for anionic dicarboxy cellulose green flocculation material. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: dissolving cellulose through a sodium hydroxide and urea system, adding an anionic reagent, and generating anionic cellulose; and then preparing the anionic dicarboxy cellulose green flocculation material after two stages of oxidation. The method is simple in operation, the raw materials are easy to obtain, the production cost is low, and the method is easy for popularization and application. According to the material disclosed by the invention, chemically modified cellulose is used as a flocculation material, so that the utilization rate of cellulosic feedstocks is sufficiently improved; no poison or byproduct is generated, so that the flocculation efficiency of the existing flocculation cellulose-based material can be significantly improved, and the environmental pollution is reduced; and meanwhile, raw material dependence of traditional synthetic polymer flocculants on petroleum resources is greatly reduced, and the generated anionic dicarboxy cellulose green flocculation material is completely biodegradable and does not cause secondary pollution. The prepared anionic dicarboxy cellulose green flocculation material is widely applied in the flocculation process of papermaking waste water, dyeing waste water, chemical waste water and municipal sewage, and thus has significant environmental and social benefits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Preparation method of biodegradable regenerated polyester staple fibers
ActiveCN102828276APrevent volatilizationBalanced moistureFilament forming substance formingArtificial filament heat treatmentPolyesterPolymer science
The invention discloses a preparation method of biodegradable regenerated polyester staple fibers, which is characterized by comprising the steps of drying spinning materials by a vacuum drum, mixing with biodegradable master batch dried by a master batch drying system at the feed inlet of a screw extruder; preparing primary fibers after mixing and fusing by the screw extruder and extruding by a spinneret plate; cooling primary fibers by an annular blowing device; successively carrying out winding, falling, bundling and time balancing on the primary fibers in a constant temperature and constant-humidity room; stretching the primary fibers in oil bath and stream respectively; performing curling, relaxation heat setting, cutting and packaging to obtain biodegradable regenerated polyester staple fibers, wherein physical properties and mechanical properties of the biodegradable regenerated polyester staple fibers produced by the method do not change, and therefore, the subsequent processing and usage are not influenced; after being used, the fibers can be decomposed into inert humus, carbon dioxide and water in a microorganism-enriching environments such as refuse landfill or composting site, thereby returning to nature and achieving real biodegradation.
Owner:福建鑫华股份有限公司
Composite material of complete degradable polymer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1687234AHigh glass transition temperatureHigh mechanical strengthPolymer scienceFilling materials
The present invention relates to a polymethyl ethylene carbonic ester / polyvinyl alcohol composite material which can be completely degraded and its preparation method. Said composite material adopts degradable plastics polymethyl ethylene carbonic ester as base body, and uses polyvinyl alcohol with various polymerization degrees and alcoholysis degrees as filling material, and adopts solution blending process to prepare the invented composite material, in which the polyvinyl alcohol content can be 10-40%.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Glutathione response-type dual-drug carrier as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107510849AGood synergyAchieve biodegradationKetone active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDrug synergismEnd-group
The invention discloses a glutathione response-type dual-drug carrier as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biomedical engineering materials. The preparation method comprise the following steps: performing Michael addition reaction to obtain hyperbranched poly(amide amine)s; then connecting a hydrophobic drug onto an end group amino of a high polymer by amidation reaction, so as to form a prodrug micelle molecule; then loading another hydrophobic drug by subject-object assembly of the prodrug micelle molecule, thus effectively increasing drug loading capacity and promoting an synergistic effect of the drugs; preparing to obtain the glutathione response-type dual-drug carrier. The method is mile, the operation is convenient, byproducts are fewer, and a product is easy to separate and purify, thus facilitating the material biocompatibility. The glutathione response-type dual-drug carrier has the advantages of simple material components, easy-to-get raw materials and good biocompatibility, and is hopefully widely applied to the field of the biomedical engineering materials as a great amount of surface functional groups capable of being modified provide support for the application of the carrier in preparing the biomedical engineering materials.
Owner:广州元合生物科技有限公司 +1
Method for deep treatment on difficultly-degraded organic nitrogen-containing industrial wastewater
ActiveCN102976552AOvercome the problem that the removal effect is not good and the effluent is difficult to meet the standardRealize quality reuseWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeMoving bed biofilm reactor
The invention relates to a method for deep treatment on difficultly-degraded organic nitrogen-containing industrial wastewater and belongs to the field of industrial wastewater treatment methods. The method comprises the following steps of 1, putting a suspended filler into a moving-bed biomembrane reactor, carrying out biomembrane culture, after the biomembrane culture, inputting difficultly-degraded nitrogen-containing industrial wastewater subjected to biochemical treatment into the moving-bed biomembrane reactor, and carrying out treatment, wherein the moving-bed biomembrane reactor operates by continuous water feeding, continuous draining and continuous aeration methods, 2, inputting the wastewater treated by the moving-bed biomembrane reactor into a membrane bioreactor, wherein the membrane bioreactor is added with activated sludge and operates by the continuous water feeding, continuous draining and continuous aeration methods, and 3, through a cartridge filter, treating the wastewater treated by the membrane bioreactor, and then filtering the treated wastewater by a reverse osmosis device. According to recycle water demands, it is determined if the step 3 is adopted so that quality-classification recycle is realized.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Degradable antibacterial preservative film product and preparation method thereof
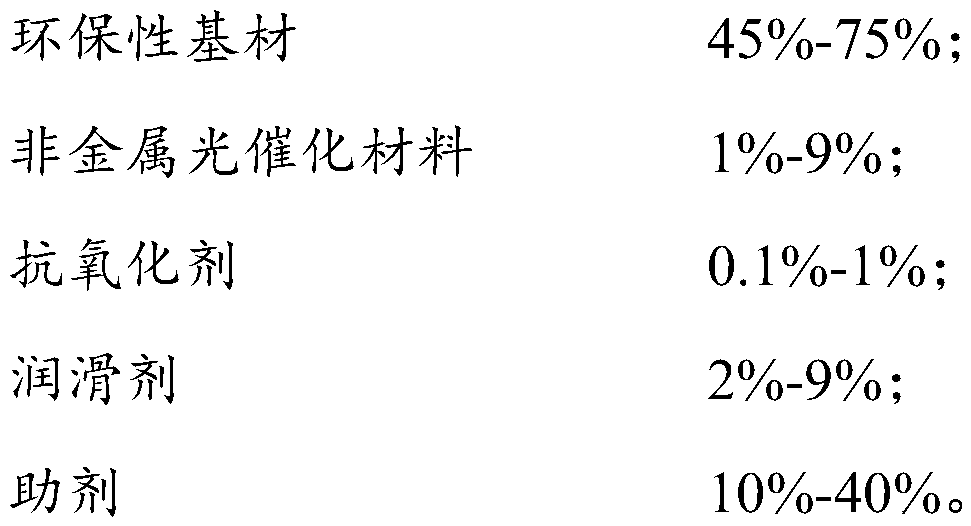
The invention relates to the technical field of packaging materials, in particular to a degradable antibacterial preservative film product and a preparation method thereof. The degradable antibacterial preservative film product is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 45%-75% of an environment-friendly base material, 1%-10%% of a nonmetal photocatalytic material, 0.1%-1%of an anti-oxidant, 2%-9% of a lubricant and 10%-40% of auxiliaries. The degradable antibacterial preservative film product has efficient, broad-spectrum, long-acting and safe antibacterial properties, and facilitates reduction of the use of additives such as the preservative and the like in food and drugs, so that the food and drugs can be stored for a longer time and can be transported further.The degradable antibacterial preservative film product is an environmentally-friendly type material, can be quickly decomposed in a natural environment, is beneficial for ecological environmental protection, reduces pollution and damages to environment, has a wide application prospect, and is widely applied to the packaging and freshness-retaining fields such as food, drugs, fruits and vegetables, fresh food and the like.
Owner:赵梓俨 +2
A degradable sticking plank which gradually release insect sex lures and its production methods
InactiveCN106280334ABiodegradableBiodegradable to achieveInsect catchers and killersEcological farmingZoology
This invention discloses a degradable sticking plank which gradually release insect sex lures and its production methods, which includes: (1) prepare compound plank which contains 80-95% weight degradable material, 1-10% weight porous material with insect sex lures, 1-8% weight color and 2-10% weight filler. (2) coat one side or both side of the plank with glue and release paper, then shape it up and make holes. This plank is biodegradable and gradually release sex lure which increase disinsection effect and can be applied to eco-agriculture industry.
Owner:上海盛谷光电科技有限公司
Biodegradation method of methyl tert-butyl ether in ground water
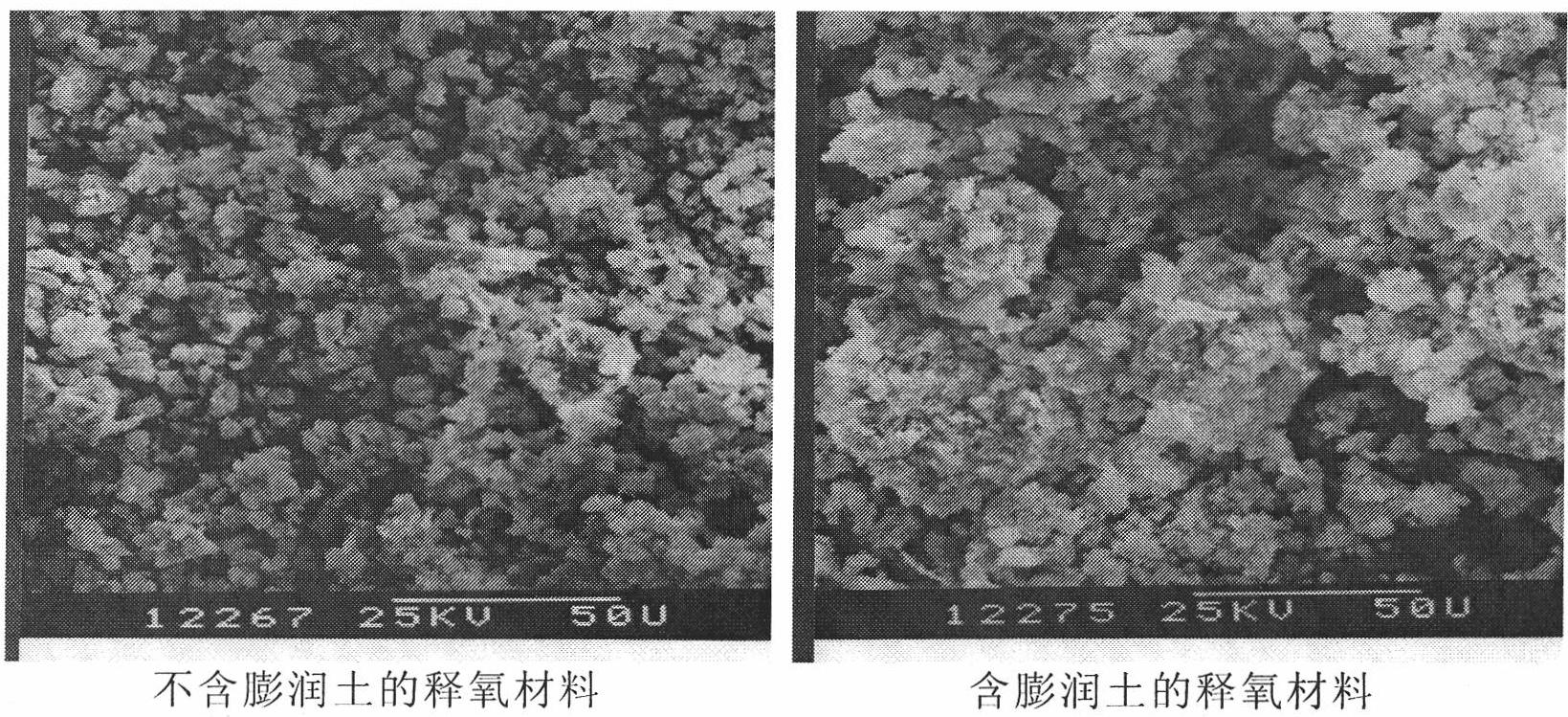
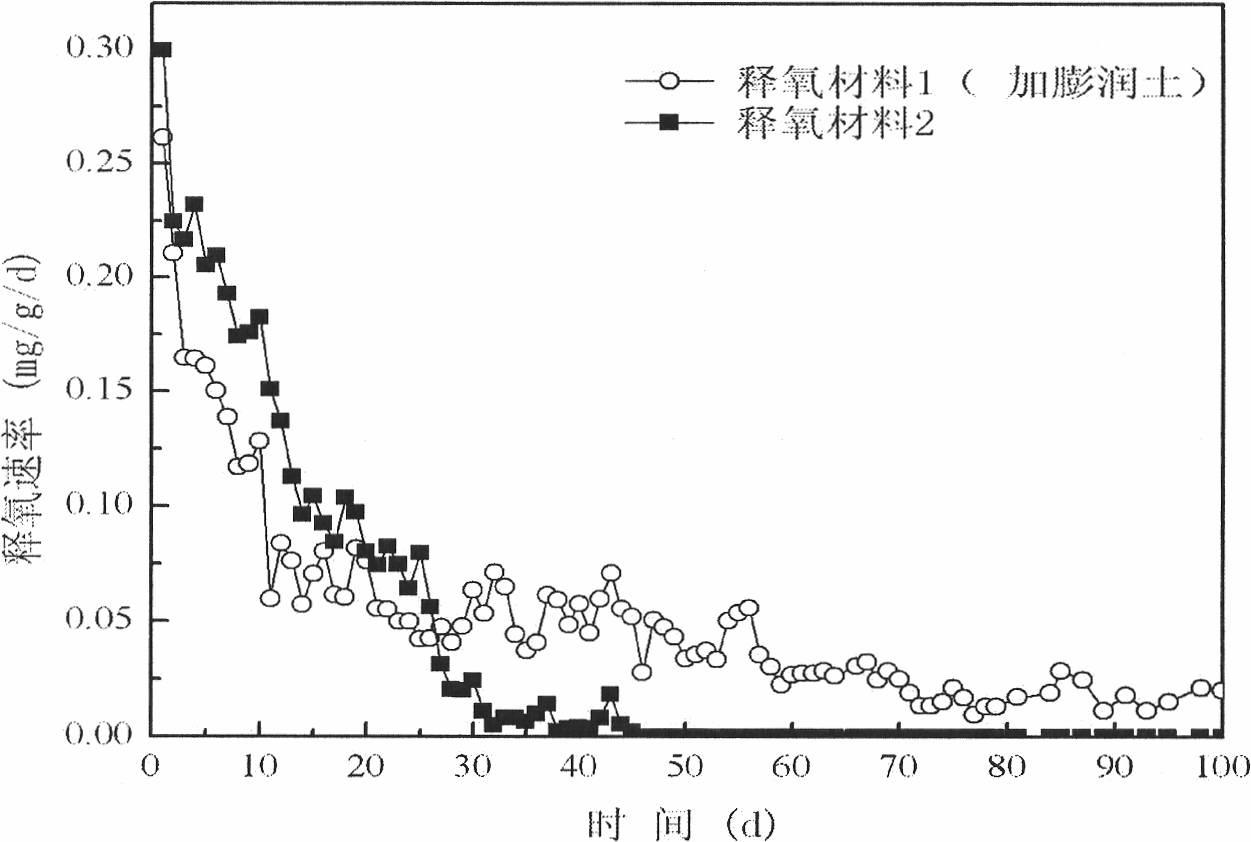
InactiveCN101805057AAchieve biodegradationInitial oxygen contentWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentSodium BentoniteWater flow
The invention relates to a biodegradation method of methyl tert-butyl ether in ground water. The invention is characterized in the following steps: utilizing the material which releases oxygen and which contains bentonite as the padding of a reaction grating or well for the aerobes to purify the ground water contaminated by the methyl tert-butyl ether. The ingredients and proportioning of the materials are: 5-20 weight percent of oxygen releasing compounds, 5-20 weight percent of bentonite, 10-30 weight percent of sand and / or coal ash, the balance being coagulant. A reaction grating or a reaction well for the aerobes are placed at the lower reaches of the pinnate body flowing on the underground water contaminated by the methyl tert-butyl ether. The reaction grating or the reaction well for the aerobes is vertical to the flow of the underground water.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Biodegradable packaging material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of packaging materials, in particular to a biodegradable packaging material and a preparation method thereof. The biodegradable packaging material is prepared from starch, cellulose, chitin, protein, polyvinyl alcohol, a polymerizing agent, a plasticizer and a biodegradable additive; the material is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 20-40 parts of starch, 15-25 parts of cellulose, 15-25 parts of chitin, 10-20 parts of protein, 2-6 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 1-3 parts of a polymerizing agent, 2-4 parts of a plasticizer and 3-5 parts of a biodegradable additive. The material is good in hydrophobic capacity, oil resistance, water resistance and high temperature resistance, and has the excellent properties of proper strength, grease resistance, flexibility, transparency, odorlessness, odorlessness, easiness in degradation, and has the good film forming characteristic; The biodegradable packaging material is high in decomposition rate, can realize biodegradation, improves environmental protection, and has better biodegradation characteristics.
Owner:YUYAO SUN RAIN SPRAYER
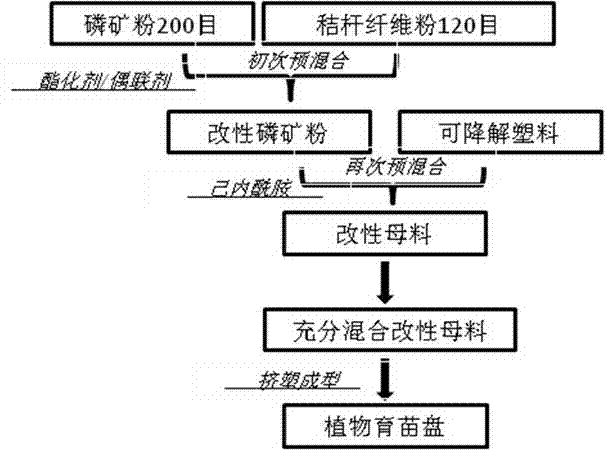
Mineral containing nursery seedling plate and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a mineral containing nursery seedling plate and a preparation method thereof. The mineral containing nursery seedling plate is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 80 to 120 parts of powdered rock phosphate, 40 to 200 parts of fiber powder, 20 to 90 parts of degradable powder, and 1 to 25 parts of additives. The experiment shows that the powdered rock phosphate and straw fiber powder are added to the degradable plastic, the powdered rock phosphate added can be slowly released by a long-lasting manner during the plant growing, so that the oxygen supply is improved and the fertilizer effect of the nursery seedling plate is improved; meanwhile, the plastic degrading is improved; the mineral containing nursery seedling plate has a transverse partition and is easily broken to be directly buried into the soil for degrading or recycling, thus the transplanting process is saved, the survive rate of seedlings can be increased, and meanwhile, the environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of porous zinc support material for composite ZnO nanorod
InactiveCN108553692AHighlight substantivePenetration thoroughlySurgeryMetallic material coating processesApparent densityNatural bone
The invention relates to a preparation method of porous zinc support material for composite ZnO nanorod, and relates to a prosthesis inorganic material or a prosthesis-coated inorganic material. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing a porous zinc support material with an apparent density in the range of 1.5+ / -0.1-3.5+ / -0.1g / cm3 and an open-rate range of 48.4 + / -1.5-78.2+ / -1.2%, which is similar to the natural bone of the human body, and preparing a ZnO nanorod in-situ on the surface of the pore wall of the porous zinc support material, in addition, obtaining the porous zinc support material of the composite ZnO nanorod. The preparation method of porous zinc support material for composite ZnO nanorod overcomes that different kinds of nitrates are needed in the process of preparing the ZnO nanorod on the surface of the substrate by the prior art, or a ZnO seed layer or a seed layer is firstly prepared on the surface of the substrate; oxygen is continuously introduce into the sodium chloride solution, and the obtained ZnO is a non-nano rod during preparation of ZnO on the surface of the zinc sheet; and the prepared degradable open-hole porous zinc and the zinc alloy biological material do not have the defects of antibacterial and sterilization performance.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Manufacturing method for environment-friendly paper-plastic compound bag
InactiveCN108995298AImprove toughnessIncrease temperatureLamination ancillary operationsBag making operationsPhosphorous acidLactase
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for an environment-friendly paper-plastic compound bag. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps that raw materials are matched, specifically, the raw materials comprise 10-20 parts of ethylene, 2-3 parts of emulsified silicone oil, 2-3 parts of lactase, 2-3 parts of lubricants, 1-2 parts of phosphorous ester, 1-2 parts of solubilizers,10-20 parts of biodegradable plastic and 2-3 parts of degradable substances, the polyethylene, the emulsified silicone oil, the lubricants, the phosphorous ester, the solubilizers and the degradable substances are mixed firstly, a mixed master batch A is obtained, and then the master batch A is put into an extruding machine to be subjected to extrusion molding and is machined to be manufactured into an easily degradable plastic film; the extruding machine comprises an adding section, a middle section and an extruding machine head which are connected in sequence, and the working temperature ofthe extruding machine is that the adding section is 110-130 DEG C, the middle section is 130-160 DEG C, and the extruding machine head is 210-280 DEG C. The environment-friendly paper-plastic compoundbag is excellent in mechanical property and easy to degrade, the raw materials are simple and easy to obtain, and the paper-plastic compound bag manufactured through the manufacturing method is durable and environmentally friendly and is suitable for being widely used.
Owner:桐城市万方纸塑包装有限公司
Degradable spinning raw material, degradable fiber membrane and degradable protective cover
PendingCN111286175ANo pollution in the processAvoid pollutionProtective equipmentSynthetic resin layered productsFiberPolymer science
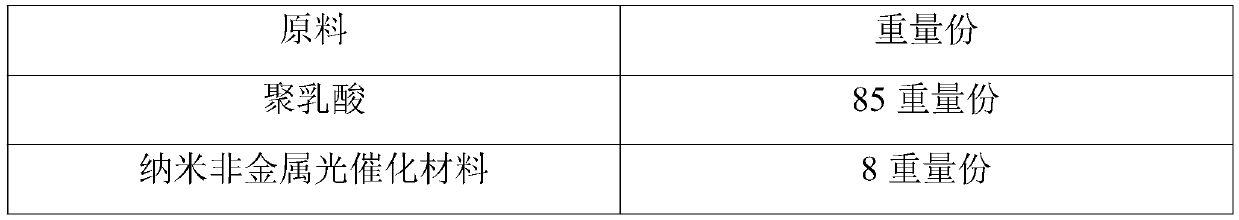
The invention belongs to the field of manufacturing of articles for daily use, and discloses a degradable spinning raw material, a degradable fiber membrane and a degradable protective cover. The degradable spinning raw material comprises the components in parts by weight: 55-85 parts of a medical-grade or food-grade polymer base material, 0.5-8 parts by weight of a nano non-metal photocatalytic material, 0.5-5 parts by weight of an auxiliary agent, and 2-44 parts by weight of a solvent, wherein the auxiliary agent comprises an antioxidant and a lubricant. The degradable spinning raw materialis environmentally friendly, has the performance of killing viruses and bacteria, and is suitable for being used as an antibacterial filtering material of protective covers such as masks and facial masks.
Owner:CHENGDU QINHUAN TECH CO LTD
High-shrinkage biaxially-oriented polylactic acid film and preparation method thereof
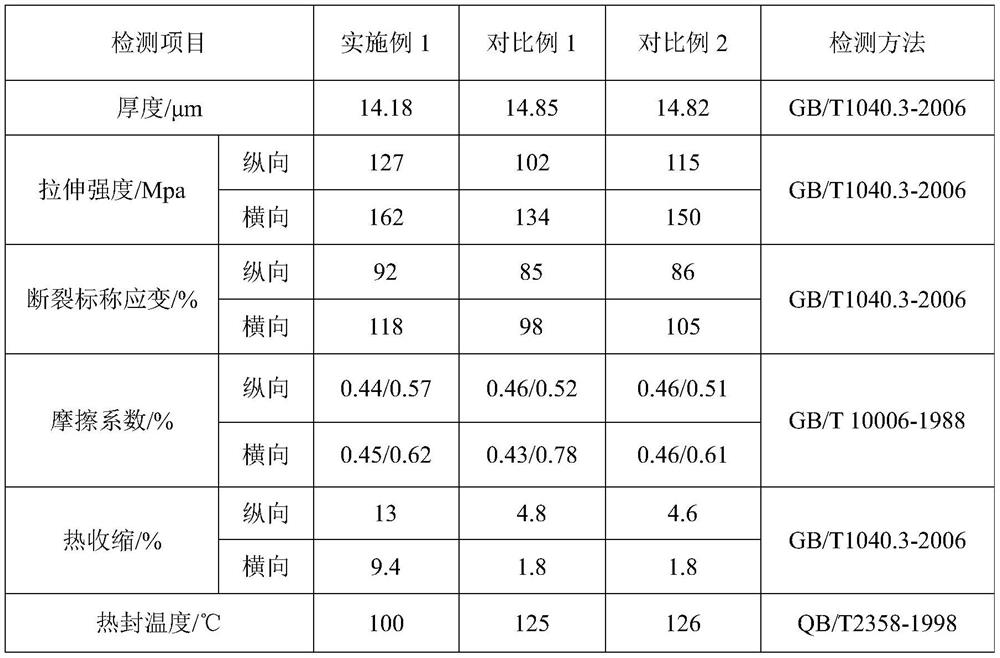
PendingCN113895126AImprove shrinkageHigh mechanical strengthFlexible coversWrappersPolymer scienceBoPET
The invention discloses a high-shrinkage biaxially-oriented polylactic acid film which sequentially comprises a surface layer I, a core layer and a surface layer II, wherein the surface layer I and the surface layer II are prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 97-99 parts of a heat sealing material and 1-3 parts of an anti-sticking master batch,and the heat sealing material is polylactic resin I; the core layer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 93-96 parts of polylactic resin II, 1-3 parts of antistatic master batch and 3-4 parts of smooth master batch. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the polylactic acid film. The biaxially-oriented polylactic acid film disclosed by the invention not only can meet conventional performance requirements of haze, glossiness, mechanical strength and the like of a packaging film, but also has a relatively high shrinkage rate, and can be used as a cigarette packaging material instead of a BOPP film.
Owner:GETTEL GRP TONGCHENG PLASTIC IND
Preparation method of polybutyrate adipate terephthalate (PBAT) composite material
InactiveCN107216621AImprove mechanical propertiesAchieve biodegradationDispersityMaterials preparation
The invention provides a preparation method of a polybutyrate adipate terephthalate (PBAT) composite material, and relates to the technical field of material preparation. The preparation method comprises the steps of firstly, dissolving dry PBAT into a solvent, and mixing the obtained solution with acetylated nanocrystalline cellulose to obtain a premixed material; removing the solvent in the premixed material, and then carrying melt blending and extruding by using a double-screw extruder so as to obtain the PBAT composite material. After the technology is adopted, the completely biodegradable composite material is prepared, the good dispersity of the acetylated nanocrystalline cellulose in the PBAT is guaranteed, the mechanical properties of the PBAT are improved, and the application space of the PBAT is enlarged.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
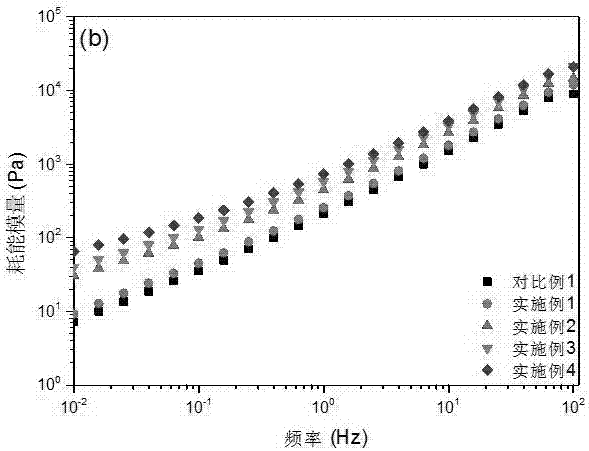
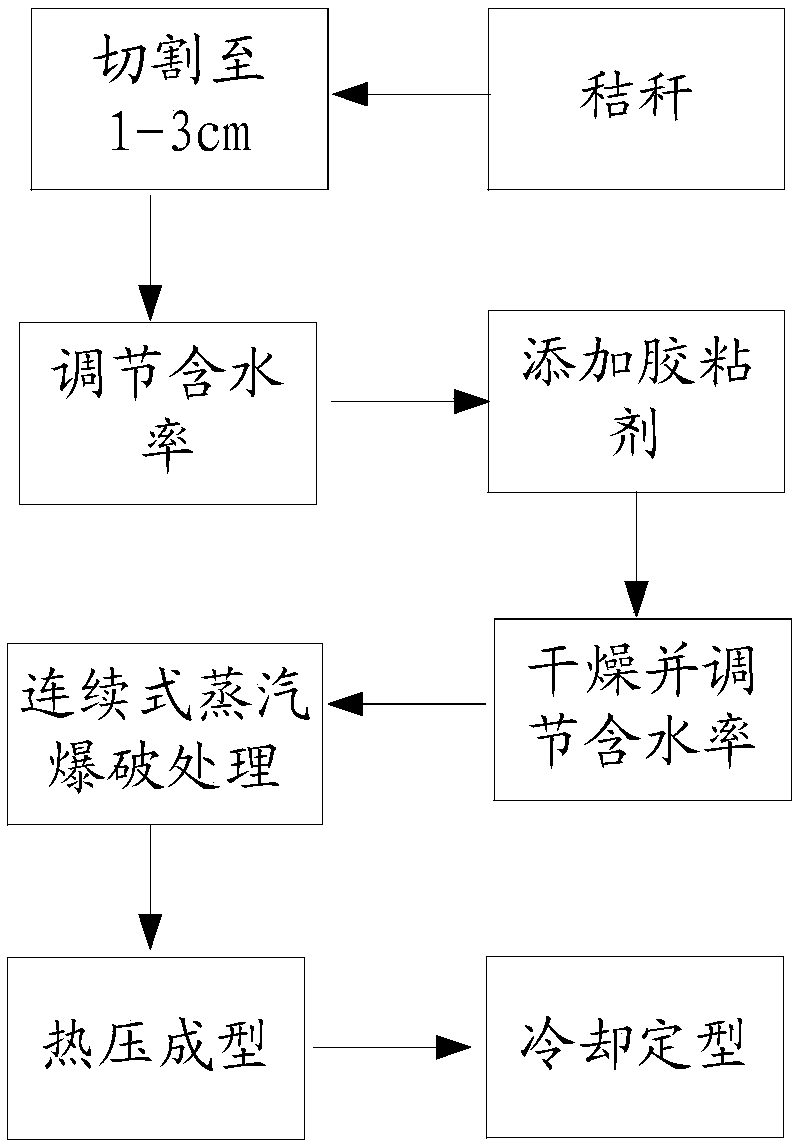
Straw biomass container and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108129865AImprove blasting effectEasy to separateFlexible coversWrappersFiberPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method for a straw biomass container. The preparation method comprises the following steps: weighing straws and water, carrying out stirring, and adjusting the content of water to 40 to 60%; placing an obtained mixture in a sealed bag for 8 to 14 h; carrying out steam explosion so as to obtain straw fiber, and carrying out drying until the content of water is5 to 15%; adding an adhesive, and carrying out uniform mixing, wherein the ratio of the straw fiber to the adhesive in terms of absolute dry weight is 10: (1-3), and the adhesive is polyvinyl alcohol;carrying out hot-press molding; and carrying out cooling molding. The preparation method for the biomass container provided by the invention is a complete treatment manner with integrity, has the characteristics of environmental friendliness, low energy consumption and simple and easy operation, and is applicable to popularization; and the straw biomass container prepared by using the preparationmethod provided by the invention has the advantages of good moldability, excellent mechanical properties, strong load capacity, environment protection, degradability, and capability of realizing secondary molding processing after curing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
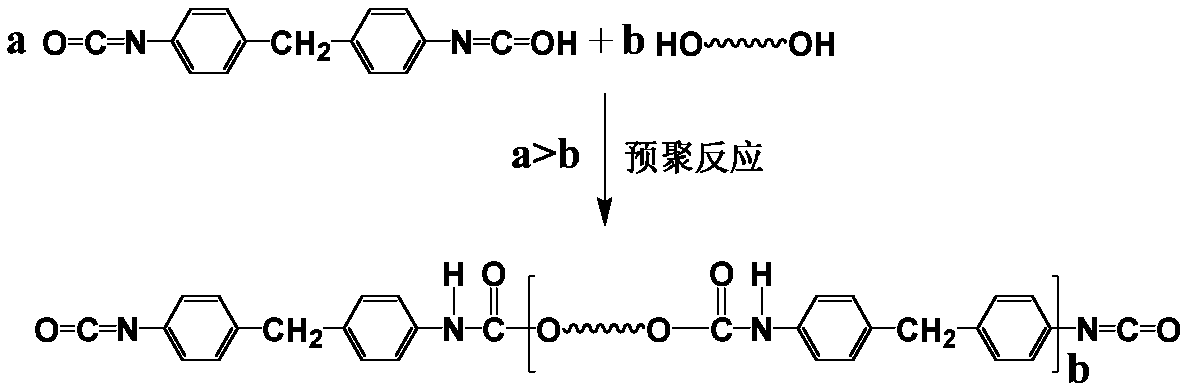
High-performance polyurethane for biological easily degradable spandex and preparation method of high-performance polyurethane
ActiveCN109338504AHigh strengthBiodegradableMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentArtifical filament manufacturePolyesterUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses high-performance polyurethane for biological easily degradable spandex and a preparation method of the high-performance polyurethane. The high-performance polyurethane is prepared by synthesizing biological easily degradable polyether polyol, polyether polyol, 4,4-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, a chain extender and a functional aid for spandex, wherein the biological easilydegradable polyether polyol accounts for 1-50% of the polyether polyol in the high-performance polyurethane for the biological easily degradable spandex; the biological easily degradable polyether polyol, the polyether polyol and the 4,4-diphenylmethane diisocyanate are subjected to a copolymerization reaction to generate a high-performance prepolymer, and high-performance spandex spinning stosteis prepared through a chain extension reaction. The polyurethane for the spandex prepared with the method has the characteristics of biological easy degradation, high strength, high modus and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAFENG SPANDEX
Method for desizing, boiling and bleaching cotton fabric by enzyme only
InactiveCN100424257CNo damageImprove wettabilityBiochemical fibre treatmentDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesChemical treatmentAlpha-amylase
The present invention relates to re-compounding and application in cotton fabric treatment of enzyme preparation, and is especially enzyme process for desizing, boiling off and bleaching cotton fabric. Different enzyme preparation is first re-compounded with alpha-amylase, PVA degrading enzyme, lipase, proteinase, alkaline pectase, xylanase, cellulase, sugar oxidase, etc based on different fabric pre-treating requirements; and then used in desizing, boiling off and bleaching cotton fabric to replace traditional concentrated alkali solution and high temperature chemical process. The present invention has low power consumption and environment friendship.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Catechin graft modified starch, degradable preservative film and preparation method thereof
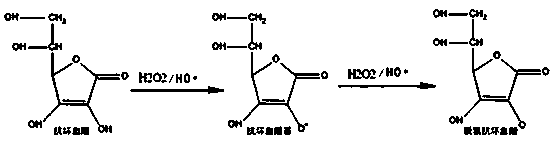
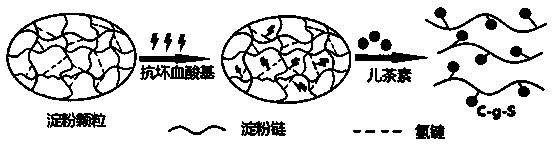
The invention relates to catechin graft modified starch, a degradable preservative film and a preparation method thereof. The catechin graft modified starch is characterized in that: an ascorbic acidand hydrogen peroxide redox initiation system is utilized to graft antioxidant molecule chlorogenic acid to the positions 2, 3 and 5 on a glucose unit ring in a starch molecule. The preparation methodincludes: (1) dissolving starch in an acetic acid solution in a closed container, then adding catechin and ascorbic acid, controlling the mass ratio of the catechin, ascorbic acid and starch at 5.225:1.08:6, adding an initiator H2O2 in a nitrogen atmosphere, and carrying out reaction at room temperature for 15-20h; and (2) adding the reaction mixture into a cut-off membrane with a molecular weight of 8000-14000Da, conducting dialysis in distilled water for 60-72h, and freeze-drying dialysate at a temperature ranging from -45DEG C to -50DEG C for 36-48h to obtain C-g-S; and making the C-g-S, PLA and PBST according to a mass ratio of 1-2:6-8:1-2 into the preservative film. The invention has the advantages that: a free radical induced grafting method is employed to prepare the catechin graftmodified starch, the initiator has good environmental affinity, is free of pollution and is low in price; the degradable preservative film has efficient and broad-spectrum antibacterial and antioxidant properties, is safe and harmless to human health, and can effectively prolong the shelf life of food.
Owner:蚌埠天成包装科技股份有限公司
Preparation method of collagen-based electrospinning fiber antibacterial agent carriers
InactiveCN108049028ASmooth releaseRelease fullyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsElectrospinningChemistry
Provided is a preparation method of collagen-based electrospinning fiber antibacterial agent carriers. The invention relates to a method for preparing degradable macromolecular carriers of which the release is controllable. According to the method, through the four steps of preparation of carrier particles, preparation of electrospinning liquid, preparation of spinning fiber membranes and post-treatment of the fiber membranes, yellow-white electric discharging fiber membranes with good biological activity, biodegradability, antibacterial properties and excellent medicine carrying properties are obtained. The fiber membranes have good biological activity and can be used through application outside bodies or implanting inside the bodies. Raw materials used are collagen, lignin, PVP and PVA with low molecular weight, and the biodegradation of the fiber membranes can be achieved even if the fiber membranes are in a long-term service in the alkaline environment of body fluid, which can notonly ensure the stable release of antibacterial agents, but also enable the antibacterial agents to be fully and thoroughly released; simultaneously lignin nanoparticles encapsulated in spinning fibers prepared can make the fiber membranes show some antibacterial properties during the degradation of the fiber membranes.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of release-controllable electrospun fiber drug carrier with nested nanostructure
ActiveCN108030775ASmooth releaseFull drug releaseFilament/thread formingKetone active ingredientsChemistryDrug carrier
The invention relates to a preparation method of a degradable and release-controllable polymer carrier, in particular to a preparation method of a release-controllable electrospun fiber drug carrier with a nested nanostructure. The method comprises the following four steps: preparing carrier particles, preparing electrostatic spinning fluid, preparing a spinning fiber membrane and carrying out aftertreatment on the fiber membrane; the obtained fiber membrane can be both applied to the exterior of a body and implanted into the body, and has good biological activity, biodegradability, antibacterial property and good drug loading property; furthermore, lignin nanoparticles wrapped in spinning fibers show a certain antibacterial property in a degradation process of the fiber membrane; in addition, the fiber membrane prepared by the method can be biodegraded in a long-term service period in the alkaline environment of body fluid, so that the stable release of a drug is ensured, and the drugis enabled to be fully and thoroughly released.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
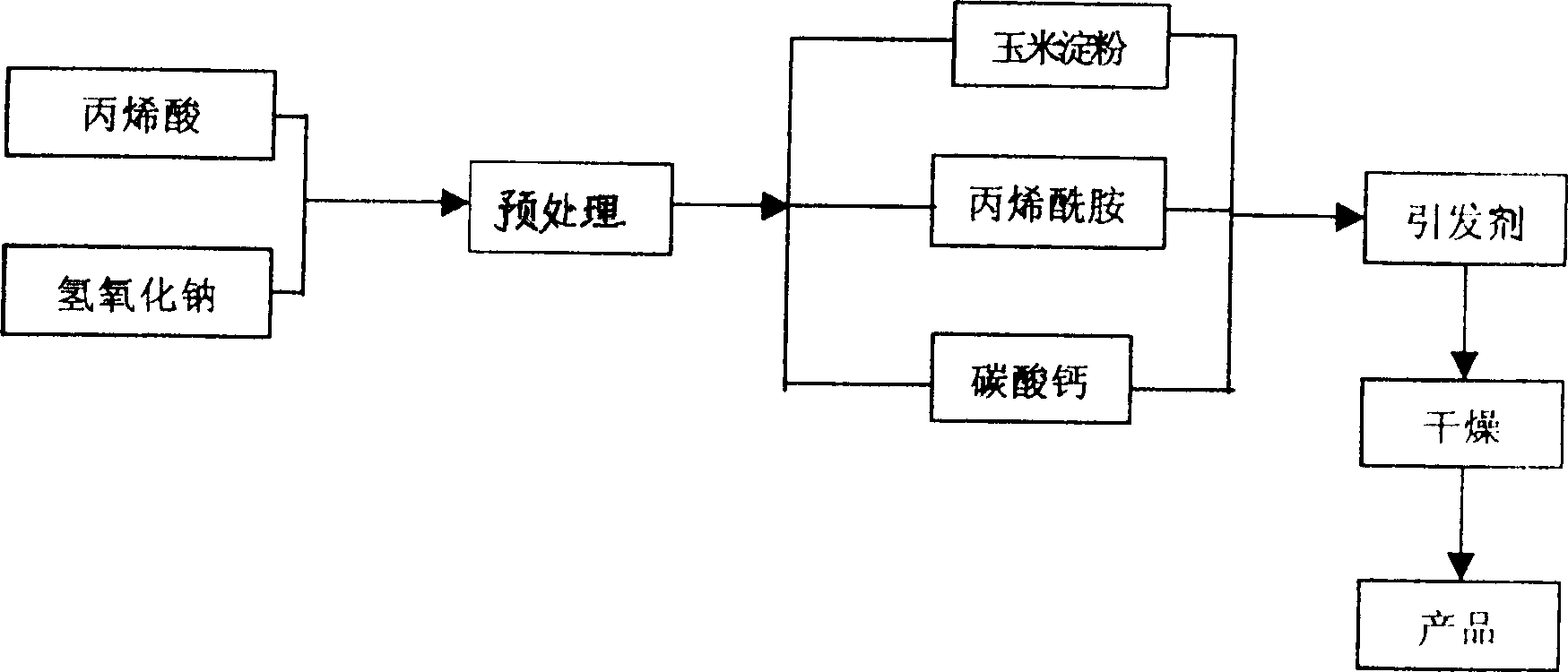
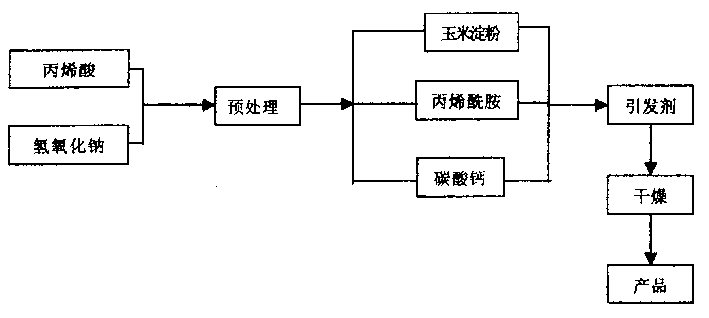
Water keeping gel and its method for producing
InactiveCN1121439CEfficient water absorptionEfficient sustained releaseAmmonium sulfateSodium hydroxide
The invention is a water-retaining gel and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the water-retaining gel is: first dissolve sodium hydroxide in water, and add acrylic acid for pretreatment; then add cornstarch, acrylamide and calcium carbonate in turn, stir and heat for reaction, and then add an initiator to carry out graft polymerization reaction ; Then pour the reacted liquid into the mold and dry at a constant temperature. The water-retaining gel includes the following components (percentage by weight): cornstarch 4.5--4.7, acrylic acid 21.4--22.5, acrylamide 9--9.5, ammonium persulfate 3.2--4.5, calcium carbonate 4.5--4.7, sodium hydroxide 9.5--9.9, water balance. The invention has the advantages of simple process, non-toxic product, biodegradability, wide application and the like.
Owner:珠海国佳凝胶研究院有限公司
Integrated biochemical treatment method for high-salt wastewater
PendingCN110372094AGuaranteed long lifeReduce energy consumptionWater treatment compoundsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesNutrientSystem stability
The invention relates to an environmental protection facility, and aims to provide an integrated biochemical treatment method for high-salt wastewater. The integrated biochemical treatment method hasthe characteristics of no need of long-term continuous dosing of salt-tolerant bacteria and good system stability. According to the technical scheme, the integrated biochemical treatment method for high-salt wastewater comprises the steps that an anaerobic tank and an facultative tank which are equipped with stirring devices and an aerobic tank with an aerating device are adopted, the anaerobic tank, the facultative tank and the aerobic tank communicate with in turn, tank water is equipped with the salt-tolerant bacteria, key activation elements and nutrients are added; the salt-tolerant bacteria are externally put in stages, or / and biochemical sludge (preferably sludge flowing back in a sedimentation tank) is used for upgrading step culture through domestication; the domestication upgrading step is 2,000mg / L-5,000mg / L; the staged external putting is that the salt-tolerant bacteria is put once at the time of increasing of the salinity, or the salt-tolerant bacteria is put once in a multiple step increasing mode; and the increasing degree of salinity single step should not exceed 0.5%, and finally a salt-tolerant biochemical system with the tolerance of salinity less than 6% is obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZONE KING ENVIRONMENTAL SCI&TECH CO LTD
Ion exchange-type gel membrane for decolorizing printing and dyeing wastewater and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109926026AImprove mechanical propertiesEfficient captureOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesHigh fluxIon exchange
The invention discloses an ion exchange type gel film for decolorizing printing and dyeing wastewater and a preparation method thereof. The prepared gel film has the characteristics of high flux, lowresistance and biodegradability. Continuous and uniform pores are formed from the surface to the interior of the gel film; due to the capillary action of the pores, high-speed sewage treatment can berealized, and subsequent pore-forming reprocessing is not needed, so that the gel membrane is easy to be used in pilot plant test and large-scale production, and can be directly used for filtering, adsorbing and decoloring printing and dyeing wastewater. The dye adsorption capacity can reach 80 mg / g to 600 mg / g, the decolorization rate is larger than 95%, and the total COD removal rate is larger than 85%.
Owner:LIMING VOCATIONAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com