Anticoagulant and application thereof
An anticoagulant and catheter technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as catheter blockage and no anticoagulant catheter, and achieve the effects of preventing blood adhesion, low cost in the preparation process, and reducing friction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1, preparation and concentration comparison of anticoagulant
[0031] 1. Dissolve sodium chloride in distilled water to make physiological saline solution for later use.
[0032] 2. Weigh heparin sodium and dissolve it in normal saline to make base solution.
[0033] 3. Use a graduated cylinder to measure glycerol, dissolve it in the base solution, and mix thoroughly.
[0034] 4. Weigh PVP, trisodium citrate, EDTA, and magnetic stirrer to fully mix and dissolve to make an anticoagulant.
[0035] Six different concentrations of anticoagulants were prepared by the above method:
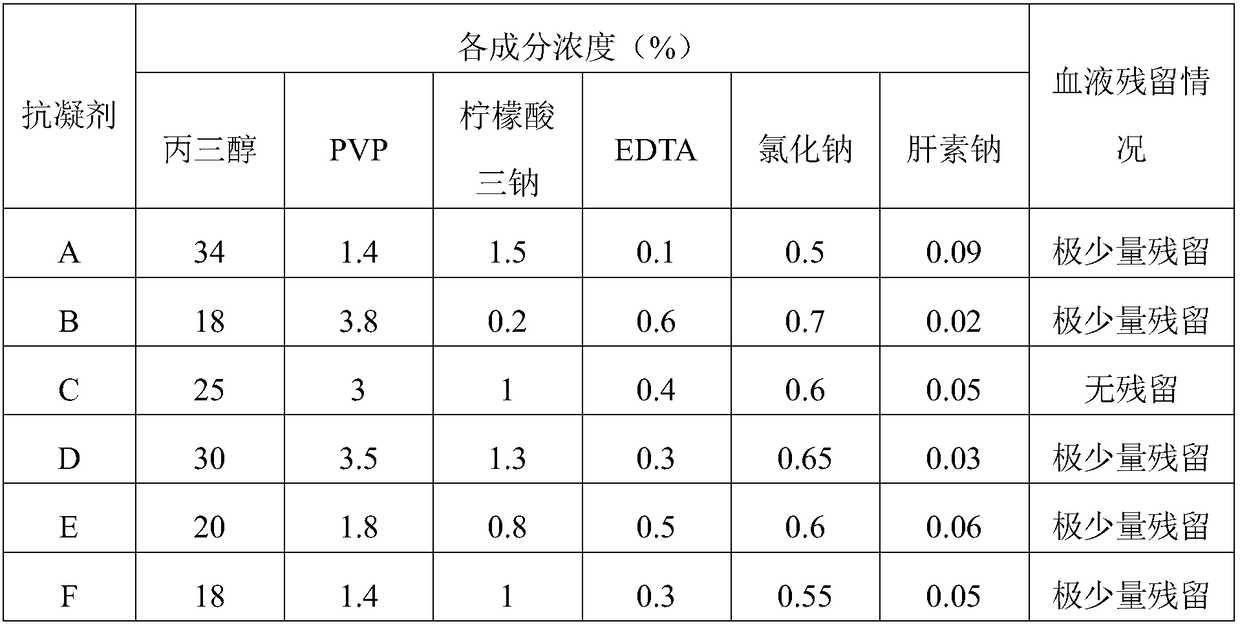
[0036] Anticoagulant A, the prepared anticoagulant comprising mass percent are 34% glycerol, 1.4% PVP, 1.5% trisodium citrate, 0.1% EDTA, 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.09% heparin sodium, and the balance is water.
[0037] Anticoagulant B, the prepared anticoagulant comprising mass percent are 18% glycerol, 3.8% PVP, 0.2% trisodium citrate, 0.6% EDTA, 0.7% sodium chloride, 0.02% of hepa...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment two, compare with single-component anticoagulant
[0055] In order to verify the effect, three common single-component blood anticoagulants, namely sodium heparin, EDTA, and trisodium citrate, were prepared in addition, and compared with the anticoagulant C in Example 1 for the catheter anticoagulant effect test.
[0056] 1. Take a 24-well plate, divide the 24 wells into 4 groups, each group has 6 wells, inject the above 4 groups of anticoagulants into the 4 groups of wells, and mark them well. Place a small section of silicone tubing in each well and soak for 10 minutes.
[0057] 2. Take out the soaked silicone tube, blot the surface liquid, put it into another clean 24-well plate, and mark it.
[0058] 3. Take 1 rat, remove the eyeballs and take blood, drop 3 drops of blood into each hole, and make the blood fully mix with the silicone tube.
[0059] 4. After soaking in the blood for 10 minutes, place the silicone tube on the surgical drape to fully ensur...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3, the experiment of inserting the silicone tube soaked in anticoagulant
[0064] Experimental animals: 27 healthy wild-type SPF grade, 8-week-old C57 mice.
[0065] Mouse carotid artery cannulation steps:
[0066] 1) Sterilize surgical instruments with high temperature and high pressure steam.
[0067] 2) Arterial catheter preparation: PE-10 catheter (about 1.2cm in length) was inserted into a 0.02-inch inner diameter silicone tube (about 5cm in length), and alcohol-sterilized for later use.
[0068] 3) Pentobarbital sodium was injected intraperitoneally, and the mouse was fixed in the supine position after anesthetization.
[0069] 4) Shave the surgical site on the neck and disinfect the surgical site with alcohol.
[0070] 5) Make a longitudinal incision about 1 cm long on the midline of the mouse neck, bluntly separate the left carotid artery with forceps, and separate it from the vagus nerve with a glass minute needle, ligate the distal end of the car...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com