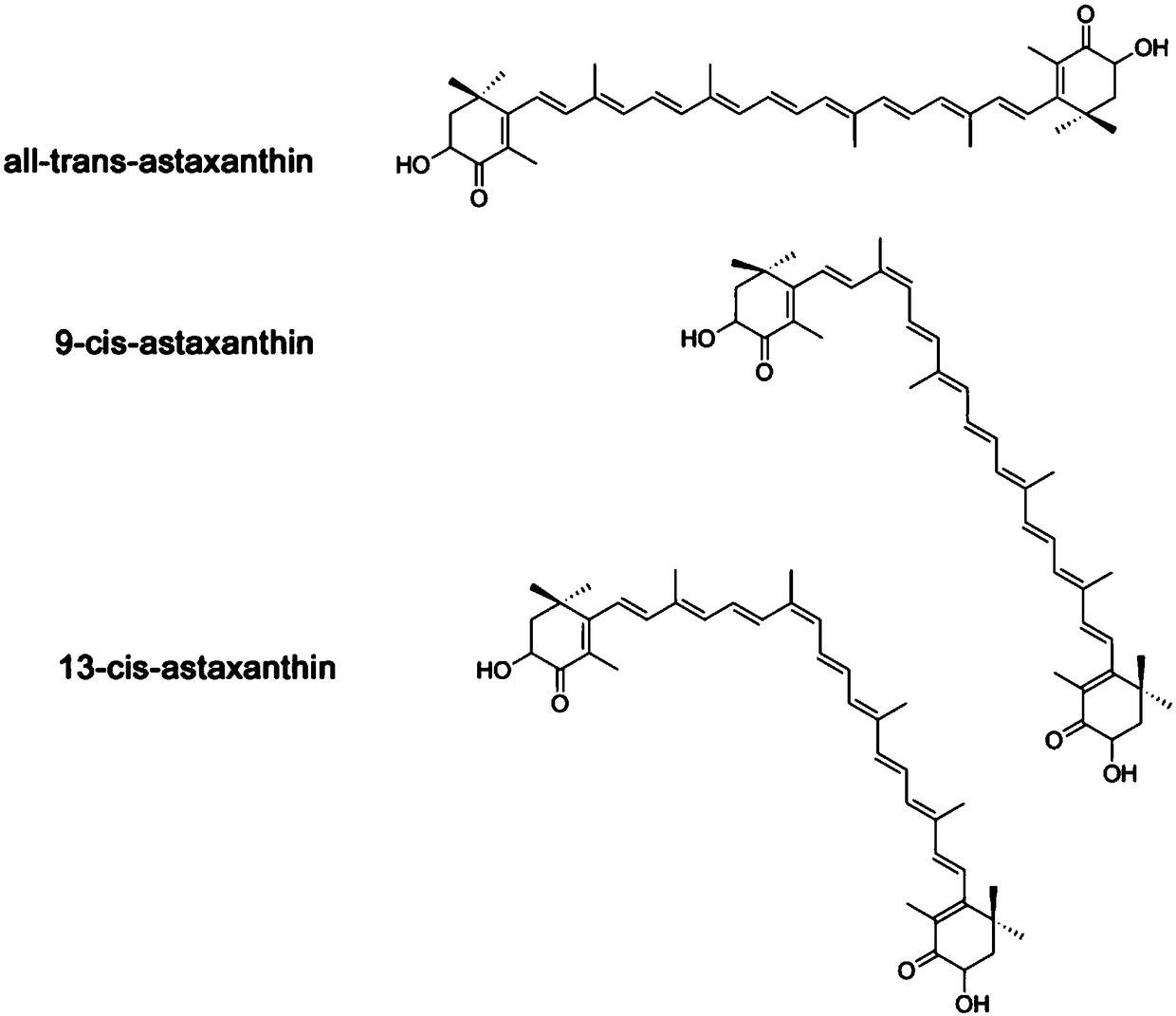
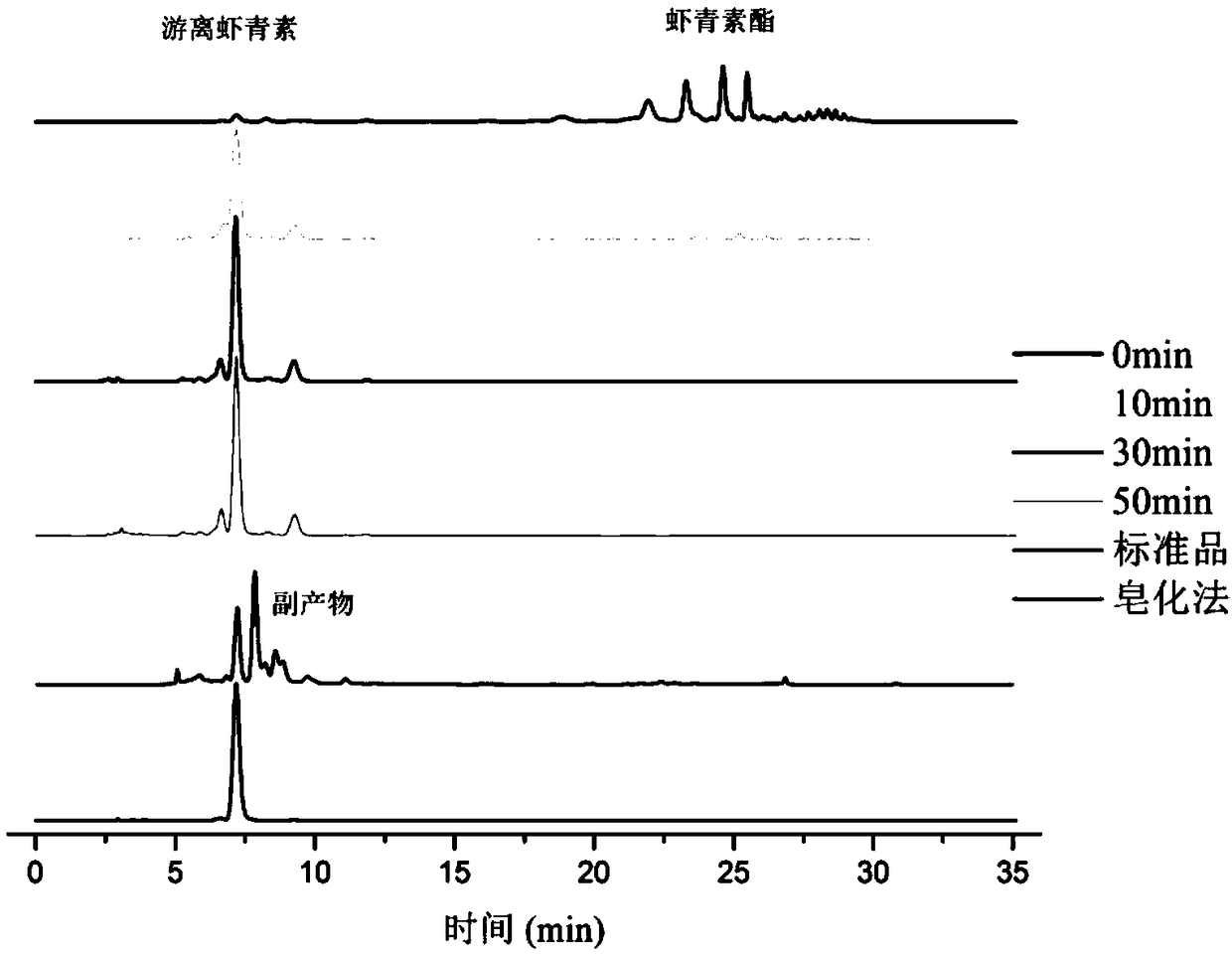
Method for efficiently and rapidly preparing free astaxanthin
A kind of astaxanthin, fast technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of long reaction time, difficult to control the product, low hydrolysis efficiency of free astaxanthin, etc., and achieve the effect of improving low efficiency and increasing conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Screening of astaxanthin ester hydrolyzed strains:
[0033] The medium formula used in this embodiment is as follows:
[0034] Screening plate solid media:
[0035] Haematococcus Pluvialls Oil, 0.05%; Triton X-100, 1.0%; KNO 3 , 0.1%; K 2 HPO 4 , 0.05%; MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.05%; NaCl, 0.05%; FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 0.001%; peptone, 1.0%; agar powder, 2.0%; H 2 O, 100 mL; pH 7.0.
[0036] Seed medium:
[0037] Peptone, 1.0%; Yeast powder, 0.5%; NaCl, 1.0%; Water, 100mL; pH 7.0; Sterilize at 121°C for 20min.
[0038] Fermentation medium:
[0039] Peptone, 1.0%; Yeast powder, 0.5%; NaCl, 1.0%; Water, 1L; pH 7.0; Sterilize at 121°C for 20min.
[0040] Enrichment culture:
[0041] Inject the preserved glycerol tube bacteria solution into the seed medium, mix well, and culture at 180 rpm on a shaker at 37° C. for 24 hours.
[0042] Plate screening bacteria:
[0043] Take the activated bacterial solution and dilute it appropriately by 100 times, and spread it on a solid ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Process optimization of hydrolyzed astaxanthin ester:
[0065] 1) Effect of reaction pH value on hydrolyzed astaxanthin ester
[0066] Weigh 2 mg of Haematococcus pluvialis oil, dissolve it with 0.5 mL of absolute ethanol, then weigh an appropriate amount of extracellular crude enzyme preparation, and dissolve the enzyme powder in buffer solutions with different pH values. The buffer solutions used are as follows: citric acid buffer solution (100mM, pH 5.0-6.0), sodium phosphate buffer solution (100mM, pH 6.0-8.0), Tris-HCl buffer solution (100mM, pH 7.0-9.0) and glycine-sodium hydroxide buffer solution (100mM, pH9.0- 10.0), added to the reaction bottle, filled with nitrogen, protected from light, placed in a 37°C water-bath shaker for 30 minutes, that is, absolute ethanol: buffer solution = 1:10 (v / v), a total of 5.5mL reaction system.
[0067] Such as Image 6 As shown, by adding different buffer solutions in the reaction system, the effect of different pH values ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com