Bamboo joint/coated non-noble metal SO2 electrochemical oxidation catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology for oxidation catalysts and non-precious metals, applied in the direction of physical/chemical process catalysts, molecular sieve catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of high cost of electro-oxidation catalysts, and achieve mass production, mass transfer, and high ratio The effect of surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Take 1g ferric ammonium citrate, add it to 20mL deionized water, the molar concentration is 0.1mol L -1 , fully stirred to disperse; take 2.4g melamine and add it to 100mL 100℃ deionized water, the molar concentration is 0.19mol L -1 , fully dissolve and stir; add ferric ammonium citrate solution into melamine solution, stir well to combine, add 0.5g NKF-11 molecular sieve, adjust temperature to 80°C, stir at constant temperature and evaporate to dryness. Put the precursor mixture into the tube furnace, Ar atmosphere, at 2 °C min -1 Rise to 600°C, keep at constant temperature for 2h; take out after cooling. At 40°C, the carbide in 1mol L -1 Stand in NaOH for 24h; wash with deionized water, then in 5% NH 4 F and CH 3 COOH mixed solution (NH 4 F and CH 3 The mass ratio of COOH is 1:1) to stand for 24h; wash and dry. Then at 10℃min -1 Rise to 700°C for secondary carbonization, and keep at constant temperature for 2 hours. Cool naturally, and grind to obtain the ca...
Embodiment 2
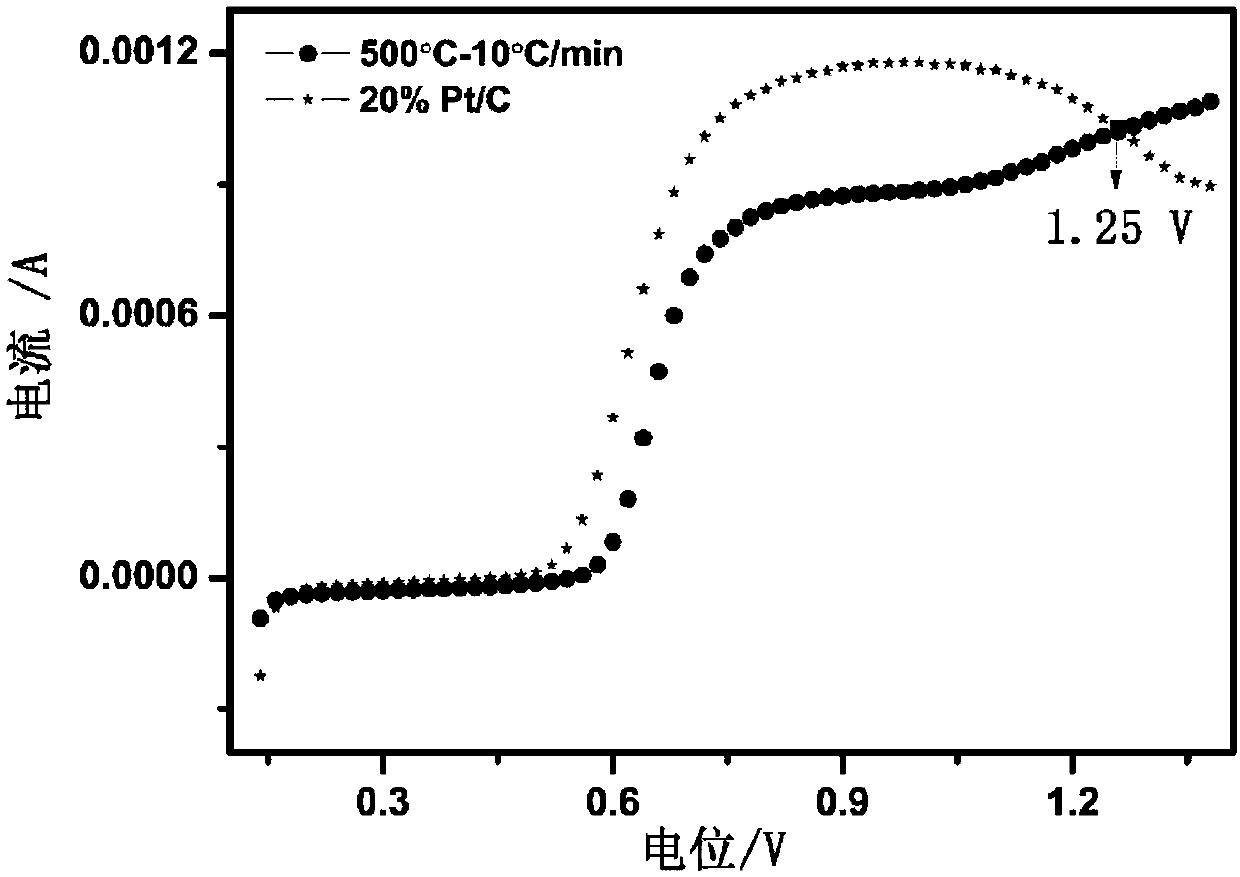
[0049] Take 1g ferric ammonium citrate, add it to 20mL deionized water, the molar concentration is 0.1mol L -1 , fully stirred to disperse; take 2.4g melamine and add it to 100mL 100℃ deionized water, the molar concentration is 0.19mol L -1 , fully dissolve and stir; add ferric ammonium citrate solution into melamine solution, stir well to combine, add 0.5g NKF-11 molecular sieve, adjust temperature to 80°C, stir at constant temperature and evaporate to dryness. Put the precursor mixture into the tube furnace, Ar atmosphere, at 10 °C min -1 Rise to 500°C, keep at constant temperature for 2h; take out after cooling. At 40°C, the carbide in 1mol L -1 Stand in NaOH for 24h; wash with deionized water, then in 5% NH 4 F and CH 3 Stand in the COOH mixed solution for 24h; wash and dry. Then at 10℃min -1 Rise to 700°C for secondary carbonization, and keep at constant temperature for 2 hours. Natural cooling, grinding to obtain the catalyst, its SO 2 Electrooxidation properties...
Embodiment 3
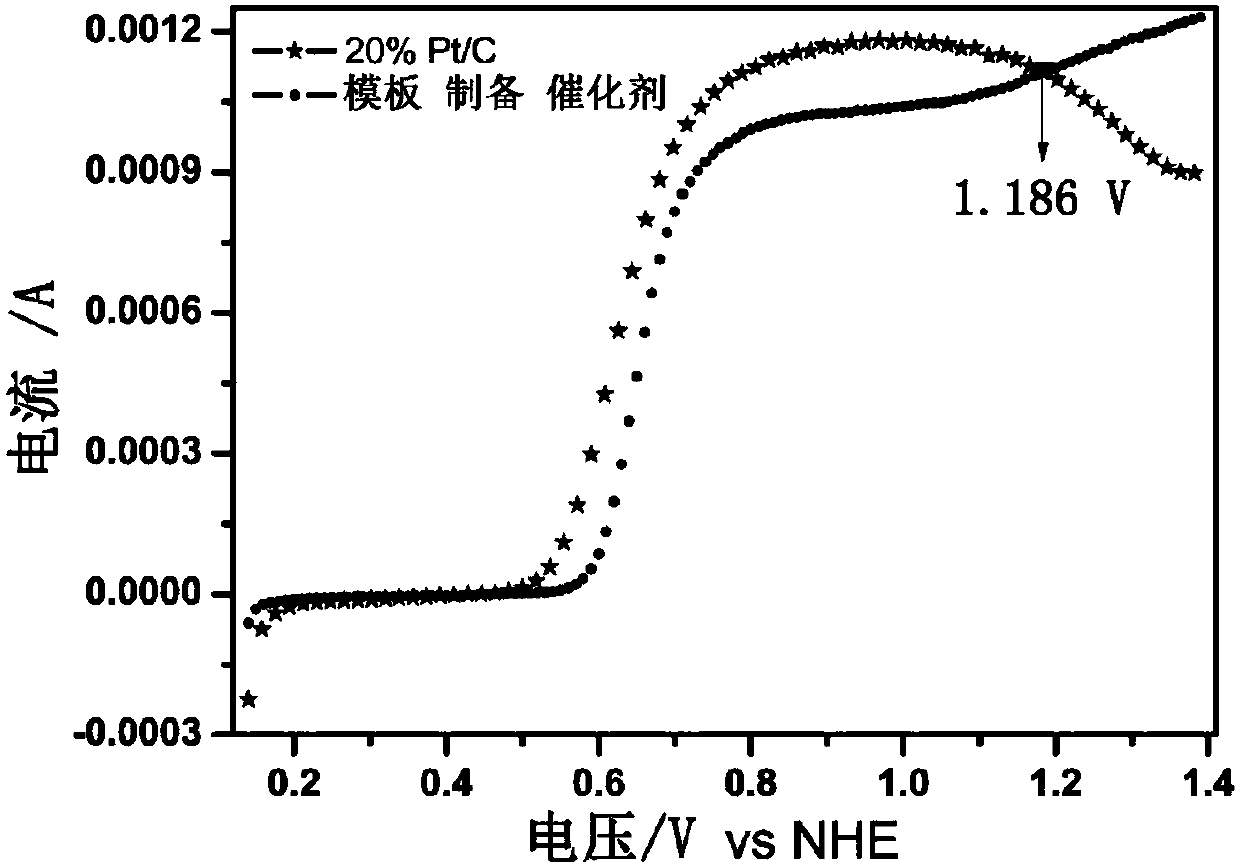
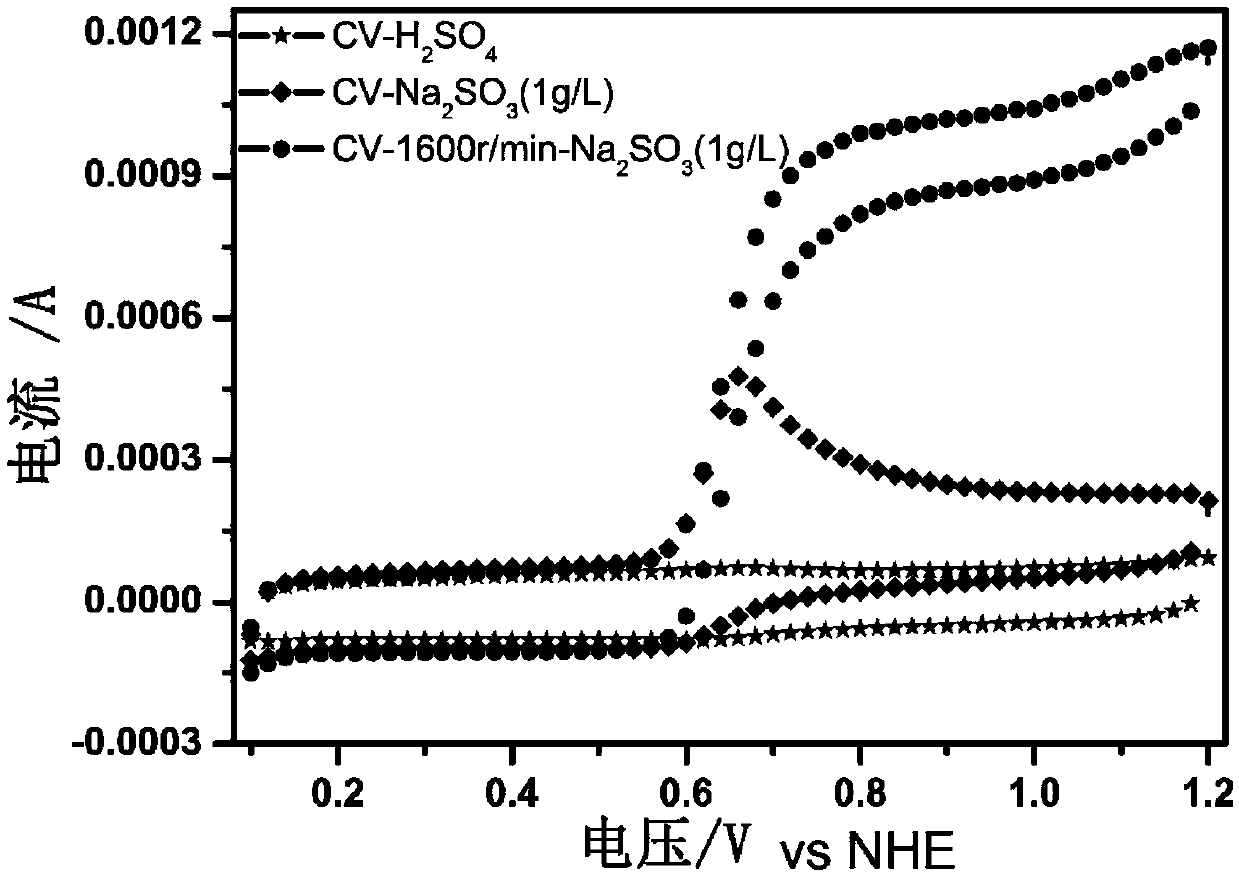
[0051] in 1g L -1 Na 2 SO 3 (H 2 SO 4 ), test the SO of the catalyst prepared by Example 1 2 Oxidation performance and compared with Pt / C catalyst. Linear voltage sweep condition: 5mV s -1 ,1600r min -1 . The catalyst has better SO in the low oxidation range 2 Oxidation performance, but there is a certain gap with Pt / C; after the oxidation potential is higher than 1.186V, it has better SO2 than Pt / C 2 Oxidation properties. Catalyst of the present invention is more suitable for the oxidation potential of 0.9-1.4V scope, test result is as follows figure 1 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com