Preparation method of controlled degradable magnesium alloy fixing screw in vivo
A technology for fixing screws and magnesium alloys, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as restricting the application of magnesium alloys, low electrode potential, and accelerating corrosion of magnesium alloys.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
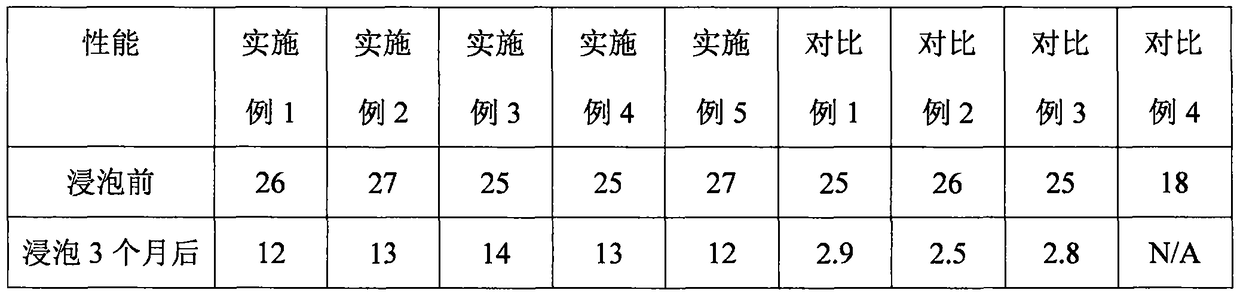
[0022] Choose a WE43A magnesium alloy screw body with a length of 5mm and a diameter of 0.5mm. Use sandpaper to polish and ultrasonically clean the surface to remove oxides and impurities, then soak in 50g / L NaOH solution for 10 minutes, take it out, and wash and dry. Then, an alternating current oxidation treatment is performed in an oxidation treatment solution to form an oxide film layer with a thickness of about 50 μm. The composition of the oxidation treatment liquid was 20 g / L oxalic acid, 2.2 g / L calcium nitrate, 1.8 g / L potassium fluoride, 2.5 g / L magnesium silicate, and the balance of water. The temperature of the oxidation treatment solution is 10℃, and the current density is 0.10A / dm 2 , The oxidation treatment time is 2 hours. Then it was immersed in a 1.0 mg / L poly-L-lactide (PLLA) solution for 20 minutes, taken out and dried to obtain a poly-L-lactide coating with a thickness of about 10 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Choose a WE43A magnesium alloy screw body with a length of 5mm and a diameter of 0.5mm. Use sandpaper to polish and ultrasonically clean the surface to remove oxides and impurities, then soak in 50g / L NaOH solution for 10 minutes, take it out, and wash and dry. Then, an alternating current oxidation treatment is performed in an oxidation treatment solution to form an oxide film layer with a thickness of about 50 μm. The composition of the oxidation treatment liquid was: 32 g / L of citric acid, 1.8 g / L of calcium nitrate, 1.2 g / L of potassium fluoride, 3.0 g / L of magnesium silicate, and the balance of water. The temperature of the oxidation treatment solution is 10℃, and the current density is 0.10A / dm 2 , The oxidation treatment time is 2 hours. Then it was immersed in a 1.0 mg / L poly-L-lactide (PLLA) solution for 20 minutes, taken out and dried to obtain a poly-L-lactide coating with a thickness of about 10 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Choose a WE43A magnesium alloy screw body with a length of 5mm and a diameter of 0.5mm. Use sandpaper to polish and ultrasonically clean the surface to remove oxides and impurities, then soak in 50g / L NaOH solution for 10 minutes, take it out, and wash and dry. Then, an alternating current oxidation treatment is performed in an oxidation treatment solution to form an oxide film layer with a thickness of about 50 μm. The composition of the oxidation treatment liquid was 20 g / L oxalic acid, 2.2 g / L calcium nitrate, 1.8 g / L potassium fluoride, 2.5 g / L magnesium silicate, and the balance of water. The temperature of the oxidation treatment solution is 10℃, and the current density is 0.10A / dm 2 , The oxidation treatment time is 2 hours. Then, it is immersed in a 1.0 mg / L polylactic acid (PLA) solution for 20 minutes, taken out and dried to obtain a polylactic acid coating with a thickness of about 10 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com