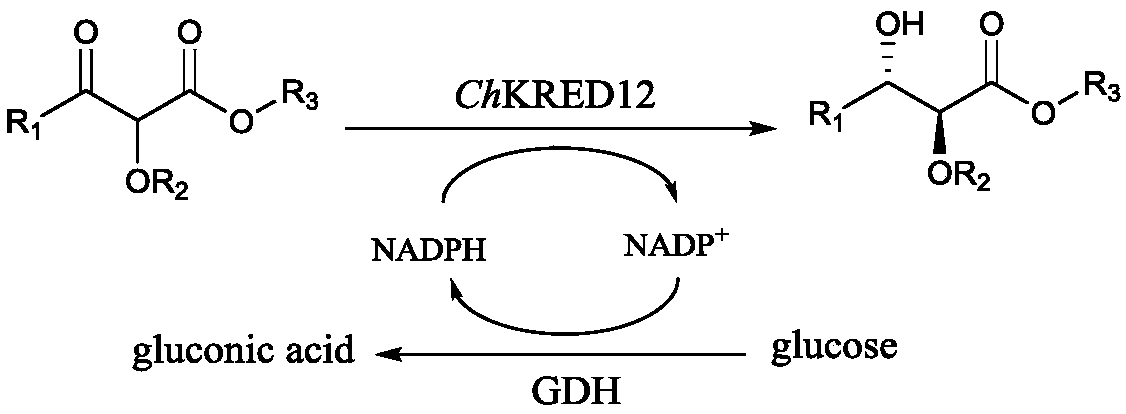
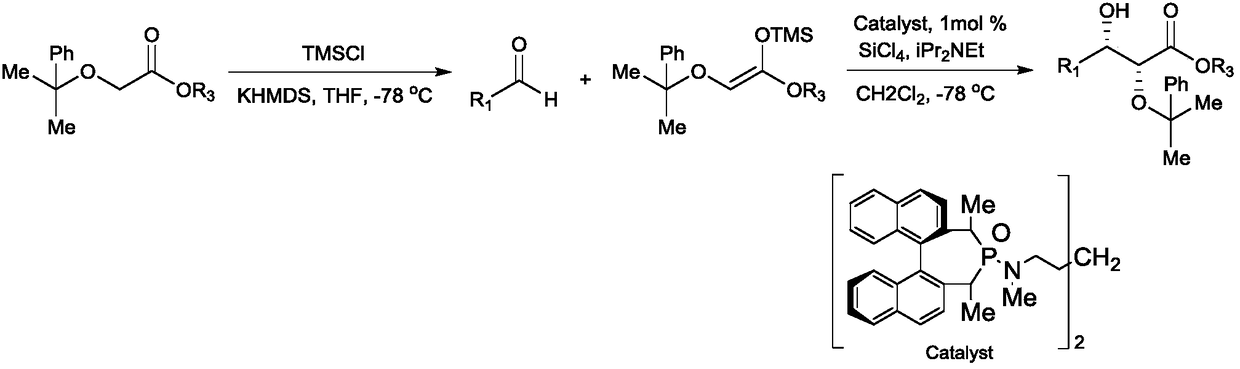
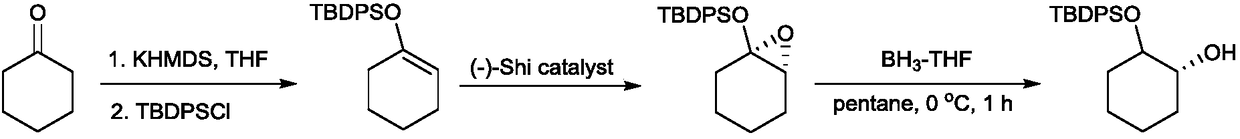
Production of chiral 1,2-diol compounds by biocatalysis of carbonyl reductase
A technology of biocatalysis and reductase, which is applied in the direction of chemical recovery and fermentation, can solve the problems of being unable to meet the needs of industrialization, low substrate input and catalytic efficiency, and affecting the stereoselectivity of catalytic products, etc., to achieve a simple reaction system, The effect of mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1: Screening of carbonyl reductase
[0041] In a method well known in the art, connect the carbonyl reductase gene into the pET28a(+) vector, transfer it into Escherichia coli BL21-DE3 for heterologous expression, centrifuge at 6,000rpm, 4°C for 10min to obtain wet cells of recombinant bacteria, resuspend in phosphoric acid Potassium buffer solution (0.1M, pH 7.0), break the cells with a homogenizer, centrifuge at 13,00 rpm, 4°C for 20 minutes, and the obtained supernatant is the crude enzyme solution, which is used as a biocatalyst. We screened our lab's toolbox of carbonyl reductases. When screening, the biocatalysis and system are: potassium phosphate buffer (0.1M, pH 7.0), carbonyl reductase crude enzyme solution 10g / l, substrate (1a) 1g / l, NAD + / NADP + Concentration 0.6 g / l, glucose dehydrogenase 3 g / l and glucose 10% (w / v). The reaction time is 12 hours, the reaction temperature is 30° C., and the rotation speed is 200 rpm.
[0042] At the same time, ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2: HPLC detection conditions of product standards of different α-alkoxy-β-keto esters
[0045] The chiral HPLC detection conditions of the anti-configuration racemate of the product are shown in Table 1. ChKRED12 catalyzed the substrate 1a to obtain the (2S,3S)-configuration product. The configurations of the corresponding products in the following examples are all the same and will not be repeated here.
[0046] Table 1 Substrates and assay conditions
[0047]
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3: Carbonyl reductase ChKRED12 crude enzyme solution catalyzes 4g / l substrate 1a
[0049] Take freshly cultured carbonyl reductase ChKRED12 recombinant bacteria and resuspend them in potassium phosphate buffer (0.1M, pH8.0), break the cells with a homogenizer, centrifuge at 13,000rpm, 4°C for 20min, and the supernatant obtained is the crude enzyme liquid.
[0050] Potassium phosphate buffer (0.1M, pH 8.0), carbonyl reductase ChKRED12 concentration 5g / l (crude enzyme solution), substrate 1a concentration 4g / l, substrate 1g / l, NADP + Concentration 0.6 g / l, glucose dehydrogenase 2 g / l and glucose 10% (w / v). The reaction temperature is 40°C, and the reaction time is 12h. An equal volume of methyl tert-butyl ether was extracted to terminate the reaction, and the sample processing method and detection method were the same as in Example 1. The results show that 4g / l substrate can be completely converted within 12h to obtain (2S,3S)-configuration alcohol, the ee valu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com