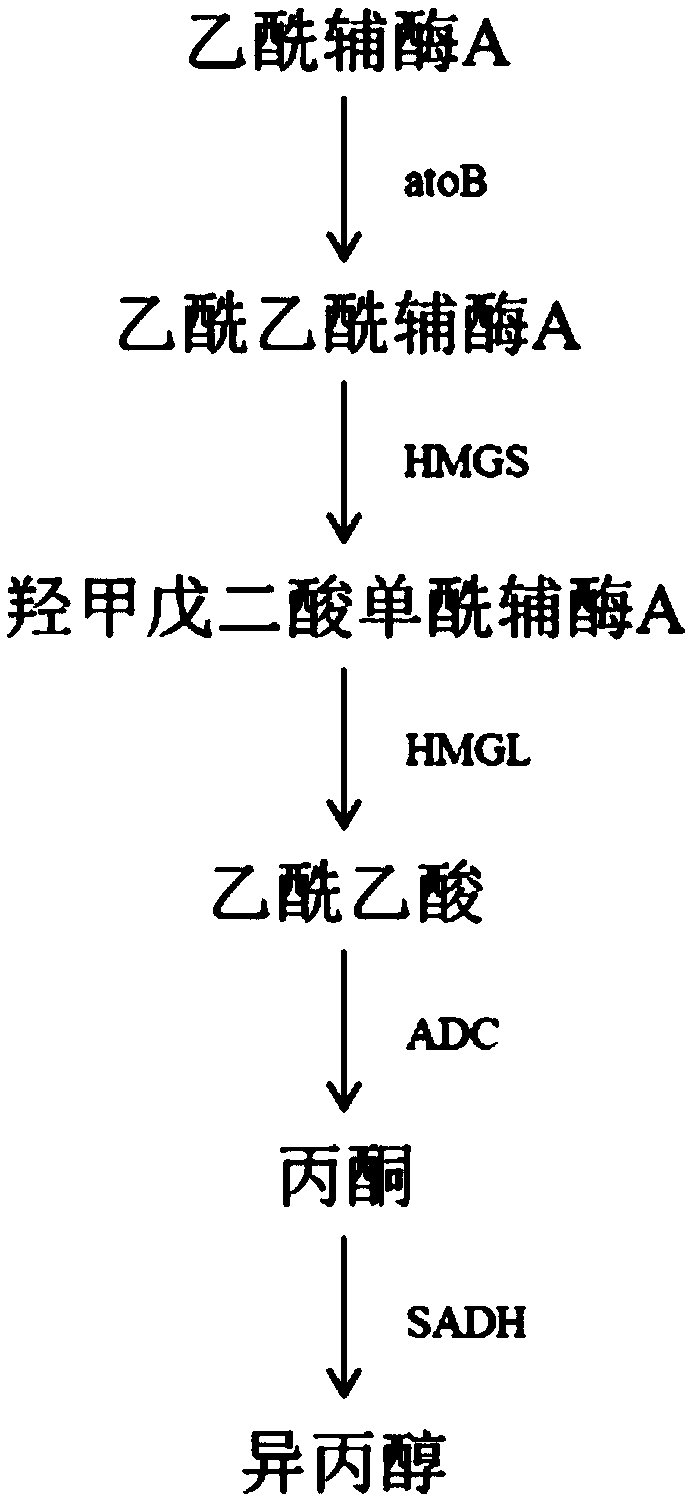
Acetic acid CoA transferase gene-deficient engineered Escherichia coli strain and application thereof
A technology of Escherichia coli and transferase, applied in the direction of transferase, enzyme, bacteria, etc., can solve the problem of synthesis of unfavorable metabolite isopropanol
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] 1. Extraction of Escherichia coli MG1655 genomic DNA
[0034] The whole genome DNA of MG1655 was extracted from 1ml of wild-type Escherichia coli MG1655 (purchased from the American Type Culture Collection) culture using a commercial bacterial genomic DNA rapid extraction kit (Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.), dissolved In 0.1mL ultrapure water.
[0035] 2. Extraction of Enterococcus faecalis genomic DNA
[0036] The whole genome DNA was extracted from the culture of Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 (purchased from the American Type Culture Collection) using a commercial bacterial genomic DNA rapid extraction kit (Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.). Dissolve in 0.1mL ultrapure water.
[0037] 3. Preparation of acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase gene atoB
[0038] The atoB gene can be prepared by the following method, or can be obtained by artificial synthesis.
[0039]Using Escherichia coli MG1655 genomic DNA as a template, PCR amplification was carried ...
Embodiment 2
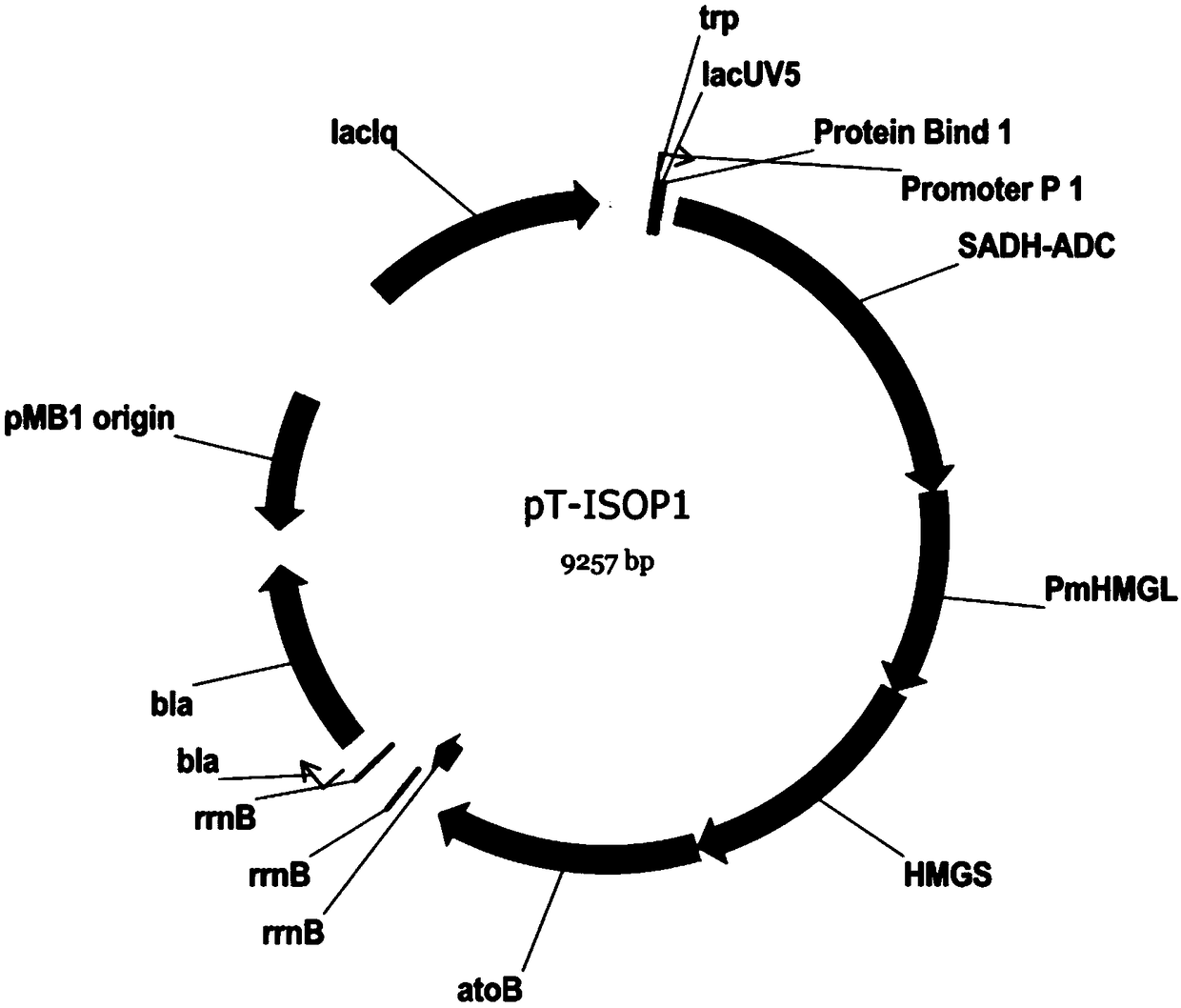
[0061] Embodiment 2: Construction of expression vector pT-ISOP1
[0062] The genes related to isopropanol synthetic metabolic pathway are constructed on expression vectors, such as pTrc99A vector. All relevant genes can be arranged in any order on the expression vector. In this example, the sequence of 5'-SADH-ADC-HMGL-HMGS-atoB-3' was arranged at the multiple cloning restriction site on the pTrc99A vector to form pT-ISOP1. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0063] Purified PCR products (each PCR product prepared in Example 1 steps 3, 4, 5, and 6) and vector plasmid pTrc99A were respectively introduced by PCR with restriction endonuclease Pme I / Xho I corresponding to the enzyme cutting site, Double digestion with Pac I / Pme I, SalI / Pac I, and Xba I / Sal I; agarose electrophoresis to recover enzyme-cut PCR and large vector fragments, and DNA ligase to ligate the digested gene fragments at 16°C The corresponding digestion product of pTrc99A. Escherichia coli D...
Embodiment 3
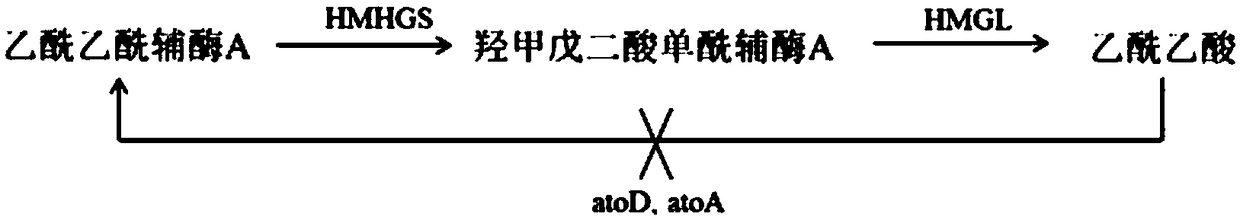
[0064] Example 3 Construction of Acetate CoA Transferase Gene Deletion Mutant Strain
[0065] The host Escherichia coli used in the isopropanol-producing Escherichia coli engineering bacteria of the present invention is a mutant strain of acetate CoA transferase gene deletion. The host Escherichia coli can be Escherichia coli BL21(DE3), BL21(DE3)pLysS, JM109, DH5α, TOP10, HB101, DH10B or wild type Escherichia coli. The genes encoding acetate CoA transferases missing in the genome are atoD and atoA. The original host bacteria used in this example is wild-type Escherichia coli MG1655, and the genes atoD and atoA encoding acetate CoA transferase were knocked out from its genome by homologous recombination, and the mutant strain was named MG1655ΔatoDA. The specific operation method is as follows:
[0066] The target genes atoD and atoA are arranged adjacent to each other on the genome, using the pKD13 plasmid (purchased from China Plasmid Vector Strain Cell Line Gene Collection ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com