Preparation method of nano-cellulose fiber dry powder
A nano-cellulose and cellulose technology, applied in the field of cellulose treatment, can solve the problems of unfavorable cost control, harsh reaction conditions, and susceptibility to microbial contamination, so as to broaden the scope of practical application, simple and rapid drying process, and avoid aggregation. The effect of junction and film formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-8
[0036] Embodiment 1-8 is prepared according to the following preparation method:
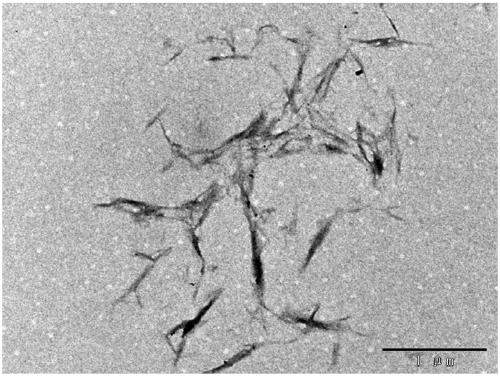
[0037] 1) Take cellulose / cellulose raw materials (wood pulp powder, M30 refined cotton, bamboo pulp, straw pulp, reed pulp, filter paper), and the scanning electron microscope image of wood pulp powder is as follows: figure 1 As shown, it can be seen that the cellulose is a large fibrous structure. As a comparison, wood pulp powder, bamboo pulp, straw pulp, reed pulp, and filter paper need to be crushed and passed through a 200-mesh sieve, and dried to obtain cellulose raw materials for use;
[0038] 2) Dissolve organic acids (citric acid, oxalic acid, malonic acid, maleic acid) in alcohols (ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, pentylene glycol, n-octanol), and configure the reaction corresponding to the volume of Table 1 liquid, the organic acid mass fraction in the reaction liquid is shown in Table 1. Under stirring conditions, the temperature of the reaction liquid is raised to the parameters i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com