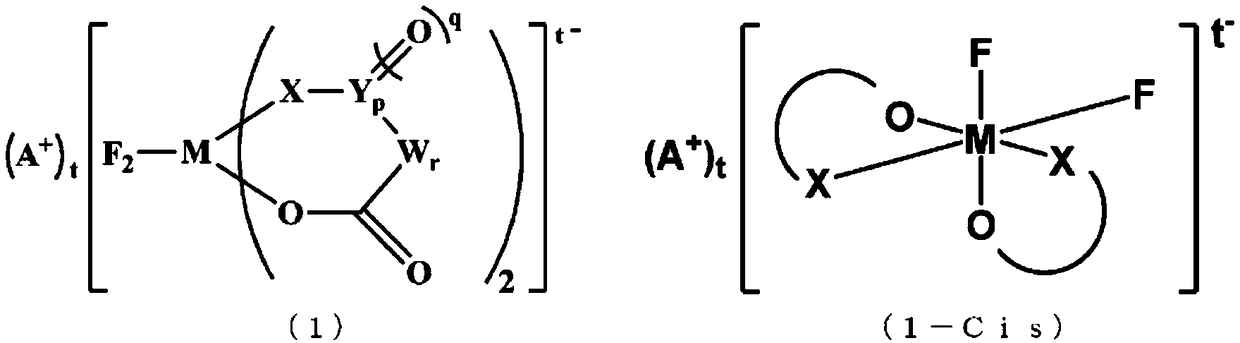Nonaqueous electrolyte solution and nonaqueous electrolyte battery using same
A non-aqueous electrolyte, non-aqueous solvent technology, applied in non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, non-aqueous electrolytes, electrolytes and other directions, can solve the problems that have not yet reached a sufficient level, cannot fully suppress the increase in internal resistance of batteries, etc., and achieve good high rate Effects of Features
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0256] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail based on examples, but the present invention is not limited by these descriptions. In addition, Examples 1-1 to 1-41 may be collectively shown as Example 1 and the like, and each Example with a sub-number may be collectively shown. Examples and respective comparative examples and electrolyte No. after Example 2 may be described in the same manner.
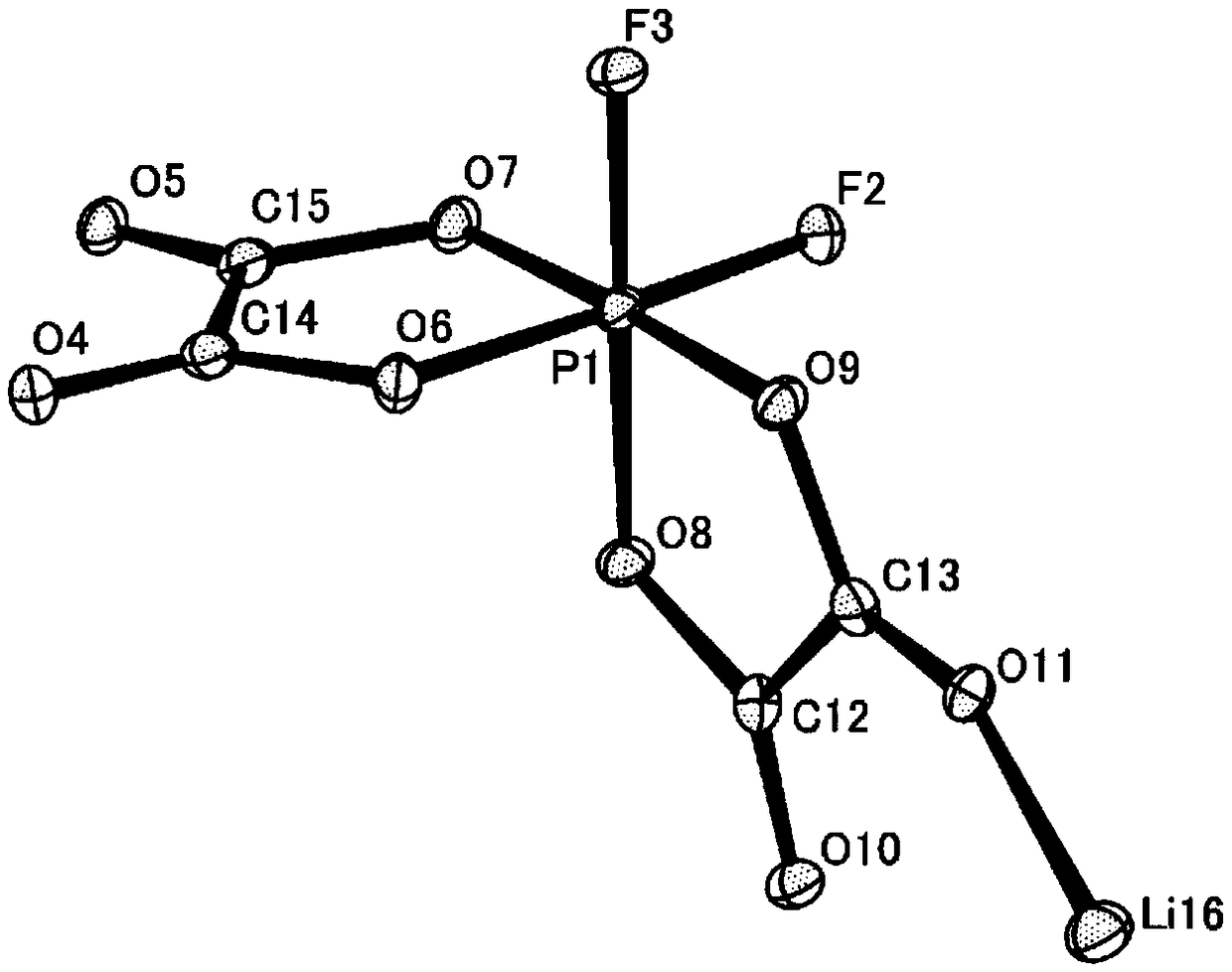
[0257] Synthesis methods of difluoroionic complex (cis-isomer / trans-isomer) and tetrafluoroionic complex are shown below. Here, the ionic complex was synthesized by using the method disclosed in Patent Document 8, or by applying the methods disclosed in Non-Patent Document 1 and Patent Document 7, but it can also be synthesized by other methods.
[0258] The operation of any raw material or product is carried out under a nitrogen atmosphere with a dew point below -50°C. In addition, the glass reactor used was dried at 150 degreeC for 12 hours or more, and ...
Synthetic example 1
[0259] [Synthesis Example 1] Synthesis of (1a-Cis), (1a-Trans)
[0260] According to the method disclosed in Patent Document 7, tricoordinate lithium trioxalatophosphate was obtained as oxalic acid. Lithium trioxalophosphate (30 g, 99.4 mmol) was dissolved in dimethyl carbonate (hereinafter referred to as DMC) (120 mL), and hydrogen fluoride (hereinafter referred to as HF) (11.9 g, 596.4 mmol) was added. After stirring at 25°C for 48 hours, residual HF and DMC were removed under reduced pressure. Then, DMC (60 mL) was added to dissolve the concentration residue as much as possible, and then concentrated until the Li salt concentration became about 45% by mass. After removing insoluble components represented by oxalic acid by filtration, 49 g of a DMC solution containing a mixture of (1a-Cis) and (1a-Trans) was obtained.
[0261] To the DMC solution of the mixture was added dichloromethane (hereinafter referred to as "CH 2 Cl 2 ") and stirred for 12 hours, thereby precipita...
Synthetic example 2
[0264] [Synthesis Example 2] Synthesis of (5a-Tetra)
[0265] The reaction was carried out with reference to the method described in Patent Document 8. 20.0g (132m moles) of LiPF 6 110 mL of dimethyl carbonate (DMC) and 11.9 g (132 m moles) of oxalic acid were added to a glass flask having a capacity of 500 mL. At this time, although the LiPF 6 Completely dissolved, but most of the dissolved oxalic acid remained. Under stirring at 25°C, 13.4 g (79 m mole) of SiCl was added dropwise to the flask 4 After that, stirring was continued for 4 hours. Then, tetrafluorosilane and hydrochloric acid were removed under reduced pressure to obtain a crude DMC solution (purity: 91 mol%) mainly composed of an ionic complex (5a-Tetra).
[0266] This solution was concentrated until the Li salt concentration became about 50 mass %, and 51 g of concentrates were obtained. After removing insoluble components by filtration, CH was added at room temperature while stirring. 2 Cl 2 . After st...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| face spacing | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com