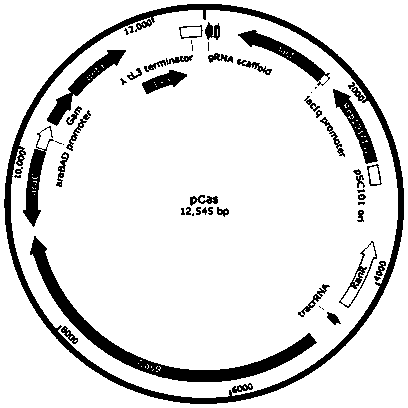
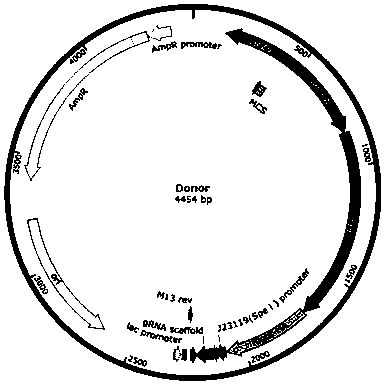
Specific marking method for enterotoxigenic escherichia coli
A technology of Escherichia coli and labeling method, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of poor stability, lack of versatility, weak strain specificity, etc., and achieve the effects of high detection sensitivity, high editing efficiency and strong penetrating power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1: Selection of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Strains
[0043] The Escherichia coli strains capable of causing intestinal pathogenicity were detected, the Escherichia coli genome DNA was extracted, and the genome DNA was identified by 0.8% agarose electrophoresis. According to the enterotoxin-producing gene sequence published on NCBI, a pair of primers were synthesized, the toxic gene was detected by PCR, and the PCR product was identified by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, such as figure 1As shown, the size is 219bp;
[0044] ST-F: 5'-CCATGGCATCTACACAATCAA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 4);
[0045] ST-R: 5'-CTCGAGTTAGCATCCTTTTGCT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 5).
[0046] figure 1 The results showed that the Escherichia coli strain capable of causing enteropathogenicity was enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2: Selection and validation of pseudogene loci
[0048] Using the Escherichia coli K12 gene sequence as a reference, 6 pseudogene positions that can be inserted into foreign genes were predicted by using ABCpred through bioinformatics analysis, namely yaiT, yai X, yge O, yheO, wbb L and ykg A. PCR primers were designed according to the above pseudogene loci, and the enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli genome in Example 1 was used as a template for detection.
[0049] According to the yheO gene sequence (GenBank accession number NC_000913.3) published in Genbank, design primers yheO-F, yheO-R, with enterotoxic E. coli genomic DNA in Example 1 as template, complete yheO gene PCR amplification in ETEC Detection, the size of the amplified target band is 814bp, and the size of the PCR amplified band is in line with expectations, such as figure 2 , the PCR amplification product is sequenced, and the yheO sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1.
[0050] yheO-F: GTAGAAGCCGGTA...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3: Designing sgRNA target primers and constructing gene editing vectors
[0054] 1. Target sequence design
[0055] Primers were designed according to the principles of Cas9 target design: G at the 5' end, PAM sequence (NGG) at the 3' end, and a guide sequence yheO-gRNA: ATATAATTAGTGCTGGAAAGCGG (SEQ ID NO: 8).
[0056] 2. PCR amplified sgRNA fragment and double enzyme digestion ligation of plasmid
[0057] Using the pTarget plasmid as a template, design primers P1, P2, and P3, carry out PCR amplification through primers P1 and P3, obtain PCR products identified by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, and purify and reclaim it with DNA Fragment Purification Kit (sequence such as SEQ ID NO:20), and then use the recovered PCR product as a template, carry out PCR through primers P2 and P3, amplify to obtain a linearized PCR product containing the target sequence, and purify and recover the same (sequence such as SEQ ID NO:21) .
[0058] P1: ATATAATTAGTGCTGGAAAGgttttag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com