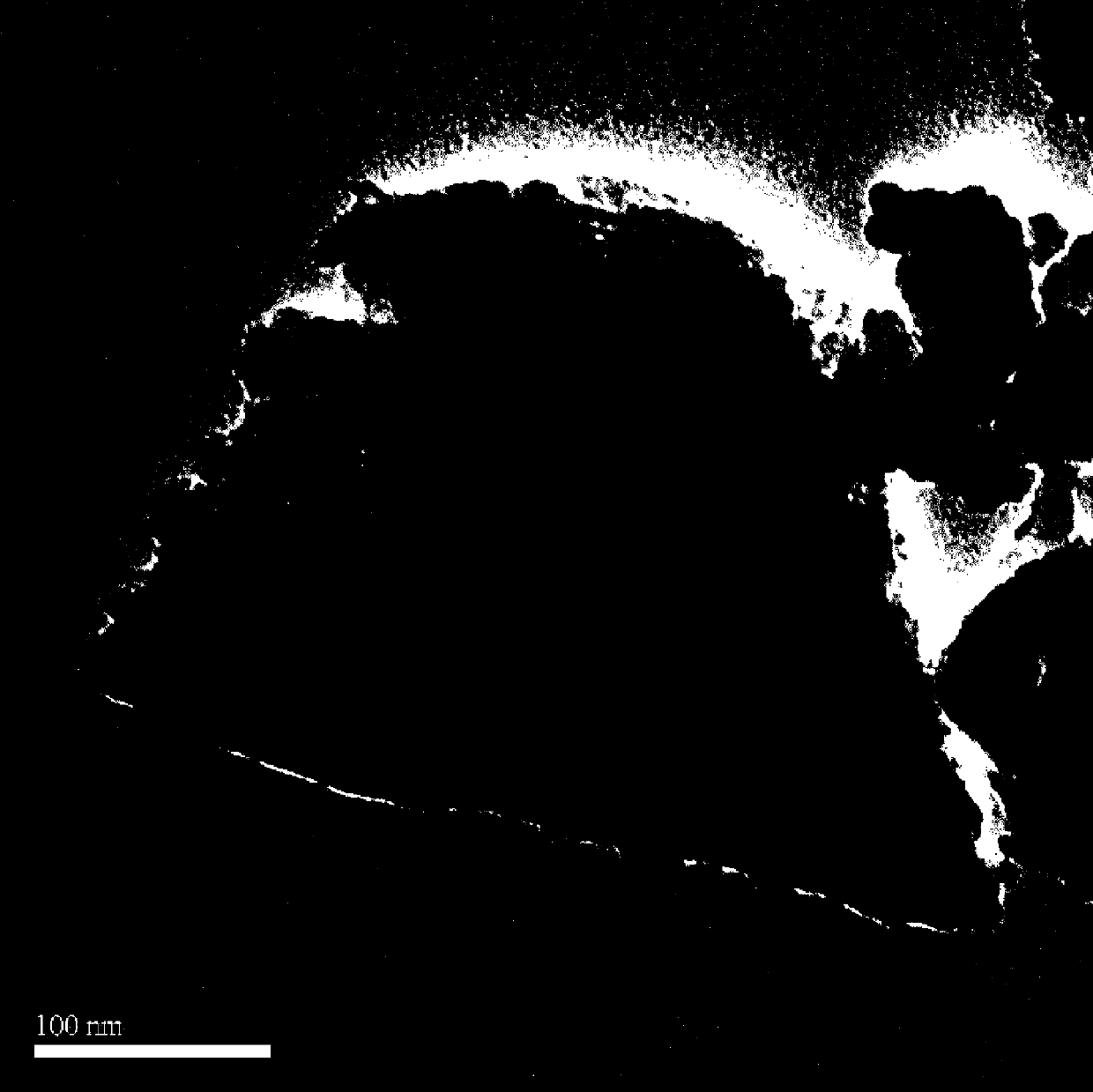
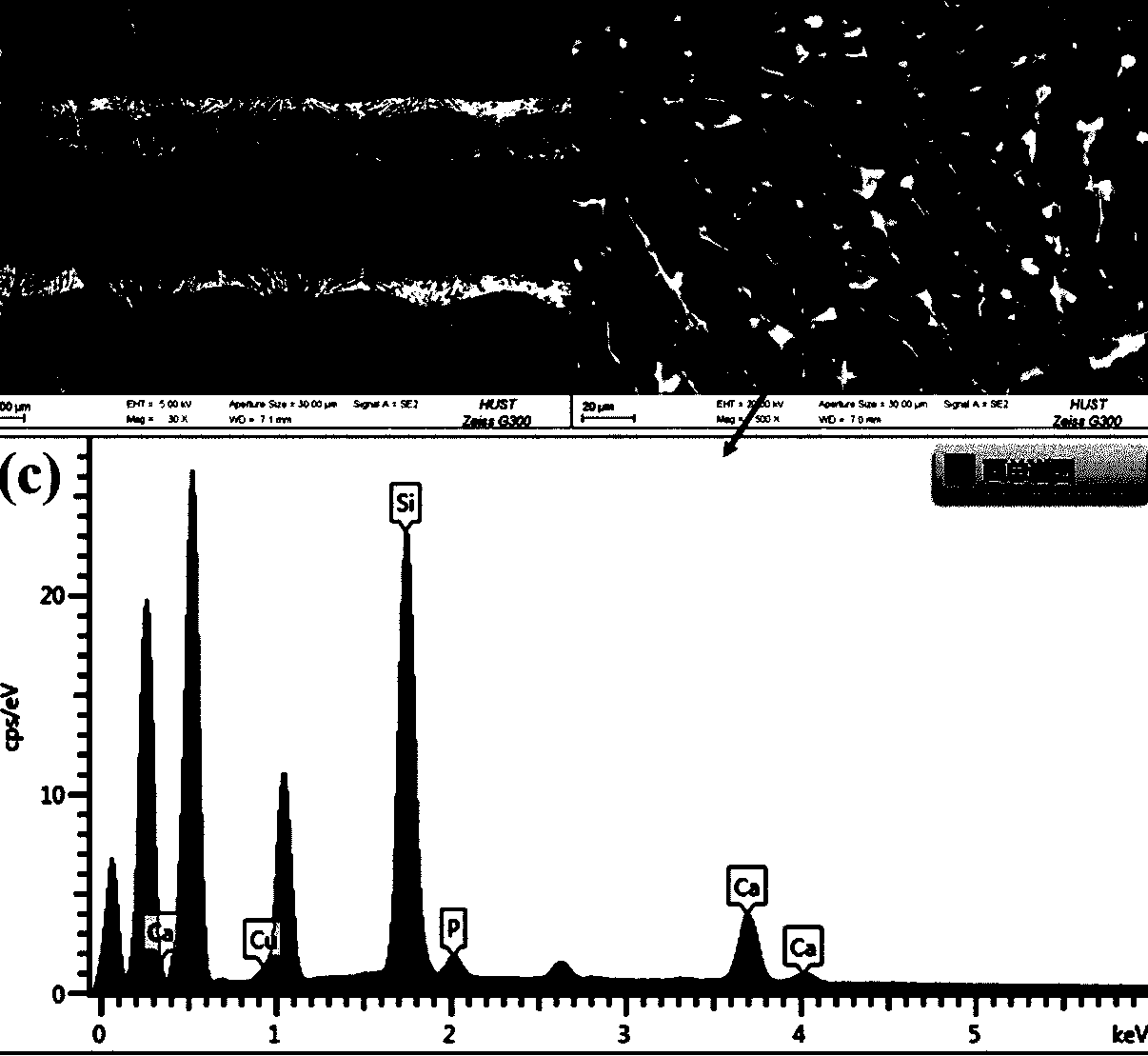
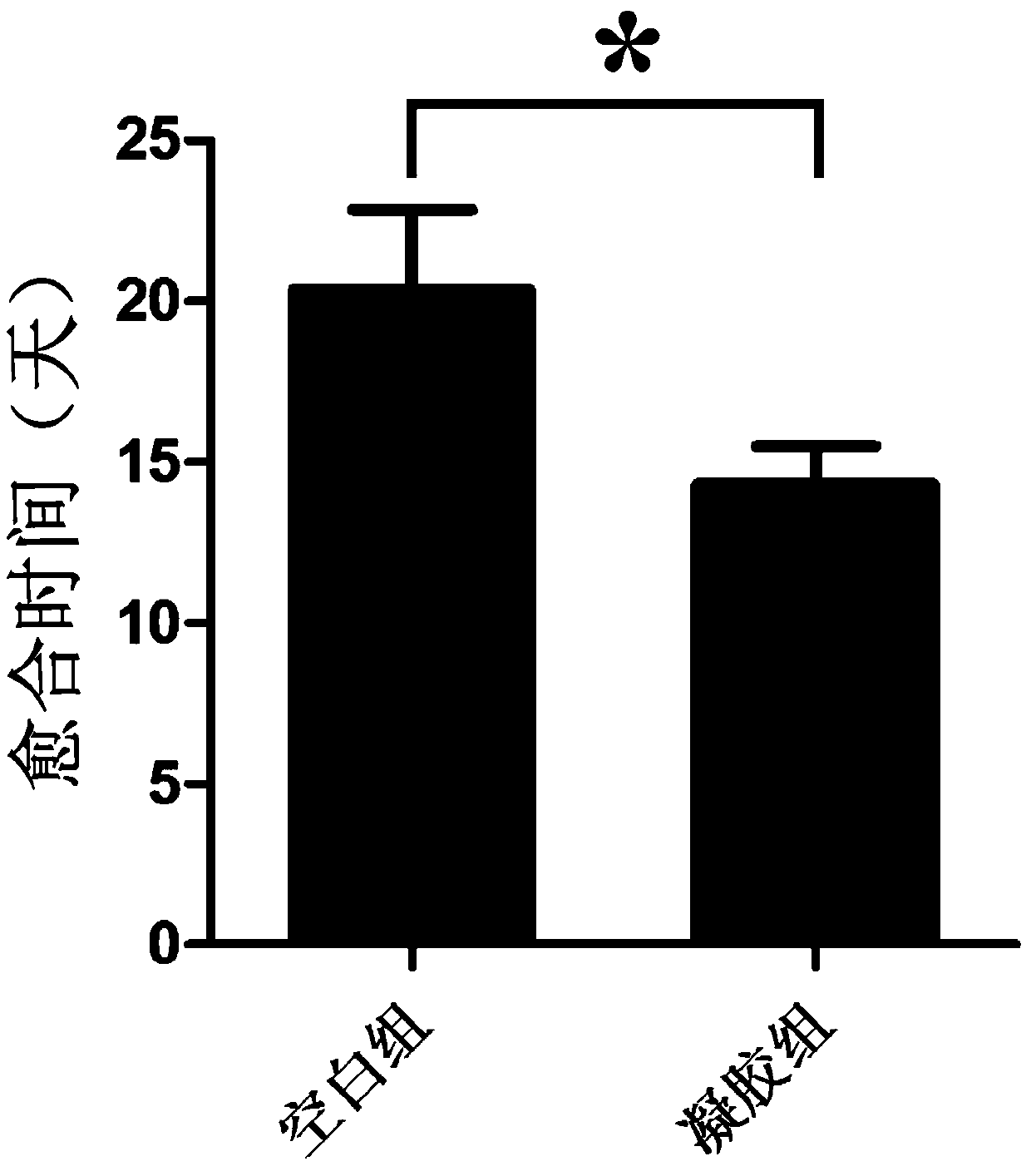
Mesoporous biological glass-loaded small intestinal submucosa wound surface dressing
A technology of small intestinal submucosa and bioglass, which is applied in the fields of biomedical engineering and skin wound repair materials, can solve the problems of single structure and cannot give full play to the excellent performance of SIS, and achieves improved antibacterial, stable and controllable manufacturing process, and large-scale production. production effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] (1) Preparation of small intestinal submucosa matrix material: the small intestinal submucosa was degreased, enzymatically hydrolyzed, descaled, freeze-dried, and low-temperature ball milled to obtain small intestinal submucosa powder; SIS powder with a mass fraction of 2.5% was dissolved in 0.01M hydrochloric acid At the same time, 0.25% pepsin was added, and magnetically stirred at room temperature for 48 hours; after SIS was completely dissolved, SIS was neutralized by 0.1M NaOH solution, and stored at 4°C.
[0031] (2) Preparation of copper and zinc mesoporous bioglass:
[0032] Add 1.5% 0.5M HCl by volume to absolute ethanol, add 10% ethyl orthosilicate, 2% calcium nitrate tetrahydrate, 0.5% copper chloride, 1.5% triethyl phosphate, 8% P 123, stirred magnetically at room temperature for 48 hours; transferred the solution to a petri dish and let it stand for gelation, and completed the self-assembly process of solvent volatilization, and obtained dry gel after 24 ho...
Embodiment 2
[0040] (1) Preparation of small intestinal submucosa matrix material: The small intestinal submucosa was degreased, enzymatically hydrolyzed, descaled, freeze-dried, and low-temperature ball milled to obtain small intestinal submucosa powder; SIS powder with a mass fraction of 1% was dissolved in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid At the same time, 0.1% pepsin was added, and magnetically stirred at room temperature for 36 hours; after SIS was completely dissolved, SIS was neutralized with 0.1 M NaOH solution, and stored at 4°C.
[0041] (2) Preparation of copper and zinc mesoporous bioglass:
[0042] Add 1.5% 0.5M HCl by volume to absolute ethanol, then add 8% ethyl orthosilicate, 1.5% calcium nitrate tetrahydrate, 2.5% copper chloride, 1.0% triethyl phosphate, 7% P 123 , magnetic stirring at room temperature for 44 hours; transfer the solution to a petri dish and let it stand for gelation, complete the self-assembly process of solvent volatilization, and obtain dry gel after 28 hours; ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] (1) Preparation of small intestinal submucosa matrix material: the small intestinal submucosa was degreased, enzymatically hydrolyzed, descaled, freeze-dried, and low-temperature ball milled to obtain small intestinal submucosa powder; the SIS powder with a mass fraction of 5% was dissolved in 0.01 M hydrochloric acid At the same time, 0.5% pepsin was added, and magnetically stirred at room temperature for 48 hours; after SIS was completely dissolved, SIS was neutralized by 0.1M NaOH solution, and stored at 4°C.
[0050] (2) Preparation of copper and zinc mesoporous bioglass:
[0051] Add 1.5% 0.5M HCl by volume to absolute ethanol, add 12% ethyl orthosilicate, 2.5% calcium nitrate tetrahydrate, 3% copper chloride, 2.0% triethyl phosphate, 9% P 123 , magnetic stirring at room temperature for 52 hours; transfer the solution to a petri dish and let it stand for gelation, complete the solvent volatilization self-assembly process, and obtain the xerogel after 30 hours; take...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com