A transgenic Arabidopsis for remediation of PCBS-contaminated soil
A technology of contaminated soil and Arabidopsis thaliana, applied in the field of bioremediation and environmental protection, can solve the problems of plant toxicity, low efficiency of microbial remediation, and insignificant degradation of monohydroxychlorinated biphenyls, so as to improve tolerance and The effect of accumulating ability and improving repairing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1: co-expression TfdB+BphC plant screening
[0040] The 2,4-dichlorophenol hydroxylase gene (TfdB) was obtained from a soil metagenomic library. Studies have shown that TfdB enzymes are substrates for chlorophenols, biphenyls, and all indoles except 3-methylindole. Indole substrates all have certain activity. The 2,3-dihydroxyoxygenase (BphC) gene also came from the soil metagenomic library. 2,3-Dihydroxyoxygenase is a key gene that plants lack to open hydroxylated biphenyls.
[0041] (1) Subcloning of TfdB and BphC genes
[0042] The subclones were derived from the 2,4-dichlorophenol hydroxylase TfdB gene (GQ403987.1) and the 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl dioxygenase BphC gene (GQ403988.1) from the soil metagenome.
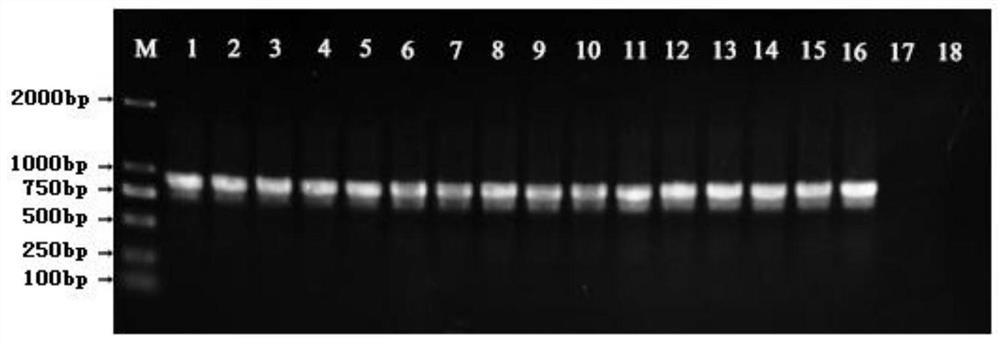
[0043] Using the plasmid stored in the laboratory as a template, the primers FBphC and RBphC containing restriction sites were used to amplify the BphC gene; the primers FTfdB and RTfdB were used to amplify the TfdB gene.
[0044] FBphC: 5'-GGAAGATCT...
experiment example 2
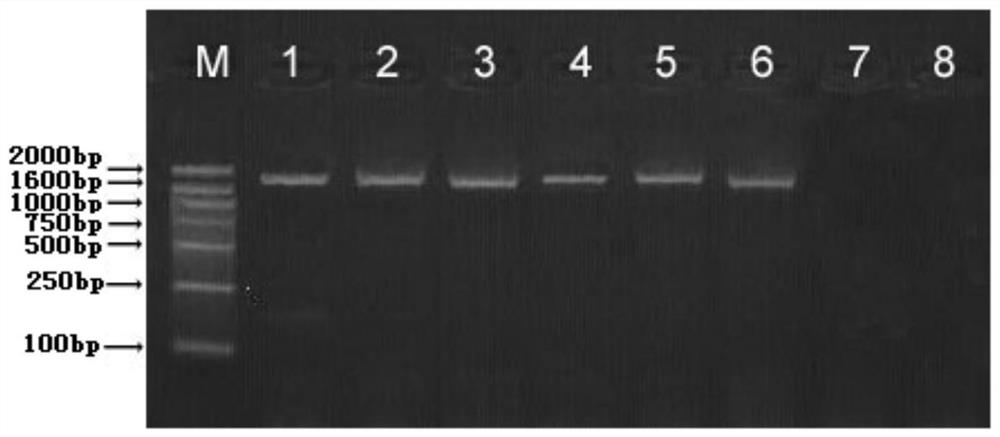
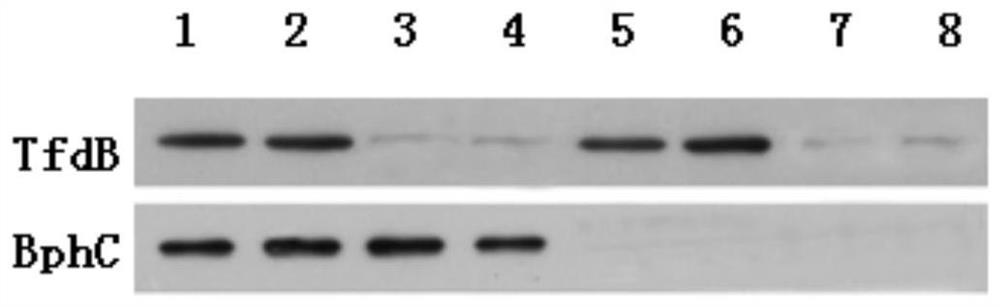
[0052] Experimental Example 2 Plant Transformation and Identification of Transgenic Plants
[0053] Use Arabidopsis as the recipient material for genetic transformation, and screen to obtain lines with target traits (co-expression of TfdB+BphC); use PCR and Western blot methods to carry out molecular identification of transgenic plants, and measure the enzyme activity of TfdB or BphC in the plants According to the biological characteristics of the plants, the plants with the strongest p-biphenyl degradation activity among the co-expressed TfdB+BphC plants were selected for subsequent experiments.
[0054] (1) Plant genetic transformation
[0055] Take an appropriate amount of Arabidopsis seeds, place them in the dark at 4°C for 2-3 days, and carry out vernalization; sow them in a mixture of vermiculite and nutrient soil at a volume ratio of 1:1, and cultivate them in a greenhouse at 22°C, with 16 hours of light and 8 hours of darkness; After about 3 weeks of growth, Arabidops...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3: hydroponic simulation restoration test
[0067] Seeds of wild type and transgenic Arabidopsis were sown on 1 / 2 MS solid medium and cultured respectively. After culturing for 15 days, the growth of Arabidopsis in each group was measured. Take Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings that grow well and are similar, and transfer them to 1 / 2MS liquid medium containing 0.05 μg / ml PCB28, and treat 20 Arabidopsis seedlings for each treatment, at 25°C, 14 / 10h alternating light and dark conditions under cultivation. After 7 days, the culture medium and plants were collected, the plant height and fresh weight of the plants were measured, and the difference in the tolerance of wild-type Arabidopsis and transgenic Arabidopsis to PCB28 was analyzed by tolerance index.
[0068]
[0069] Arabidopsis thaliana was washed and placed on tinfoil paper, and dried in an oven at 60°C for 12 hours. The plants were divided into roots and aerial parts, and the amount of dry matter was re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com