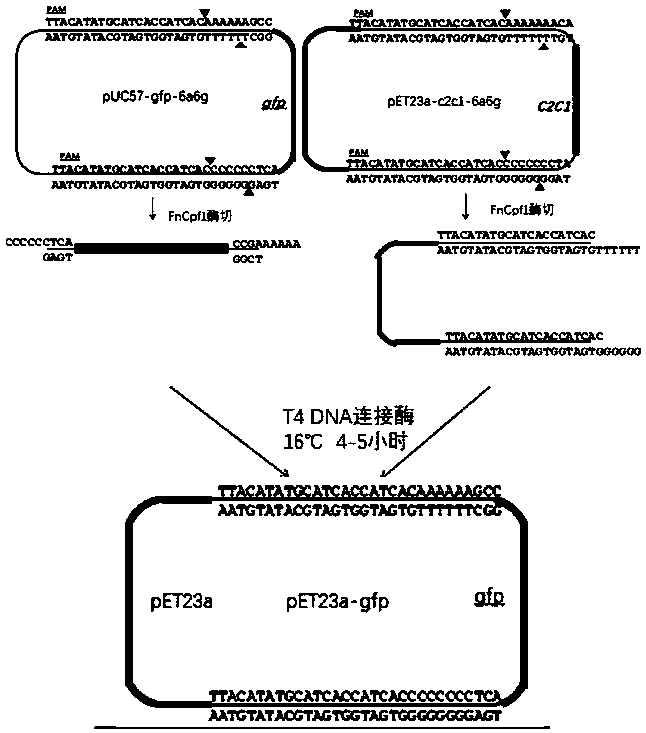
Novel method for gene assembly using improved CRISPR-Cpf1
A new method, gene technology, applied in the field of gene assembly using improved CRISPR-Cpf1, can solve the problems of low probability of recombination, reduced fragment connection efficiency, high cost, etc., to save synthesis cost, improve recombination efficiency and repeatability , the effect of improving the efficiency of recombination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1 Construction of expression vector for nucleic acid editing enzyme FnCpf1
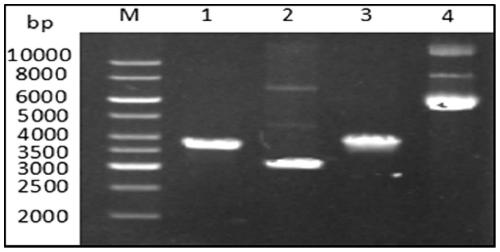
[0050] According to the T5 exonuclease-mediated cloning method, PCR amplification was performed on the nucleic acid programming enzyme FnCpf1 gene fragment and the expression vector pET23a. After the product was detected and recovered by the agarose gel, the nucleic acid concentration was measured with a Nanodrop 8000 spectrophotometer. The fragments and the vector fragments were mixed in a molar ratio of 3:1, T5 exonuclease was added and reacted in an ice-water mixture for 5 minutes, and then the conventional transformation of E. coli was carried out. Pick a single colony separately into 3ml of lysic broth liquid medium supplemented with ampicillin, culture for several hours at 37°C, extract plasmid DNA according to the alkaline lysis method, and then perform agarose gel electrophoresis detection, the size is correct and PCR identified contains The plasmid of the target fragment is sent t...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 Expression and identification of FnCpf1 nucleic acid editing enzyme in E. coli
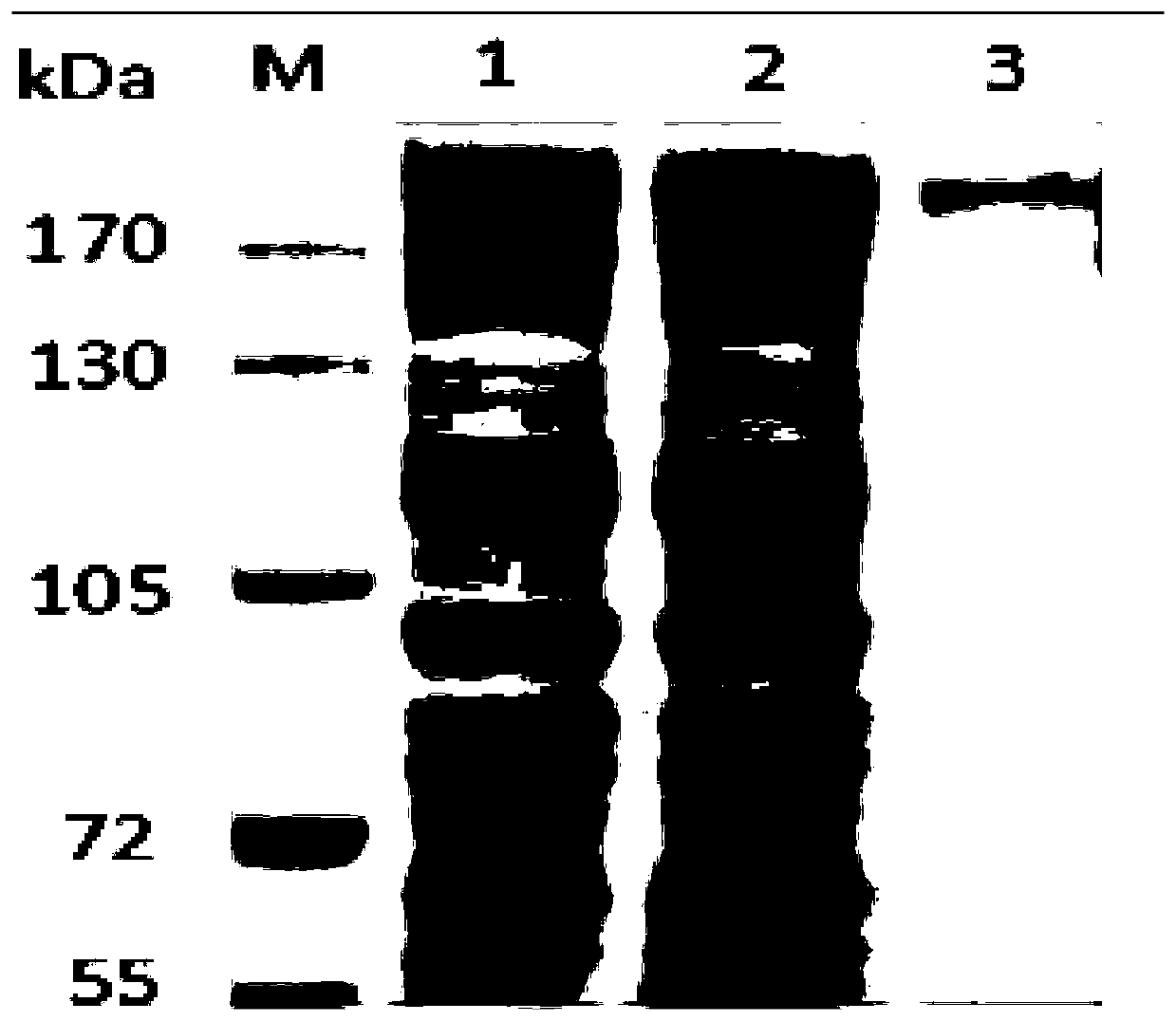
[0053] Transform the correctly sequenced recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) expression strain, pick a single colony to inoculate 100ml of lysic broth medium supplemented with ampicillin, and cultivate to OD at 37°C 600 For 0.6-0.8, add 1M IPTG (isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside) at a volume ratio of 1%, culture overnight at 18°C, 200rpm shaking; collect the bacteria and resuspend the bacteria in lysis buffer, After bacteriostasis by ultrasound, centrifuge, add 5× protein loading buffer to the centrifuged supernatant and pellet respectively, treat in a metal bath at 100°C for 10 minutes, and then perform SDS-PAGE sodium dodecyl sulfonate-polyacrylamide gel Electrophoresis, the results are as image 3 .
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Purification of nucleic acid editing enzyme FnCpf1 with nickel beads
[0055] Take a single colony containing the recombinant plasmid and inoculate it into 200ml lysing broth medium supplemented with ampicillin, and cultivate to OD at 37°C 600 Add 1% IPTG (isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside) when it reaches 0.6-0.8, and induce overnight at 18°C; collect E. coli cells, resuspend the cells in lysis buffer, and then ultrasonically break Cells, the crude lysate and the affinity resin are thoroughly mixed to bind the target protein to the nickel beads, and then the recombinant protein is eluted with different concentrations of imidazole buffer, and the effluent obtained by gradient elution is subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfonate- Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the results are as Figure 4 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com