Harmless dressing and smelting method for recycling lead, zinc, carbon, iron and tailings from water quenching slag
A water-quenched slag, harmless technology, applied in the field of carbon, zinc, recovery of lead, iron and tailings harmless, can solve the problem of changing, unable to achieve comprehensive recovery of water-quenched slag, and unable to achieve slag properties. and other problems to achieve the effect of simplifying the process steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
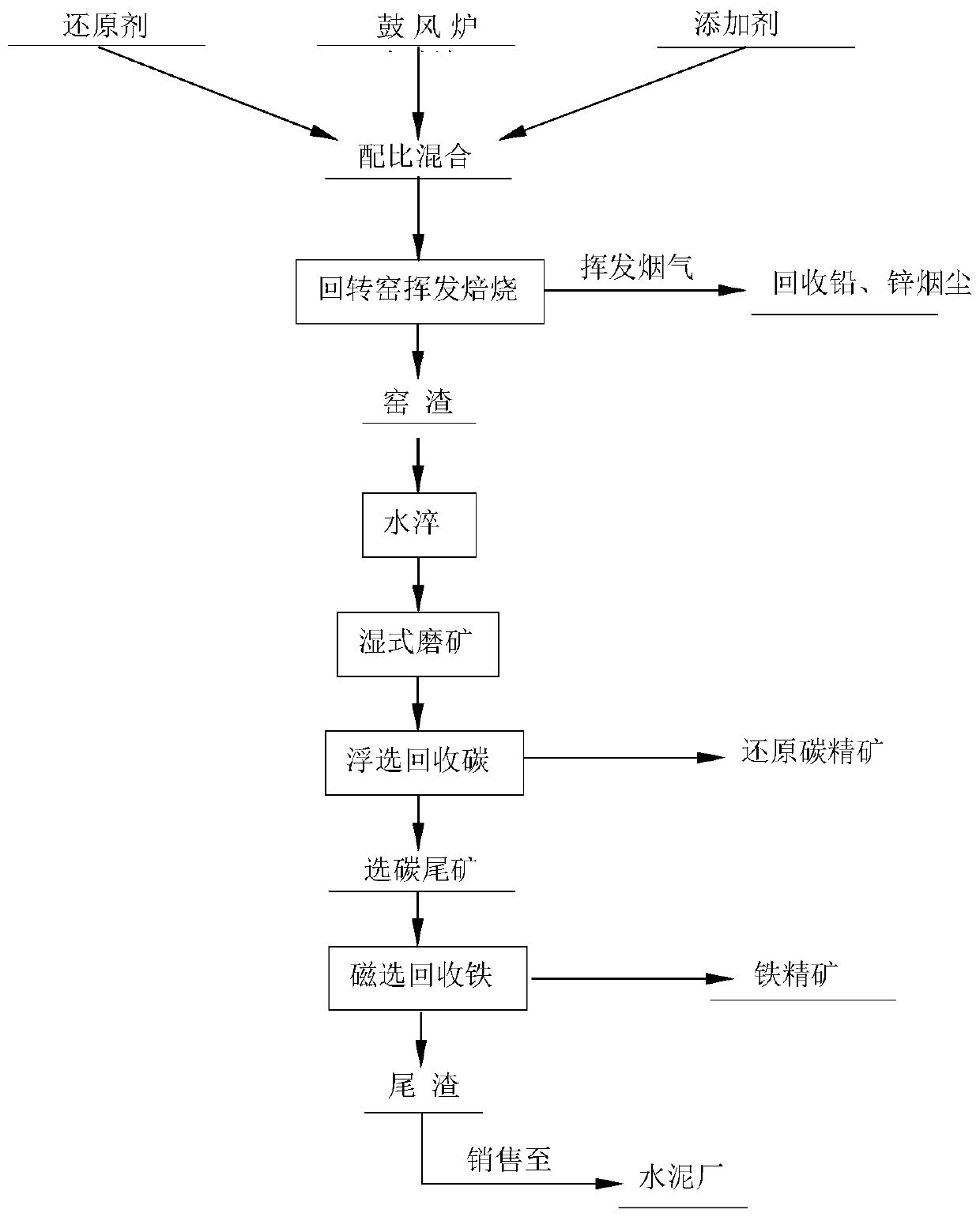
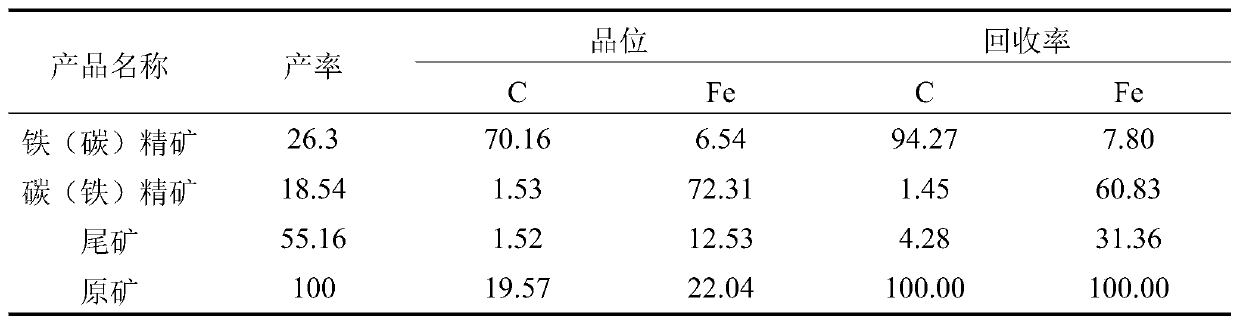
[0059] The combined method of comprehensive recovery of lead, zinc, carbon, iron and tailing slag harmless from the water-quenched slag of lead smelting blast furnace provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0060] 1. Proportion of blast furnace water-quenched slag, reducing agent and additive: take blast furnace water-quenched slag, including 1.50% lead and 14.12% zinc, reducing agent is coke, additive is lime, and the ratio of blast furnace water-quenched slag to reducing agent and additive is : 1:0.6:0.10, according to this ratio, the blast furnace water-quenched slag, coke and lime are evenly mixed to feed the rotary kiln.
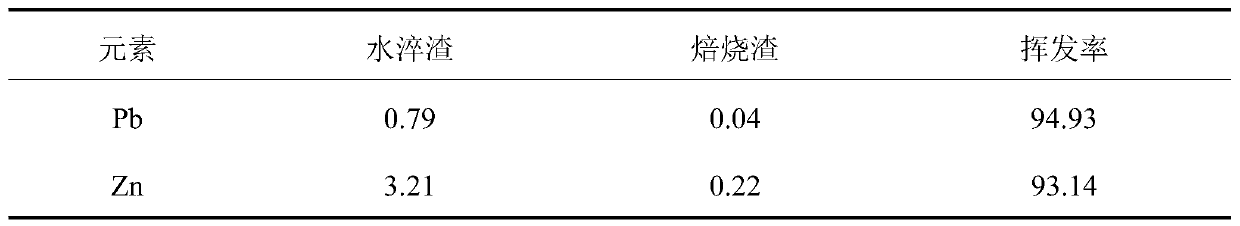
[0061] 2. The volatilization recovery process of lead and zinc: the high-temperature volatilization and roasting of the materials after the proportioning in step (1), and the recovery of lead and zinc in the water-quenched slag of the blast furnace is realized by collecting volatile smoke and dust. During volatilization and roasti...
Embodiment 2
[0067] The combined method of comprehensive recovery of lead, zinc, carbon, iron and tailing slag harmless from the water-quenched slag of lead smelting blast furnace provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0068] 1. Proportion of blast furnace water-quenched slag to reducing agent and additives: take blast furnace water-quenched slag, which contains 1.60% lead and 12.17% zinc, and the reducing agent is anthracite. The ratio of blast furnace water-quenched slag to reducing agent is: 1:0.60, According to this ratio, the blast furnace water-quenched slag and anthracite are evenly mixed to feed the rotary kiln.
[0069] 2. The volatilization recovery process of lead and zinc: the high-temperature volatilization and roasting of the materials after the proportioning in step (1), and the recovery of lead and zinc in the water-quenched slag of the blast furnace is realized by collecting volatile smoke and dust. During volatilization and roasting, the high-tempe...
Embodiment 3
[0075] The combined method of comprehensive recovery of lead, zinc, carbon, iron and tailing slag harmless from the water-quenched slag of lead smelting blast furnace provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0076] Proportioning of blast furnace water-quenched slag and reducing agent and additives: take blast furnace water-quenched slag, which contains 1.23% lead and 9.33% zinc, the reducing agent is semi-coke, and the additive is a mixture of lime and limestone (the ratio of lime and limestone is 0.6: 0.4), the ratio of blast furnace water-quenched slag to reducing agent and additive is: 1:0.35:0.06, according to this ratio, the blast furnace water-quenched slag is evenly mixed with coke and lime to feed the rotary kiln.
[0077] The volatilization recovery process of lead and zinc: the high-temperature volatilization and roasting of the materials after the proportioning in step (1), and the recovery of lead and zinc in the water-quenched slag of the bla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com