Cupriavidus and application thereof
A technology of copper greedy bacteria and strains, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problem of inability to degrade 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol, etc., and achieve a good effect of bioremediation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1: Isolation, purification and identification of bacterial strains
[0021] (1) Configure inorganic salt medium:
[0022] The inorganic salt medium is composed of disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na 2 HPO 4 12H 2 O) 14.3g; Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4 ) 3g; magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O) 0.06mg; ferrous sulfate (FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O) 0.3mg; manganese sulfate (MnSO 4 ·H 2 O) 0.28mg; copper sulfate (CuSO 4 ) 0.05mg; Zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4 ) 0.05mg; boric acid (H 3 BO 3 ) 0.05 mg. The above ingredients were dissolved in double distilled water and the volume was adjusted to 1000ml, adjusted to pH 7.0, and autoclaved at 121°C for 20 minutes.
[0023] (2) Enrichment of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol-degrading bacteria:
[0024] Sampling soil contaminated by a pesticide manufacturing plant, adding 5 g of soil to a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 100 mL of inorganic salt medium, and adding 0.3 mM 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol as the only carbon and nitrogen ...
Embodiment 2
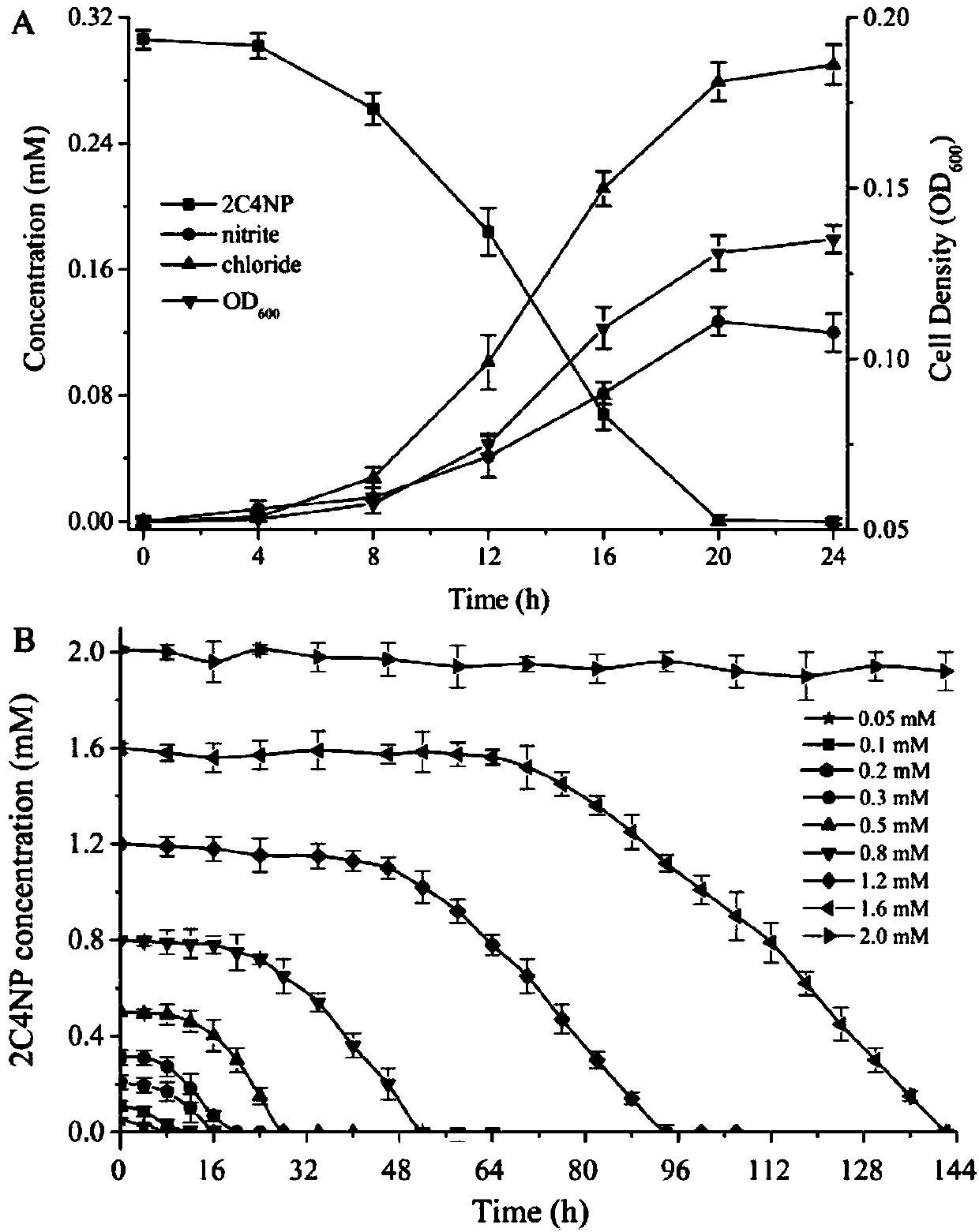
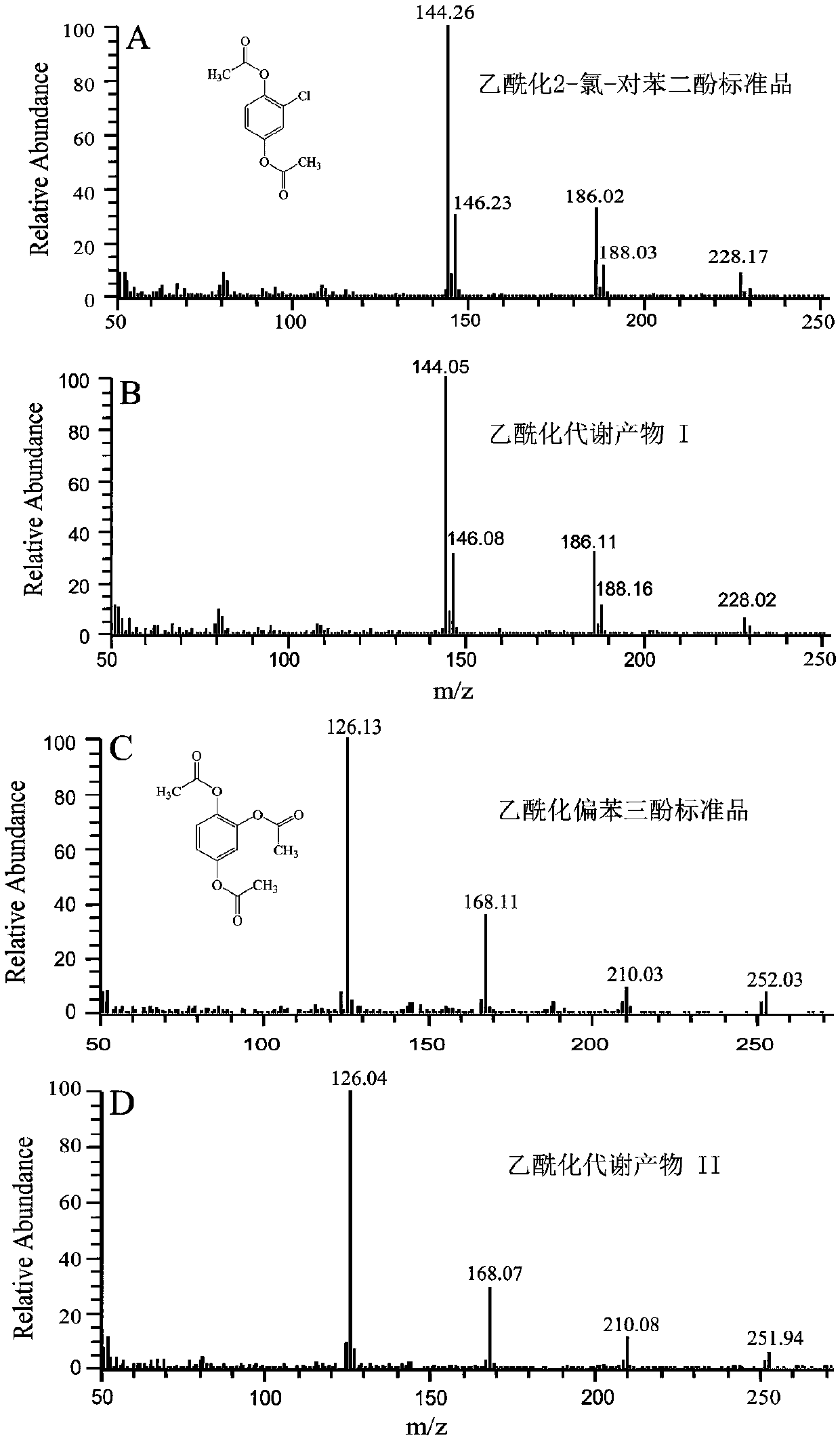
[0029] Example 2: Analysis of bacterial strains' ability to degrade 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol and identification of metabolic intermediates
[0030] (1) Analysis of degradability
[0031] Inoculate the above single colony in inorganic salt medium + LB (volume ratio = 4:1), add 0.3mM 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol, collect the bacteria after overnight culture, and wash with inorganic salt medium 2 times, then press initial OD 600 =0.05 inoculum amount was inoculated into fresh inorganic salt medium (adding 0.3mM 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol), placed in a shaker at 180rpm, cultivated at 30°C and sampled at intervals, centrifuged at 12000rpm, and the supernatant was collected. Use HPLC to detect the concentration of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol in the supernatant, and use nitrite reagent: 1% sulfanilic acid and 0.02% N-(1-naphthalene) ethylenediamine to detect nitrite , use a chloride ion selective electrode to detect chloride ions, and use a spectrophotometer to detect the bacterial concentration OD...
Embodiment 3
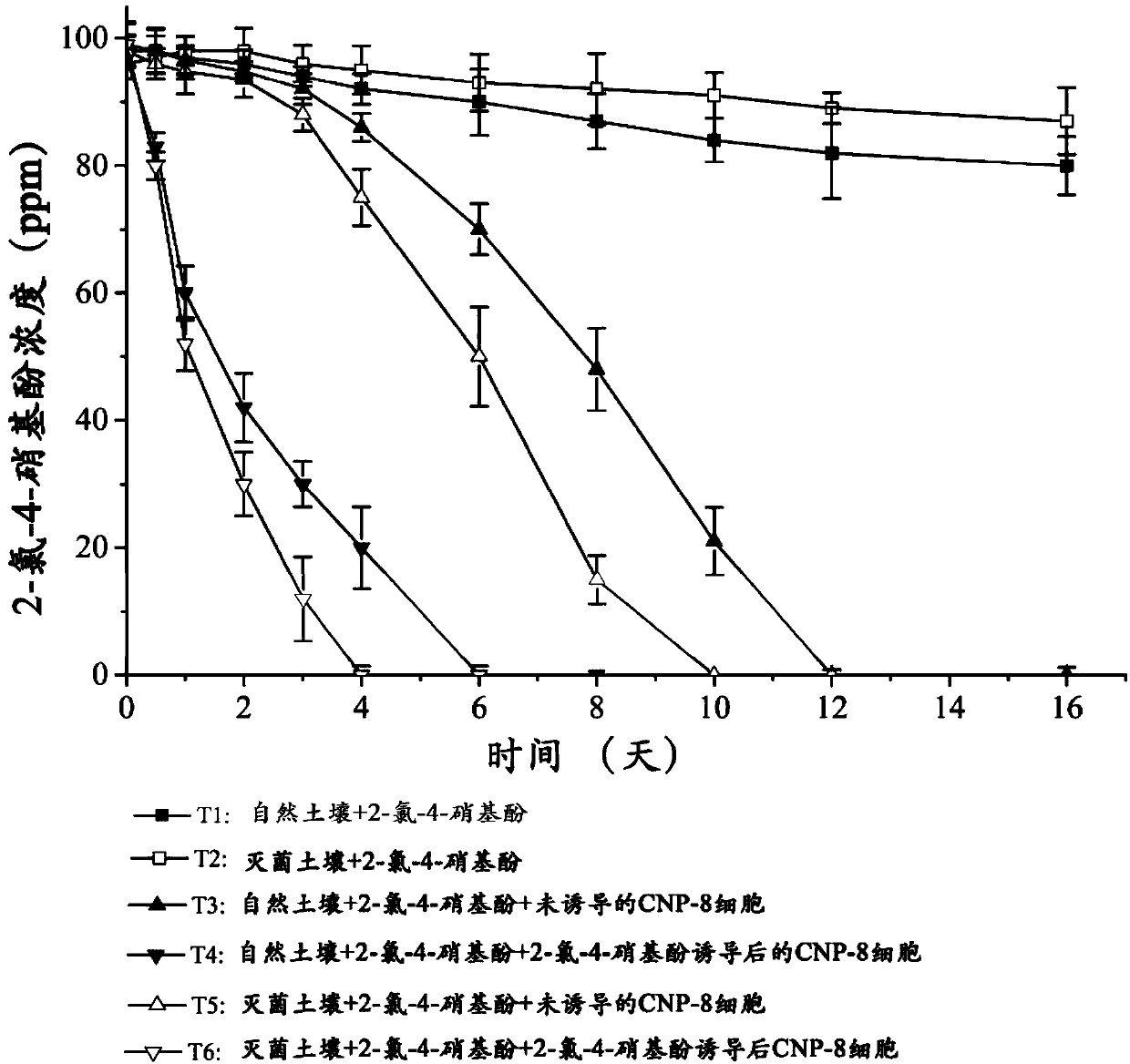
[0038] Embodiment 3: Copper greedy bacteria CNP-8 restores 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol polluted soil
[0039] (1) Soil collection and soil physical and chemical index determination
[0040] Soil samples were collected in the campus of China Agricultural University (Yantai), and there was no history of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol pollution. The 0-15cm soil was collected to remove the topsoil. Collect after passing through a 2mm sieve and store at 4°C. After testing, the total carbon, total nitrogen and water content of the soil were 0.86%, 0.074% and 10.64% respectively, and the pH value was 7.38.
[0041] (2) Preparation of Inoculated Bacteria
[0042] The strains were cultured with liquid LB medium or inorganic salt + LB (volume ratio = 4:1, and 0.3mM 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol was added at the same time) to the late logarithmic period, and the bacteria were collected by centrifugation at 6000×g for 8 minutes. Then wash twice with 0.85% sterile physiological saline, and set aside.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com