Organic/inorganic composite solid electrolyte and preparation method thereof
A solid electrolyte and inorganic composite technology, which is applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, secondary batteries, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the electrochemical cycle performance of solid-state batteries, reducing the crystallinity of organic polymers, and increasing interface resistance, so as to avoid heat treatment The effect of high temperature, inhibition of interface reaction, and reduction of interface resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Lithium sulfide and phosphorus pentasulfide were ground and mixed in a mortar at a ratio of 1:1 (molar ratio), ball milled in a ball mill for 6 hours, and heat treated at 280°C for 4 hours to obtain a sulfur-based solid electrolyte. PMMA polymer and LiClO 4 Mix at a molar ratio of 10:1, add the sulfide powder and polymer / lithium salt into n-heptane at a mass ratio of 9:1, stir magnetically at 50°C for 12 hours, remove the organic solvent by rotary evaporation, and dry at 80°C , to obtain an organic / inorganic composite solid electrolyte. The thickness of the coating layer of the organic polymer is 20-30nm, and the ion conductivity at room temperature is 10 -4 S / cm.
[0052] On the one hand, the preparation method is suitable for preparing three-phase and above sulfur-based solid electrolytes, and is also suitable for organic polymer electrolytes with low decomposition temperatures. In addition, the composite electrolyte uses an organic solid electrolyte to coat the sul...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Lithium sulfide, phosphorus pentasulfide, and germanium sulfide were ball milled in a ball mill for 12 hours at a ratio of 5:2:1 (molar ratio), and heat-treated at 600°C for 6 hours to obtain a sulfur-based solid electrolyte. PVDF polymer and LiTFSI were mixed at a molar ratio of 30:1 , add sulfide powder and polymer / lithium salt into acetonitrile at a mass ratio of 1:1, stir magnetically at room temperature for 48 hours, remove the organic solvent by suction filtration, and dry at 50°C to obtain an organic / inorganic composite solid electrolyte. The coating layer of the organic polymer has a thickness of 100-120 nm and an ionic conductivity of ~10 at room temperature -3 S / cm.
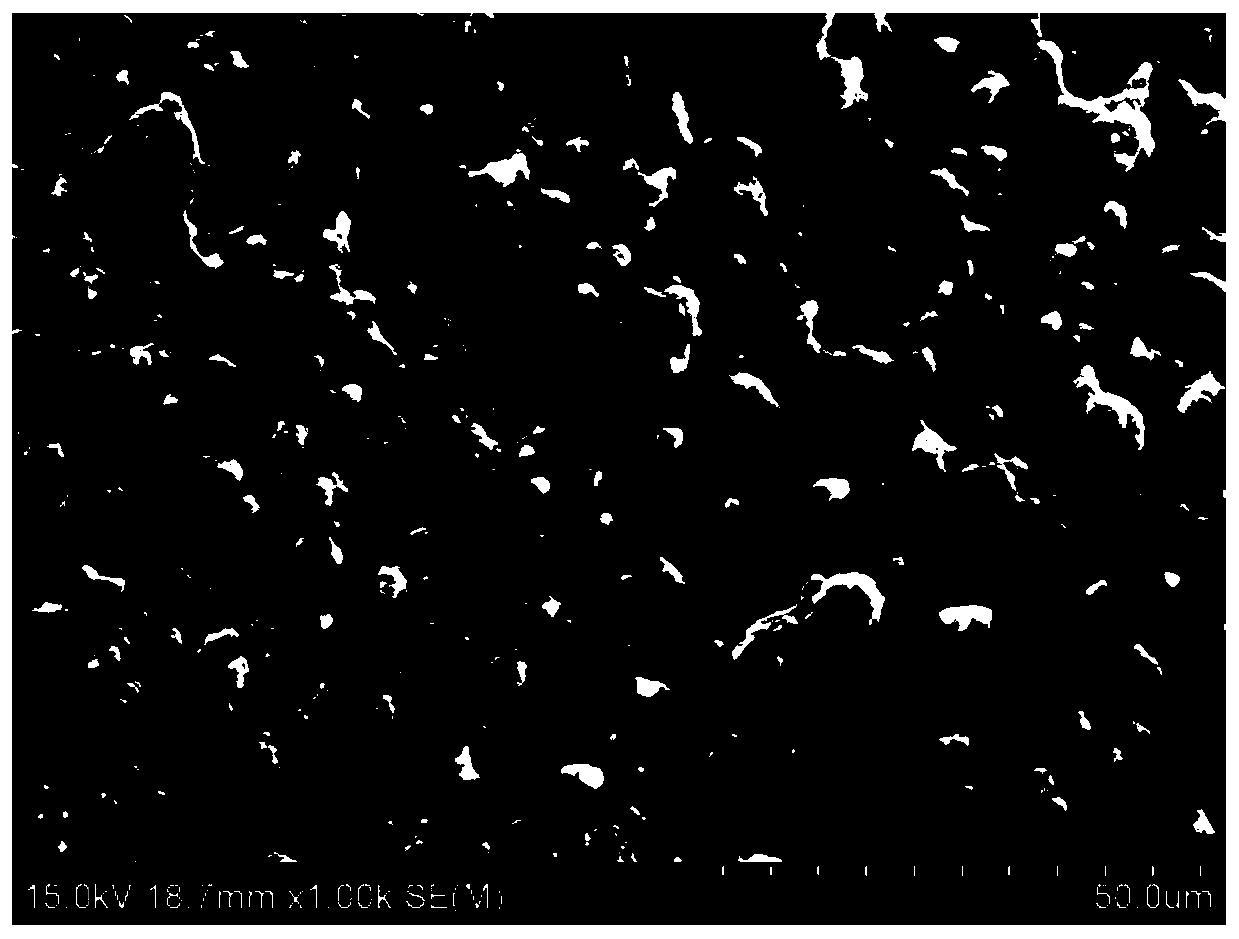
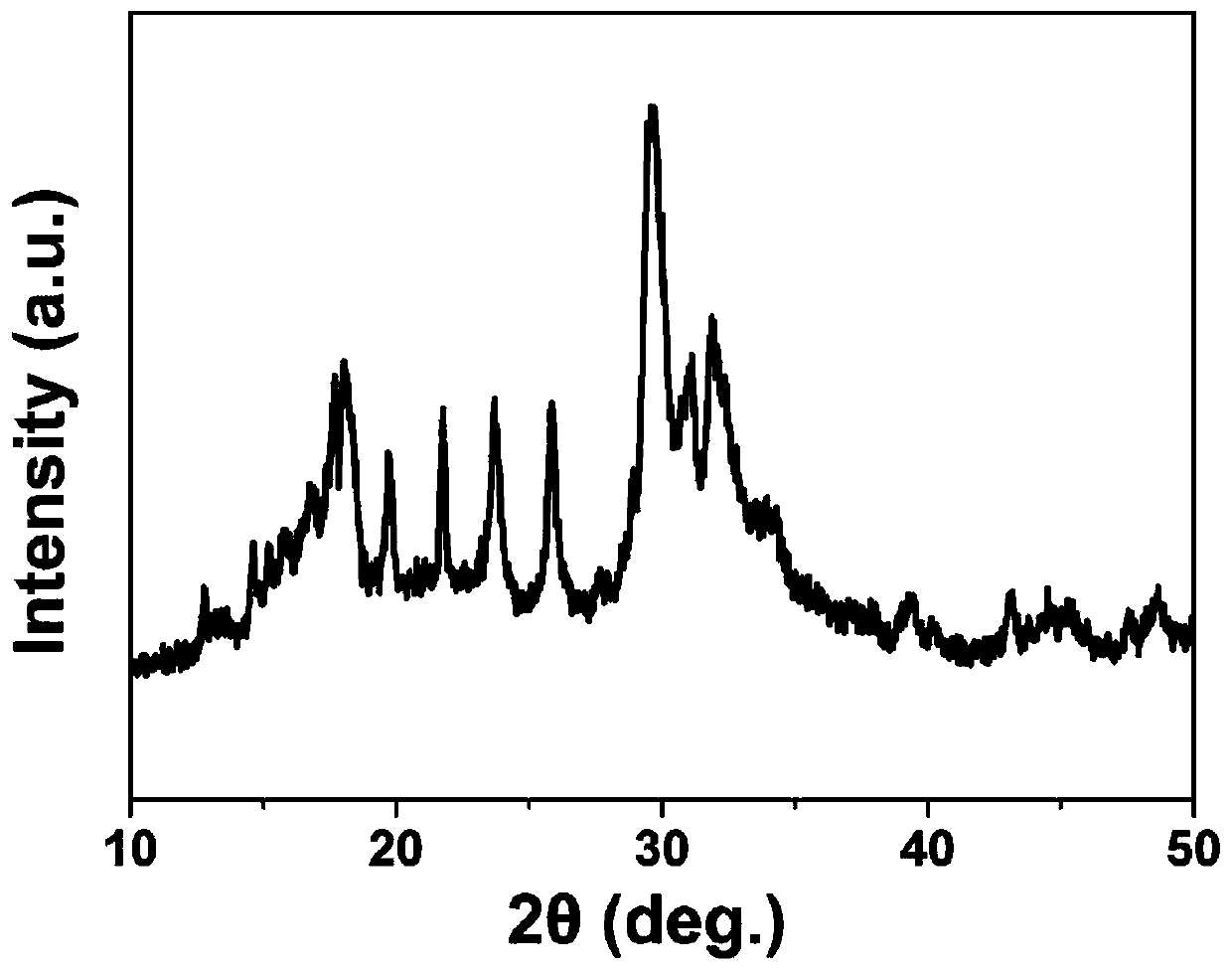
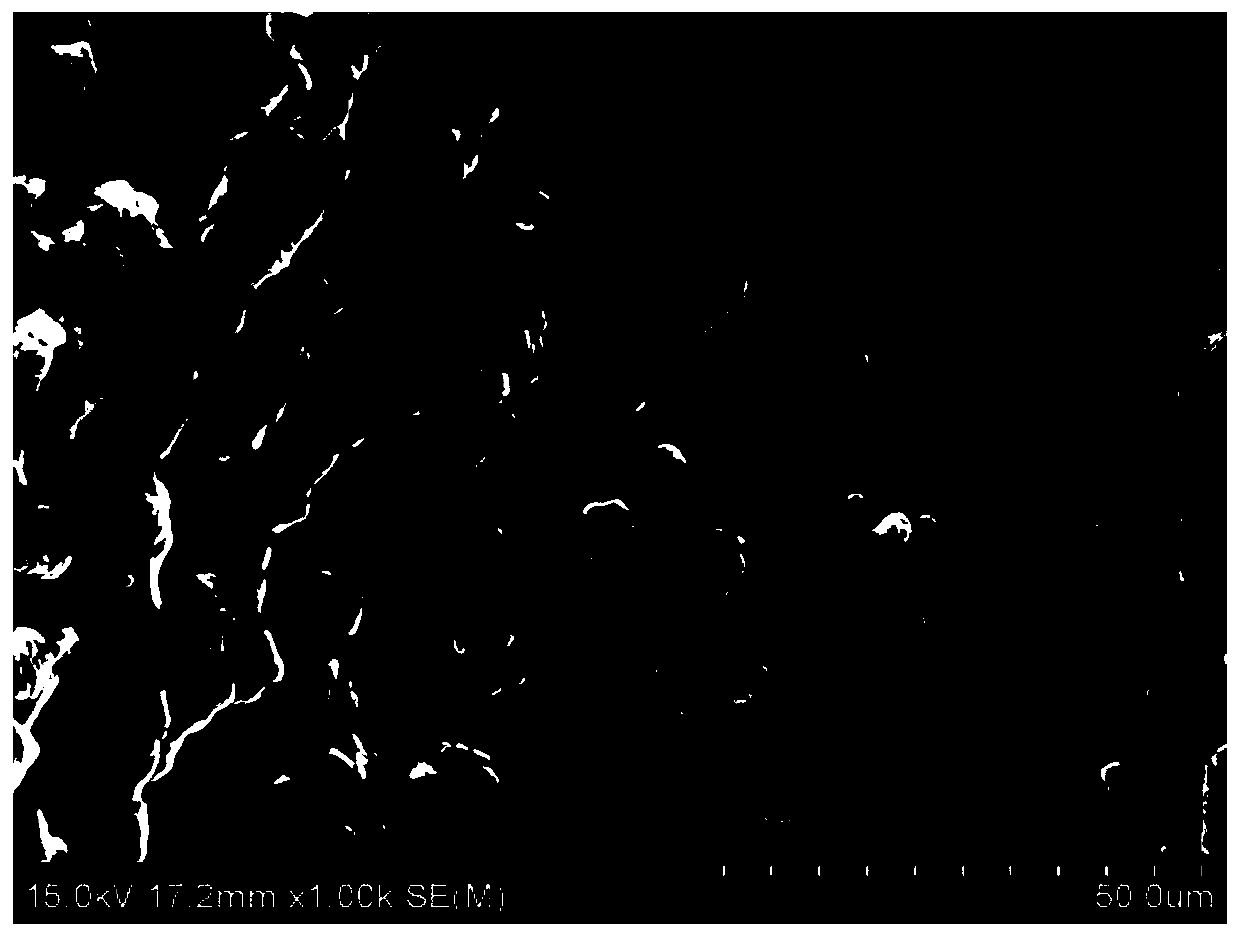
[0056] The scanning electron microscope image of the organic / inorganic composite solid electrolyte material prepared in Example 2, Figure 4 The XRD pattern of the organic / inorganic composite solid electrolyte material prepared for example 2. Depend on image 3 , Figure 4 It can be seen that...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Lithium sulfide, phosphorus pentasulfide, and aluminum sulfide were ball milled in a ball mill for 16 hours at a ratio of 6:2:1 (molar ratio), and heat-treated at 400°C for 10 hours to obtain a sulfur-based solid electrolyte. PEO polymer and LiTFSI were mixed at a molar ratio of 5:1 , adding sulfide powder and polymer / lithium salt into tetrahydrofuran at a mass ratio of 150:1, stirring magnetically at room temperature for 36 hours, removing the organic solvent by suction filtration, and drying at 120°C to obtain an organic / inorganic composite solid electrolyte. The coating layer of organic polymer has a thickness of 5-10 nm and an ionic conductivity of ~10 at room temperature -5 S / cm.
[0059] The organic / inorganic composite solid-state electrolyte prepared in Example 1 was used to assemble an all-solid-state lithium-ion battery, and the elemental sulfur was used as the positive electrode, and metal lithium sheets were used to assemble an all-solid-state lithium-sulfur ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com