Method for recovering gallium and indium elements from waste residue containing gallium and indium elements
A technology of elements and waste residues, applied in the field of separation and purification, can solve the problems of inapplicability to large-scale production, high energy consumption, and high post-processing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
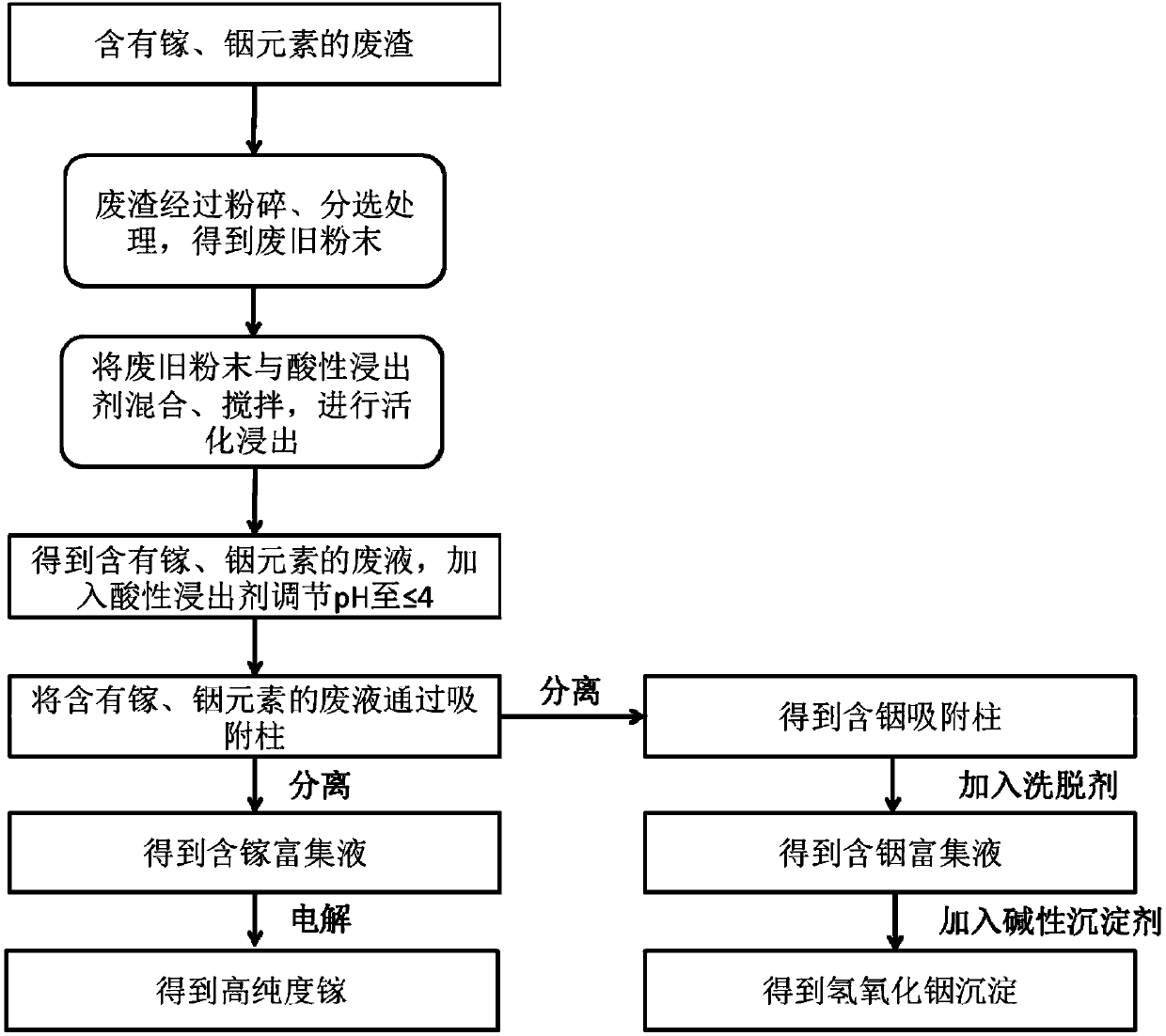
[0052] Such as figure 1 Shown, reclaim gallium, indium element from the waste slag containing gallium, indium element by following steps:
[0053] Step (1), take 1 kg of waste LED lamp beads as waste slag containing gallium and indium elements, which contains 1.01wt% gallium element and 0.23wt% indium element, and use a pulverizer to crush the waste slag into powder, and pass the powder through The sieve diameter is sieved by a sieve of 50 μm, and the sieved product is soaked in water to remove the organic components floating on the water surface, and the waste powder is obtained through filtration, and the waste powder is mixed with 17.5wt% hydrochloric acid and 30wt% hydrochloric acid at a concentration of 20g / L Mix the acidic leaching agent obtained by mixing the acetic acid at a volume ratio of 1:1, and use a mixer to stir the mixture at a speed of 300 rpm for 20 minutes to make it evenly mixed. Without turning off the mixer, the mixture is introduced into the ball mill. ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The only difference from Example 1 is that the rotating speed of ball milling in step (1) is 150 rev / min, and the time of ball milling is 50min.
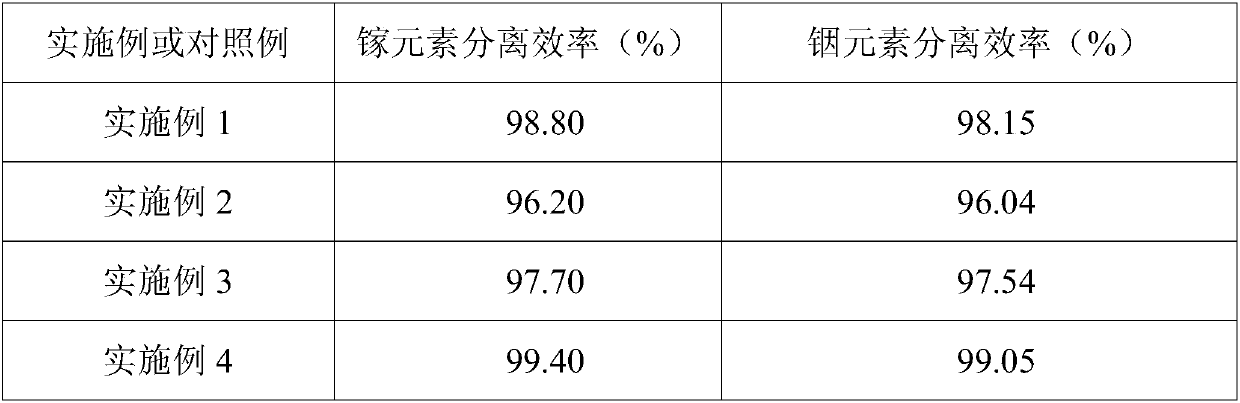
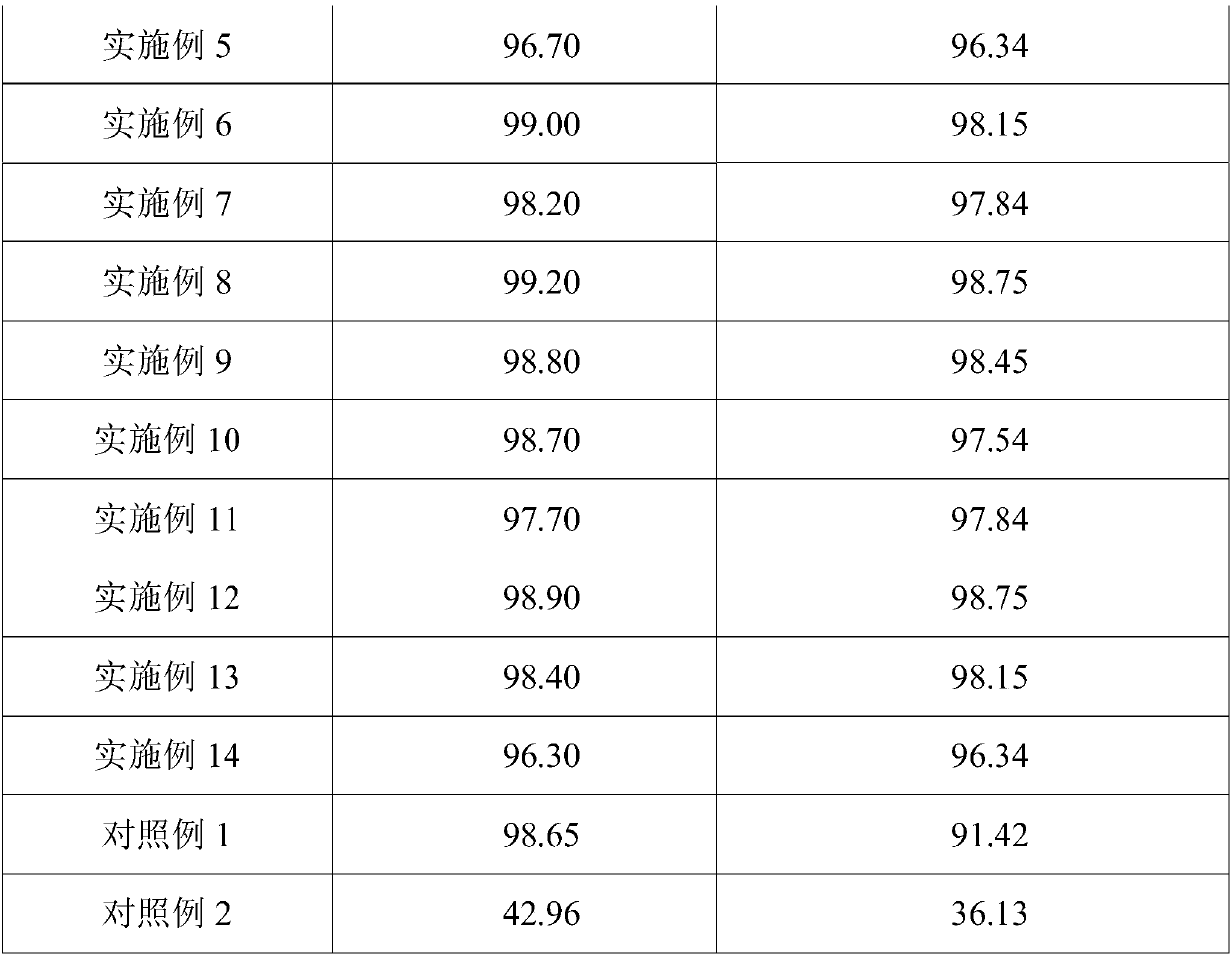
[0057] Example 2 obtained 9.63g of solid gallium with a purity of 99.9%, and 3.19g of indium hydroxide product.
Embodiment 3
[0059] The only difference from Example 1 is that the activated leaching treatment in step (1) is to treat the mixture sonicated for 100 minutes with an ultrasonic generator with a power of 200 W, and to irradiate the mixture with ultraviolet rays with a wavelength of 255 nm for 30 minutes during the sonicated treatment.
[0060] Example 3 obtained 9.78g of solid gallium with a purity of 99.9%, and 3.24g of indium hydroxide product.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| separation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com