A potent bifunctional protein for regulation of blood glucose and lipids
A bifunctional protein, application technology, applied in glucagon, peptide/protein components, animal/human proteins, etc., can solve problems such as structural instability and short in vivo half-life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0123] Example 1, construction of synergistic bifunctional protein expression plasmid
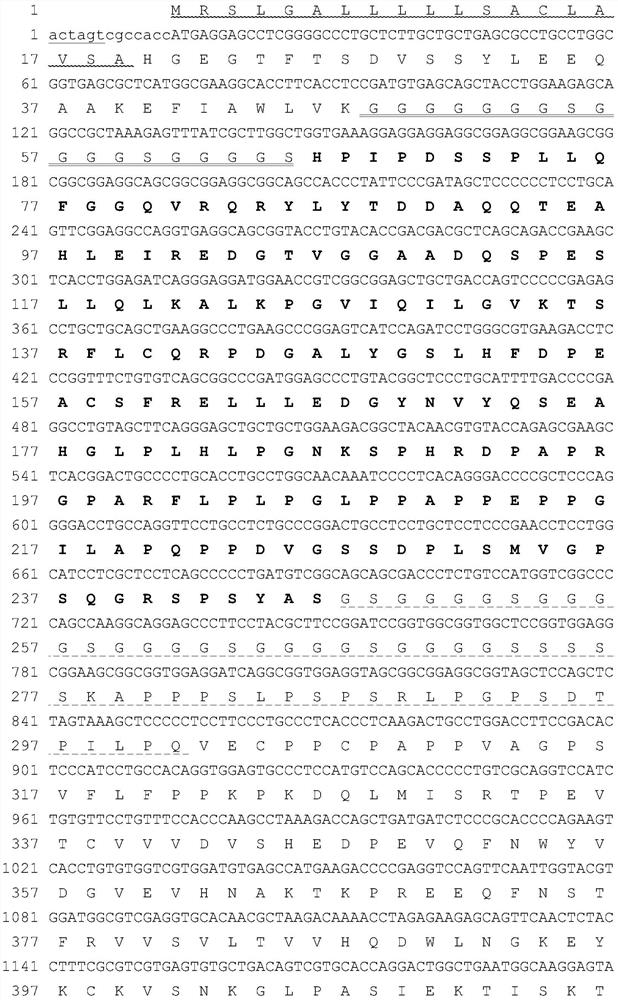
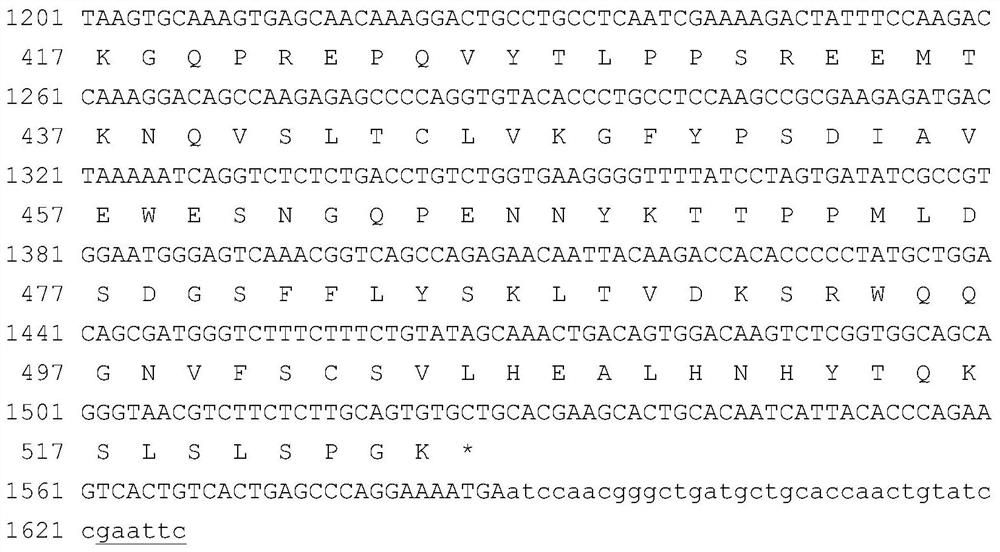
[0124] Gene sequences encoding α1 microglobulin leader peptide, GLP-1 analog, L1, FGF21 mature protein, L2 (both flexible and rigid peptide units) and human IgG Fc variants are artificially optimized CHO cell-preferred codes The full-length sequence was obtained by chemical synthesis. In order to facilitate the insertion of the target fragment into the specific site of the expression vector, there is a restriction enzyme site at the 5' and 3' ends of the synthesized fragment, respectively SpeI and EcoRI. The verified synergistic bifunctional protein gene was digested with SpeI and EcoRI, and then inserted into the corresponding restriction site of the plasmid pXY1A1 transformed by pDNA3.1 to obtain the fusion gene expression plasmid ( figure 1 The nucleotide sequence and translated amino acid sequence of the potentiating bifunctional protein FP4I-2 are exemplarily listed). The plasmid co...
Embodiment 2
[0129] Example 2, expression of synergistic bifunctional protein in transfected cell lines
[0130] The recombinant expression vector plasmid is transfected into a mammalian host cell line to express a potent bifunctional protein. In order to stably express at a high level, the preferred host cell line is DHFR enzyme-deficient CHO-cells (see US Pat. No. 4,818,679). In this example, the host cell line is the CHO-derived cell line DXB11. A preferred method of transfection is electroporation, although other methods including calcium phosphate co-sedimentation, lipofection can also be used. In electroporation, use a Gene Pulser electroporator (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA) set to a 300V electric field and a 1500 μFd capacitance, in a 5×10 cell in a cuvette. 7 Add 50 μg of high-purity expression plasmid to each cell. Two days after transfection, the medium was changed to growth medium containing 0.6 mg / mL G418. Transfectants were screened for resistance to the selective dr...
Embodiment 3
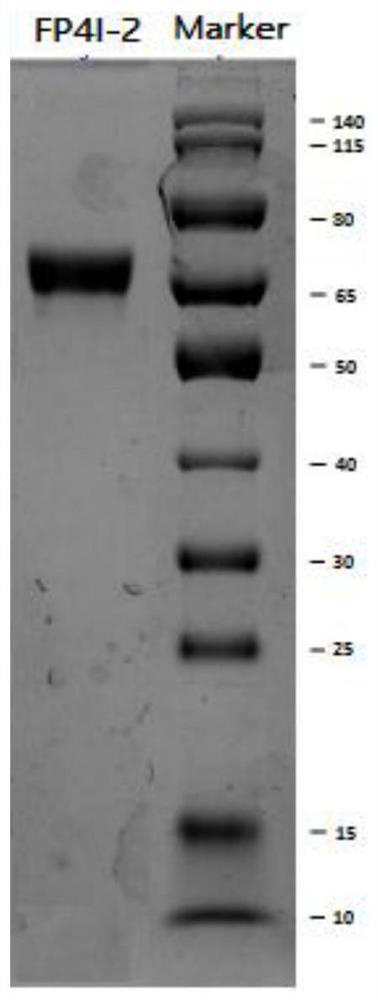
[0132] Example 3. Purification and characterization of synergistic bifunctional protein
[0133] The purification and characterization methods of FP4I-2 are exemplarily described in this example. The cell culture supernatant was clarified by high-speed low-temperature centrifugation and 0.22 μm sterile filtration, and then purified by three-step chromatography of protein A affinity, anion exchange and hydrophobicity. The specific method is as follows: the first step captures the protein A affinity layer Analysis, the balance solution is PBS buffer, the eluent is citrate buffer with pH 3.5, and the eluted target protein is then neutralized with 1M Tris solution. For intermediate purification, high-resolution anion exchange filler Q Sepharose HP (GE Company) was selected to remove residual impurity proteins. In binding mode, rinse with 20mM Tris-HCl, 0.2M NaCl, pH 7.5 solution and elute with 20mM Tris-HCl, 0.3M NaCl, pH 7.5 solution. In the purification step, Butyl Sepharose F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com