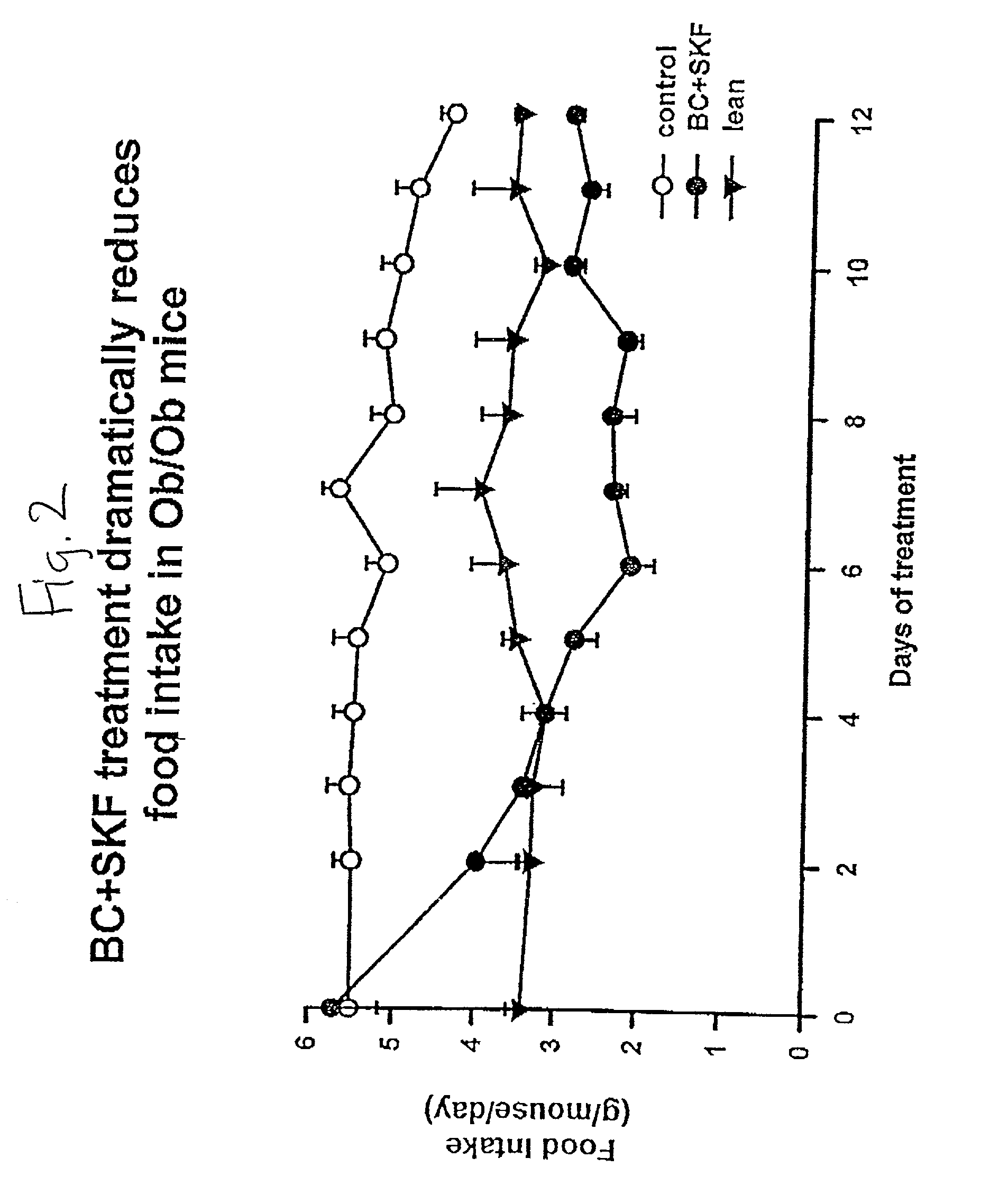
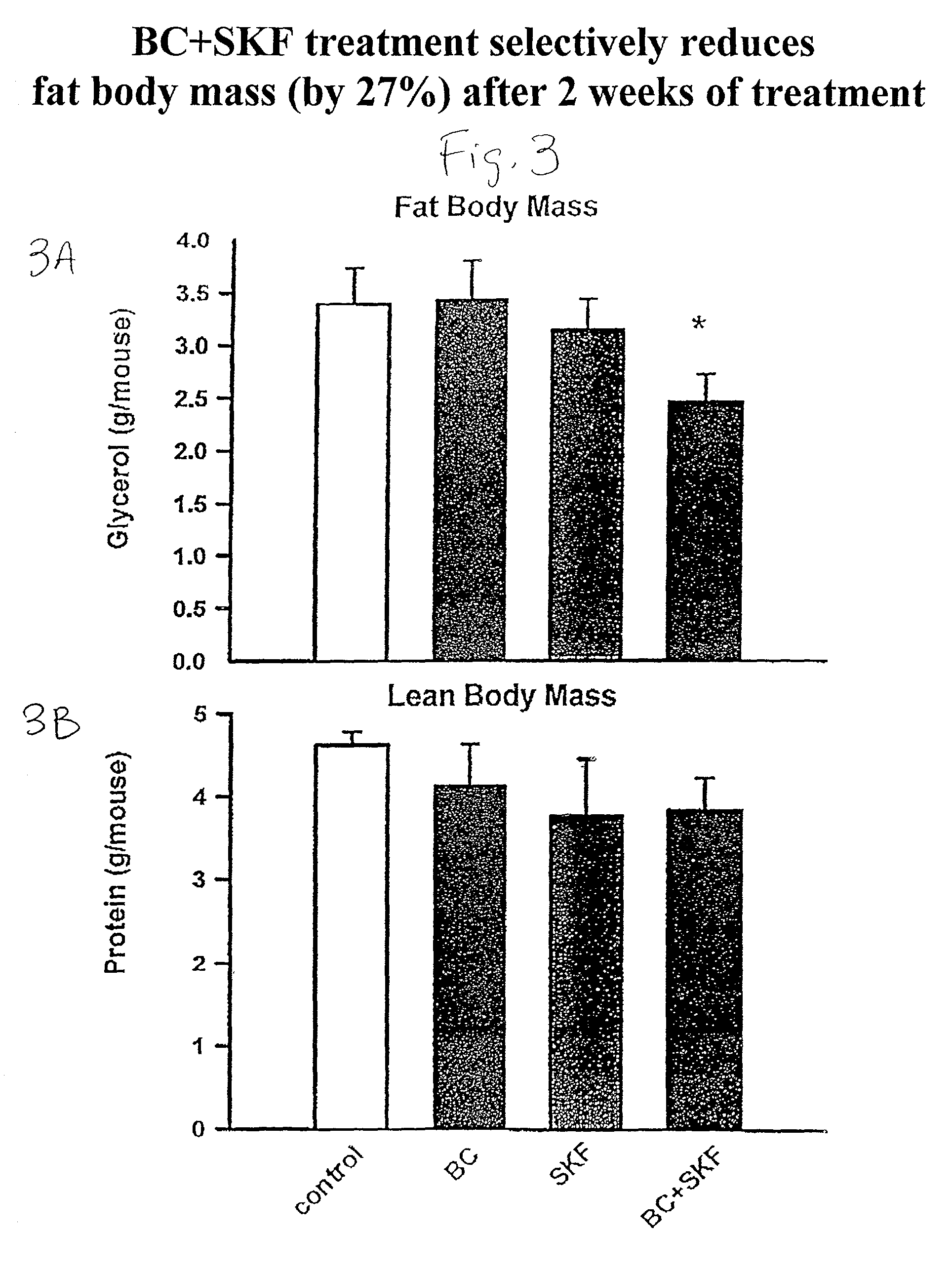
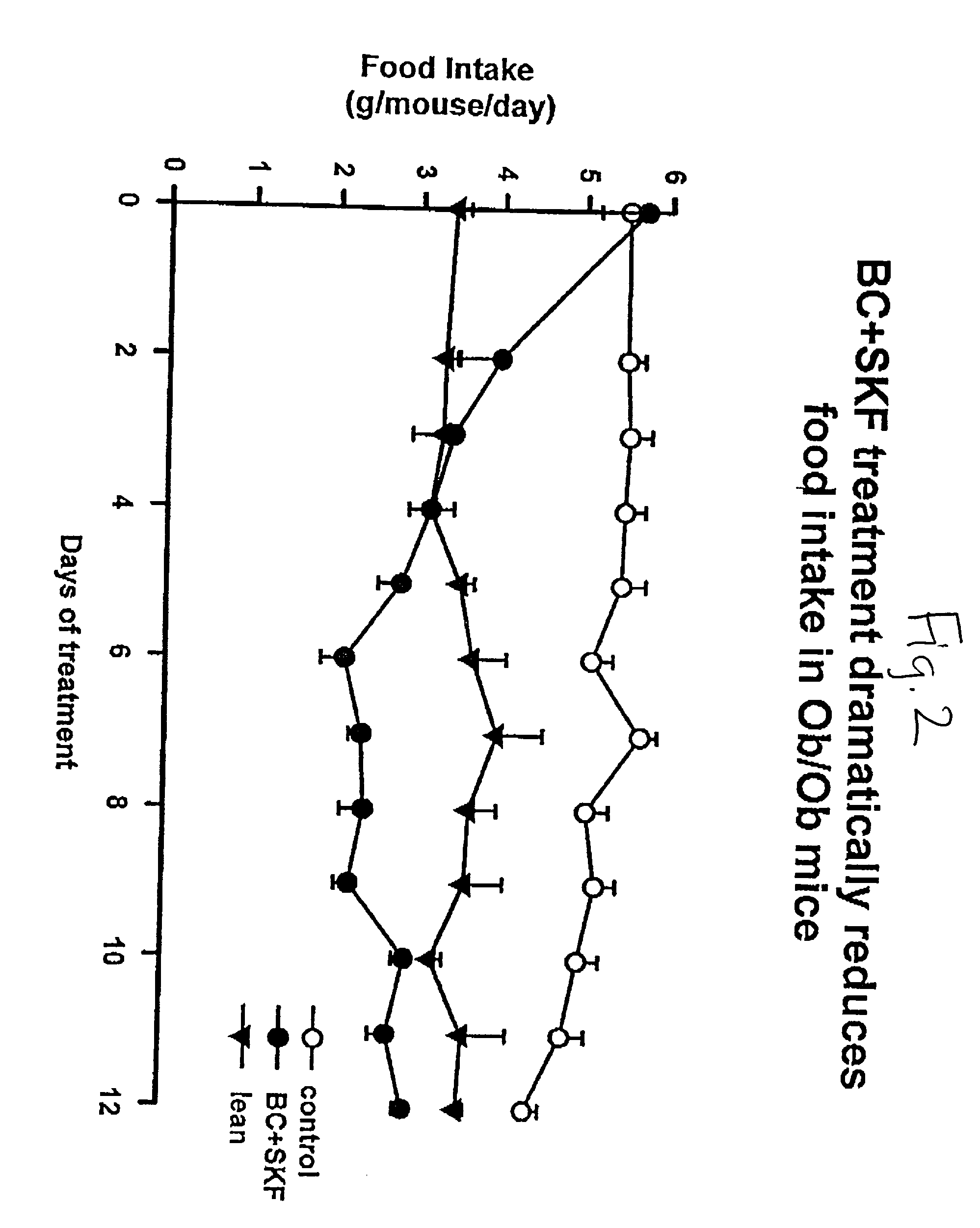
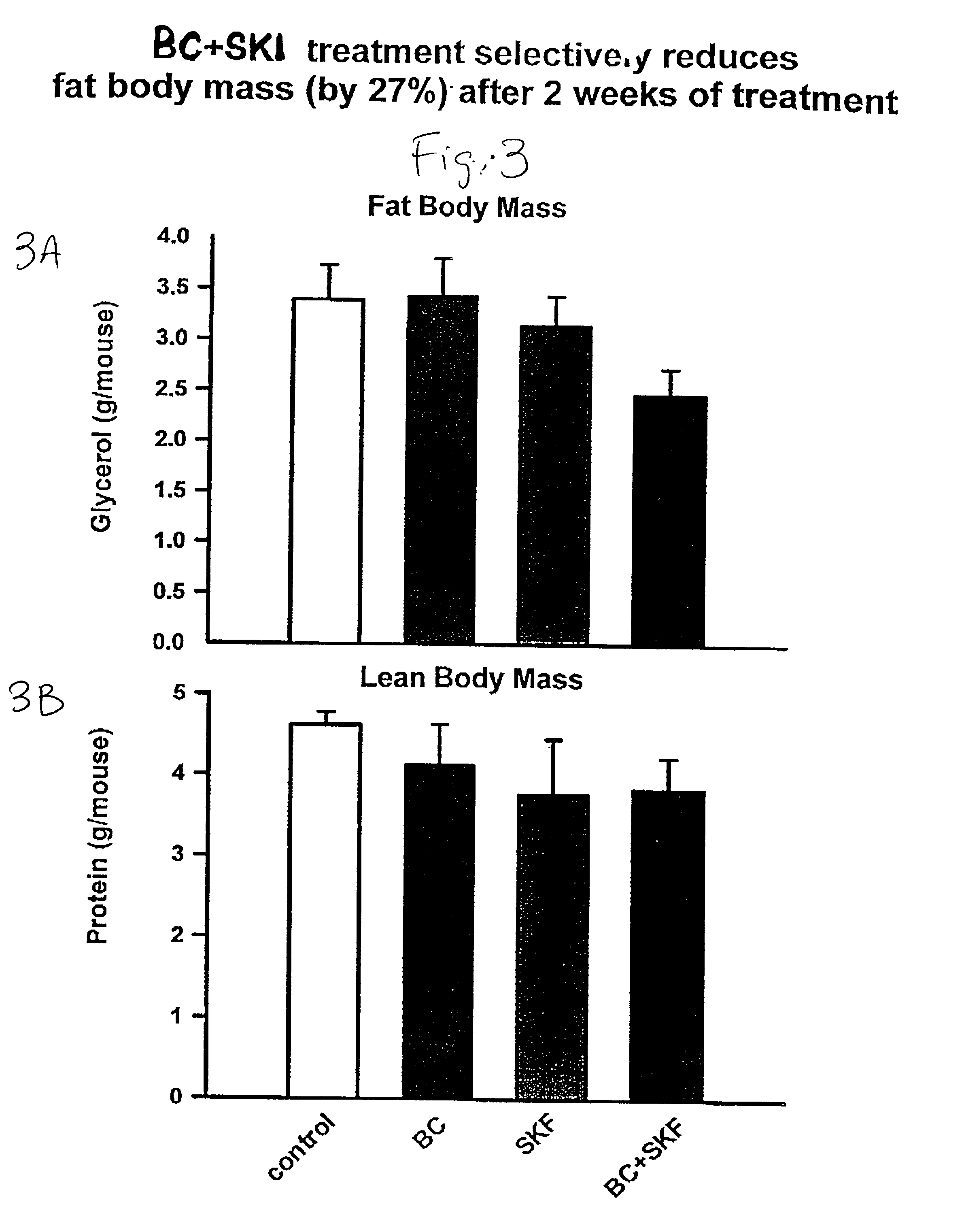
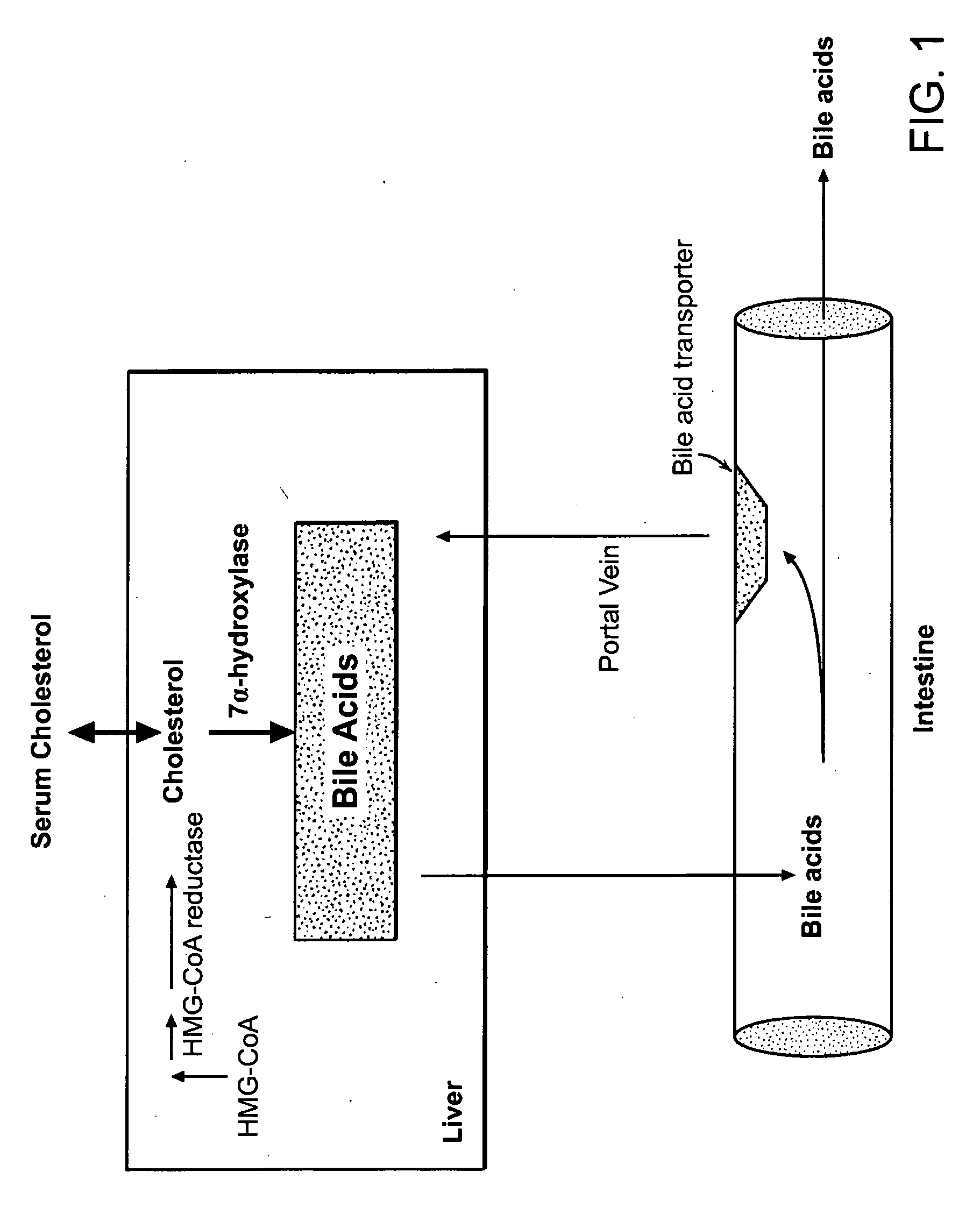
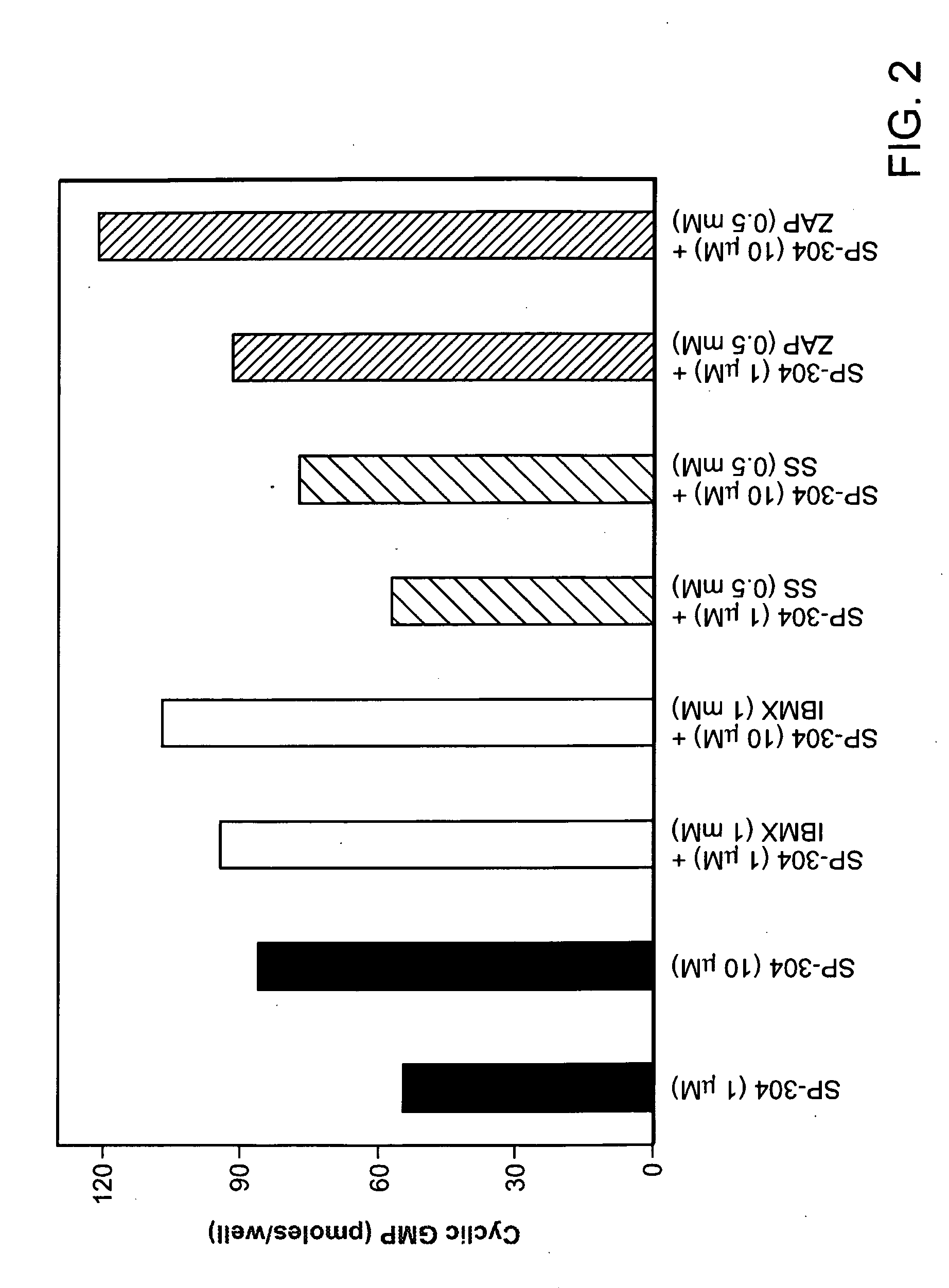
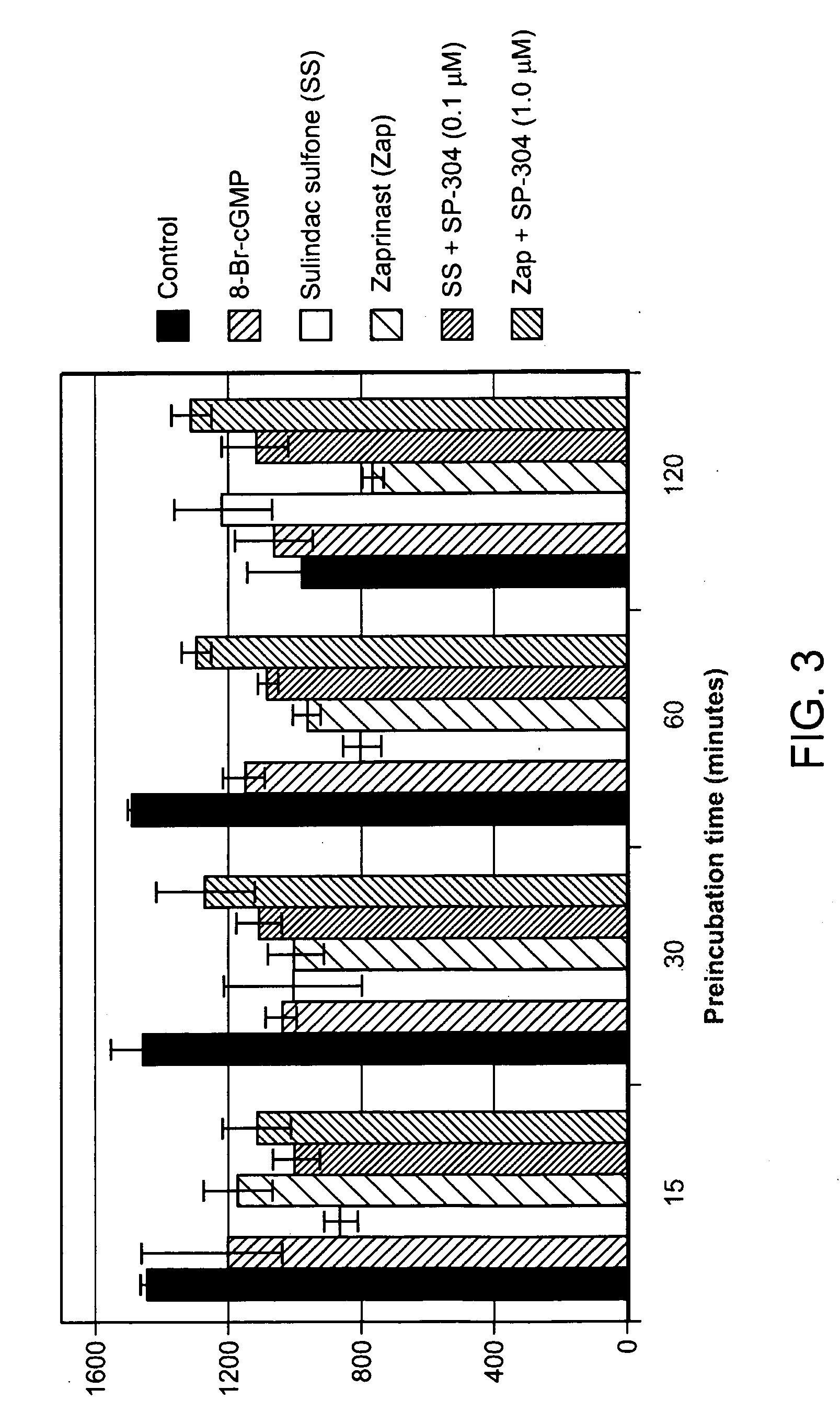
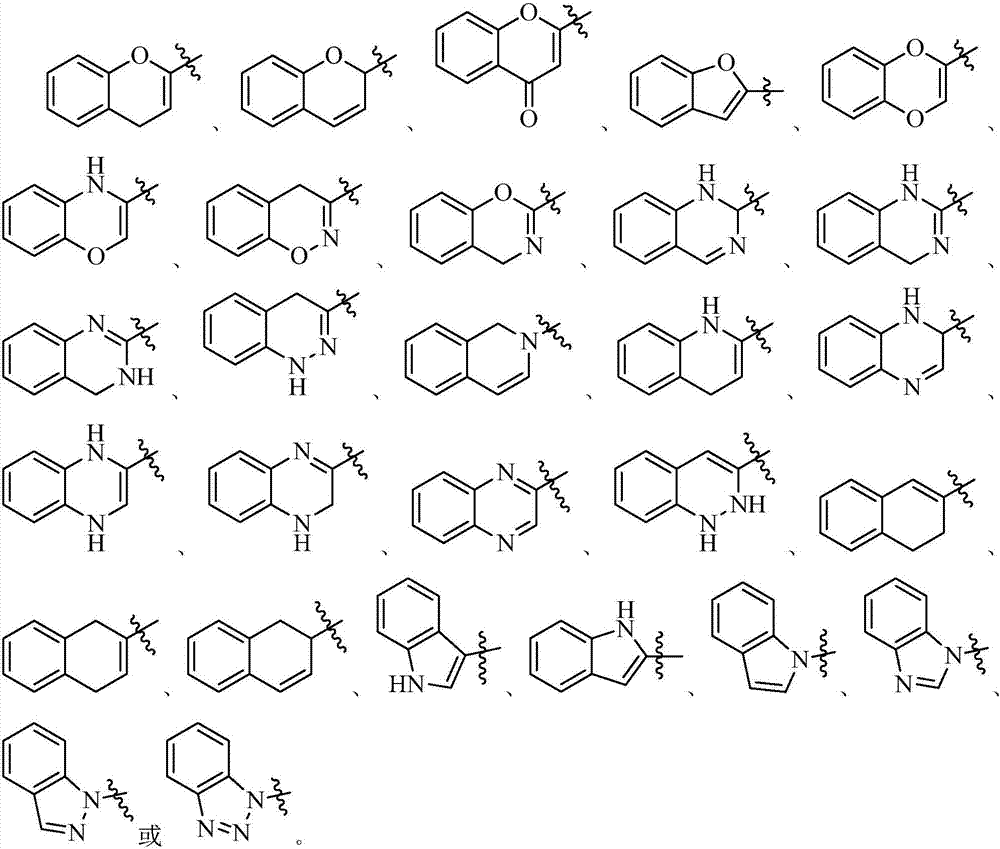
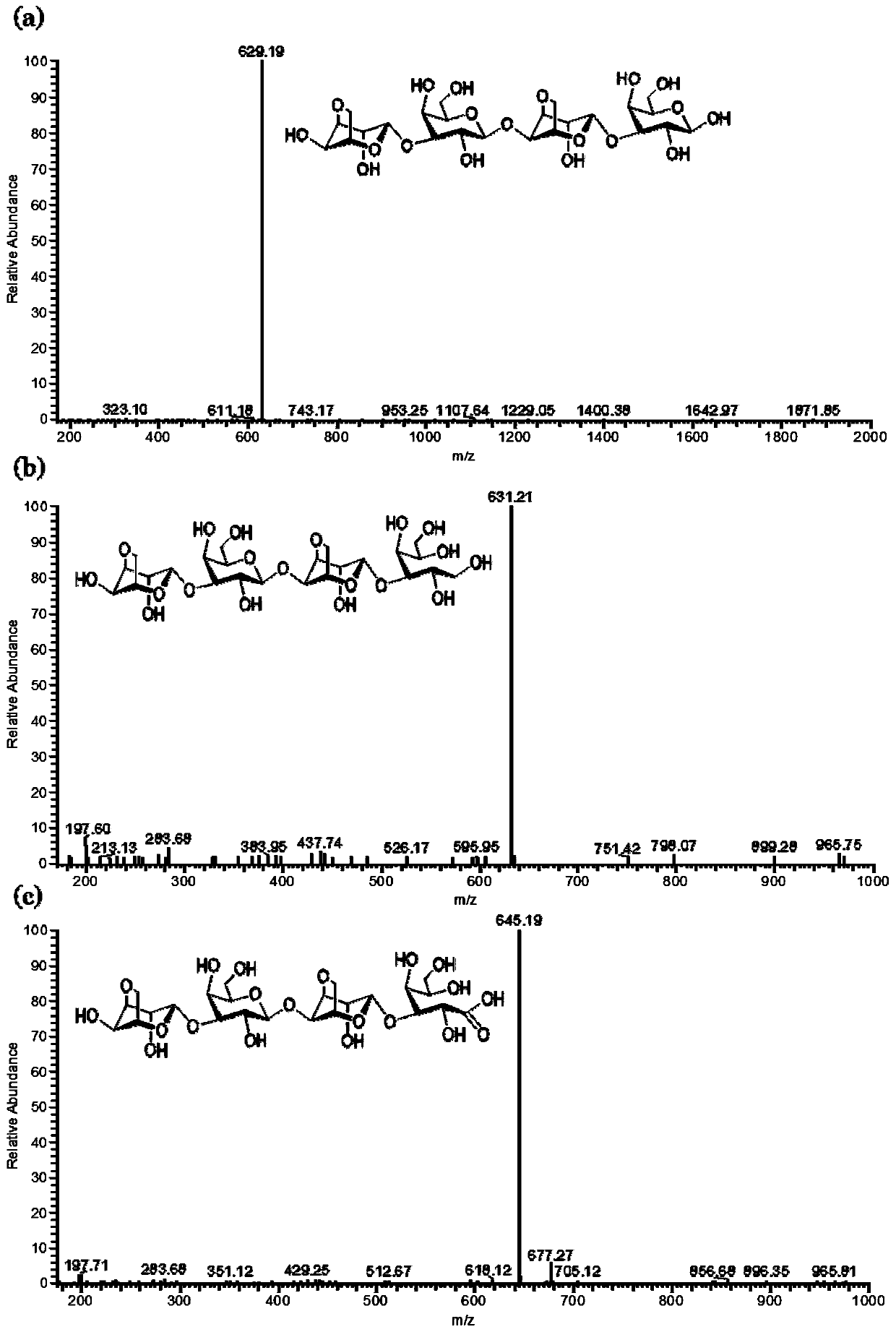
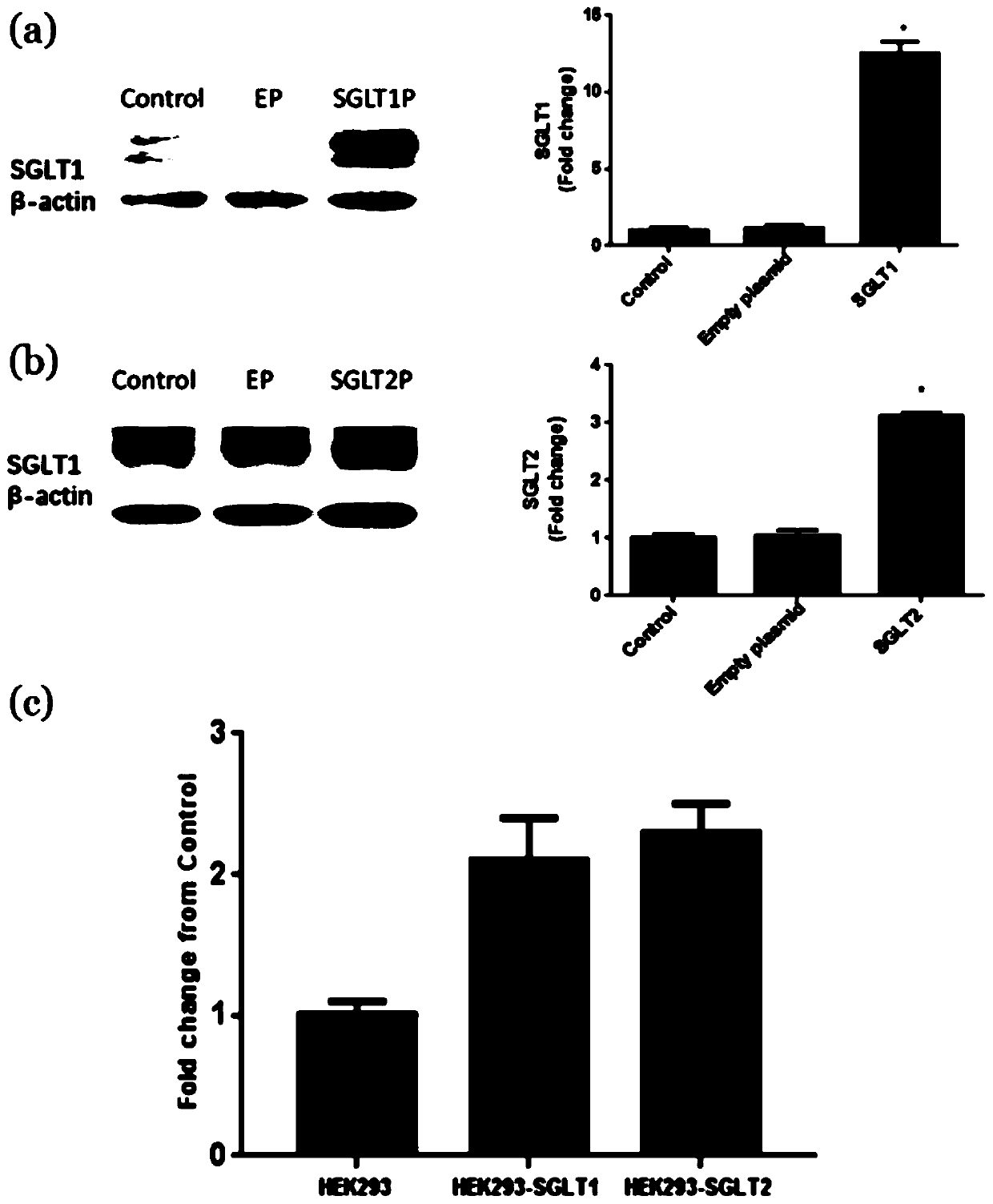
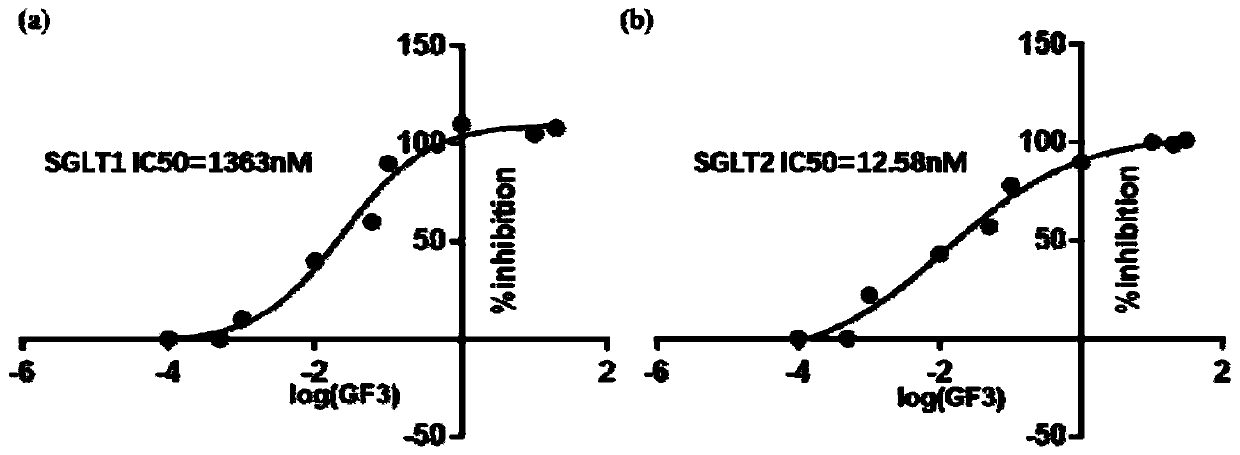
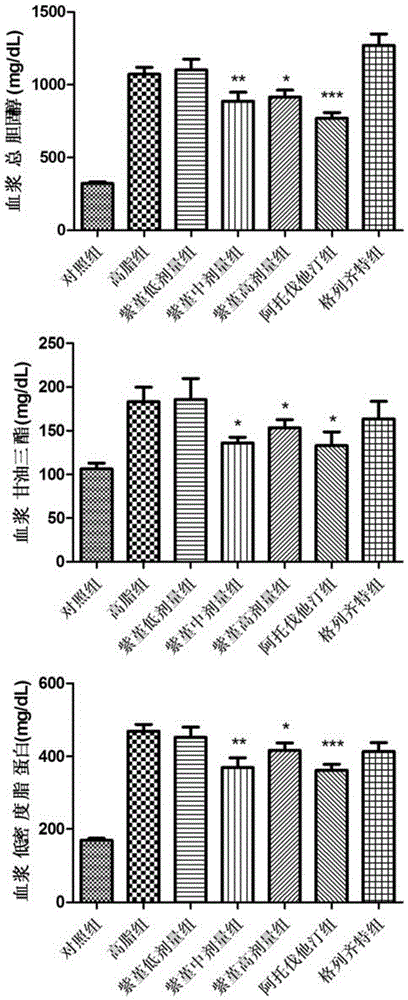
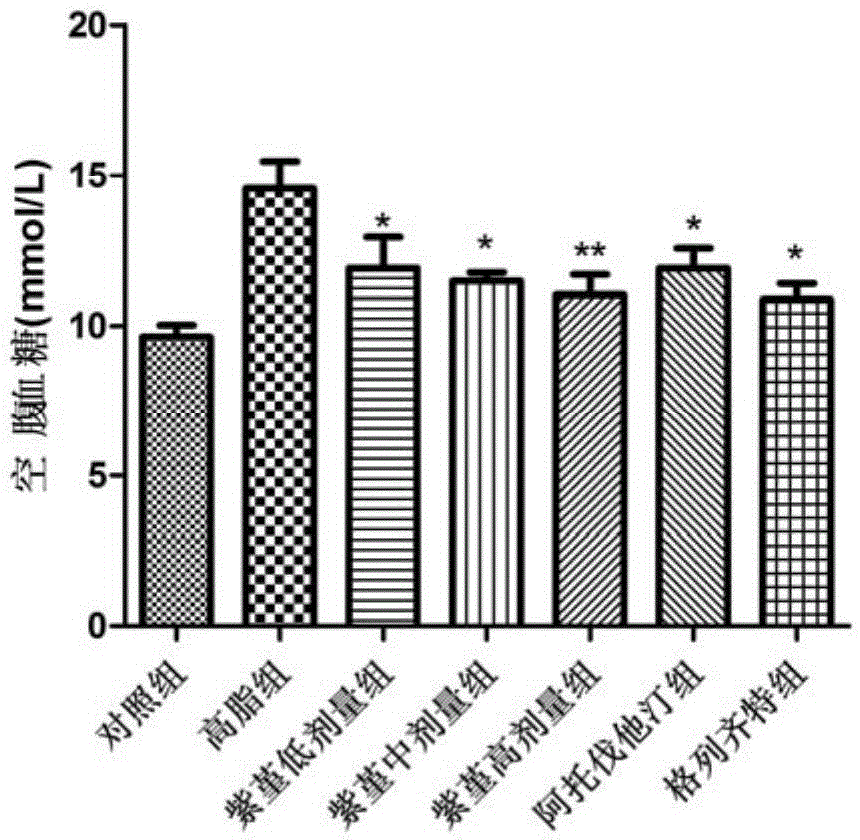
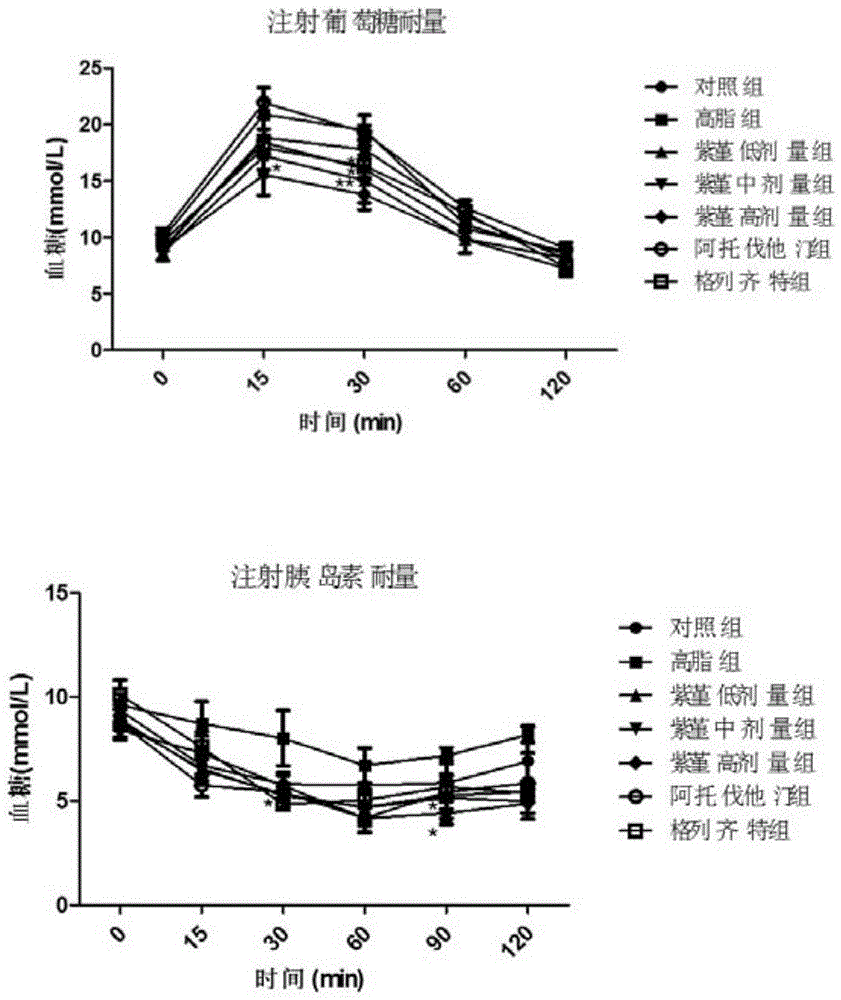
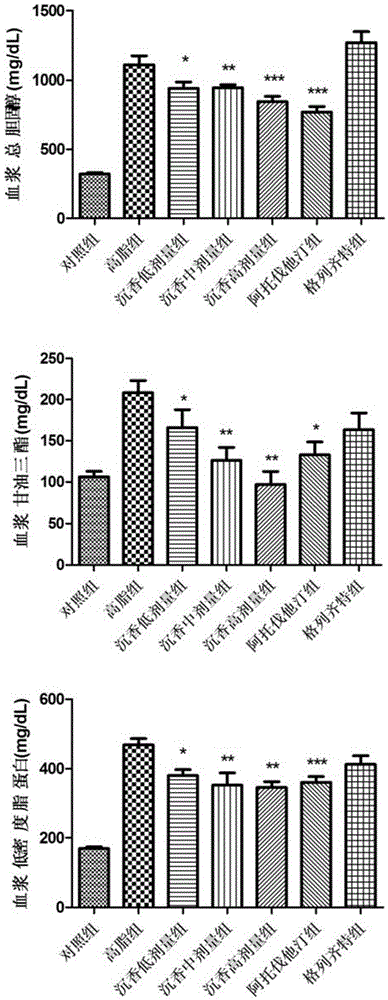
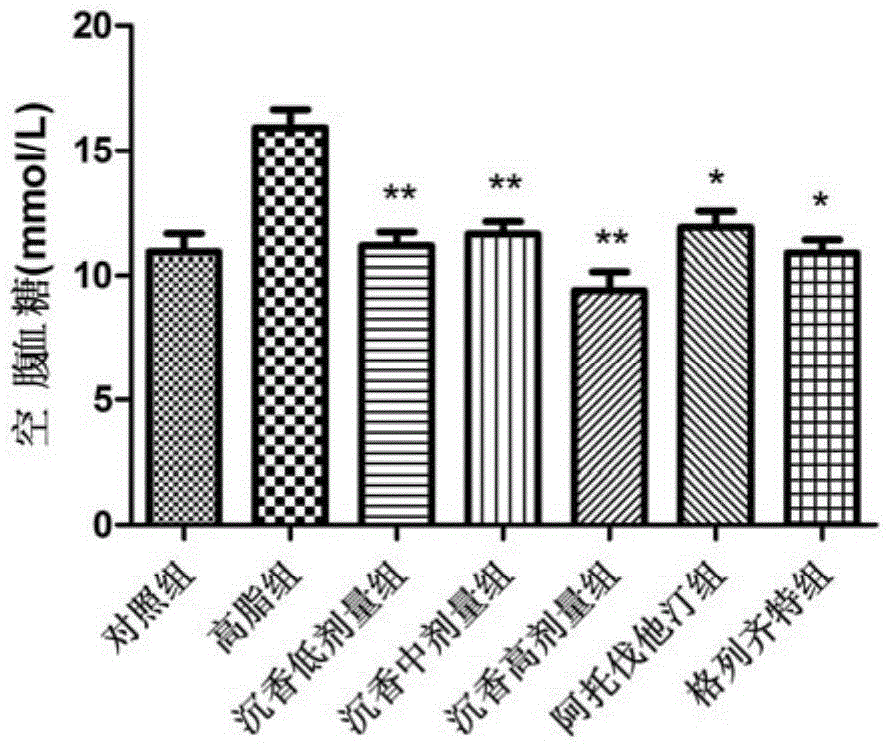
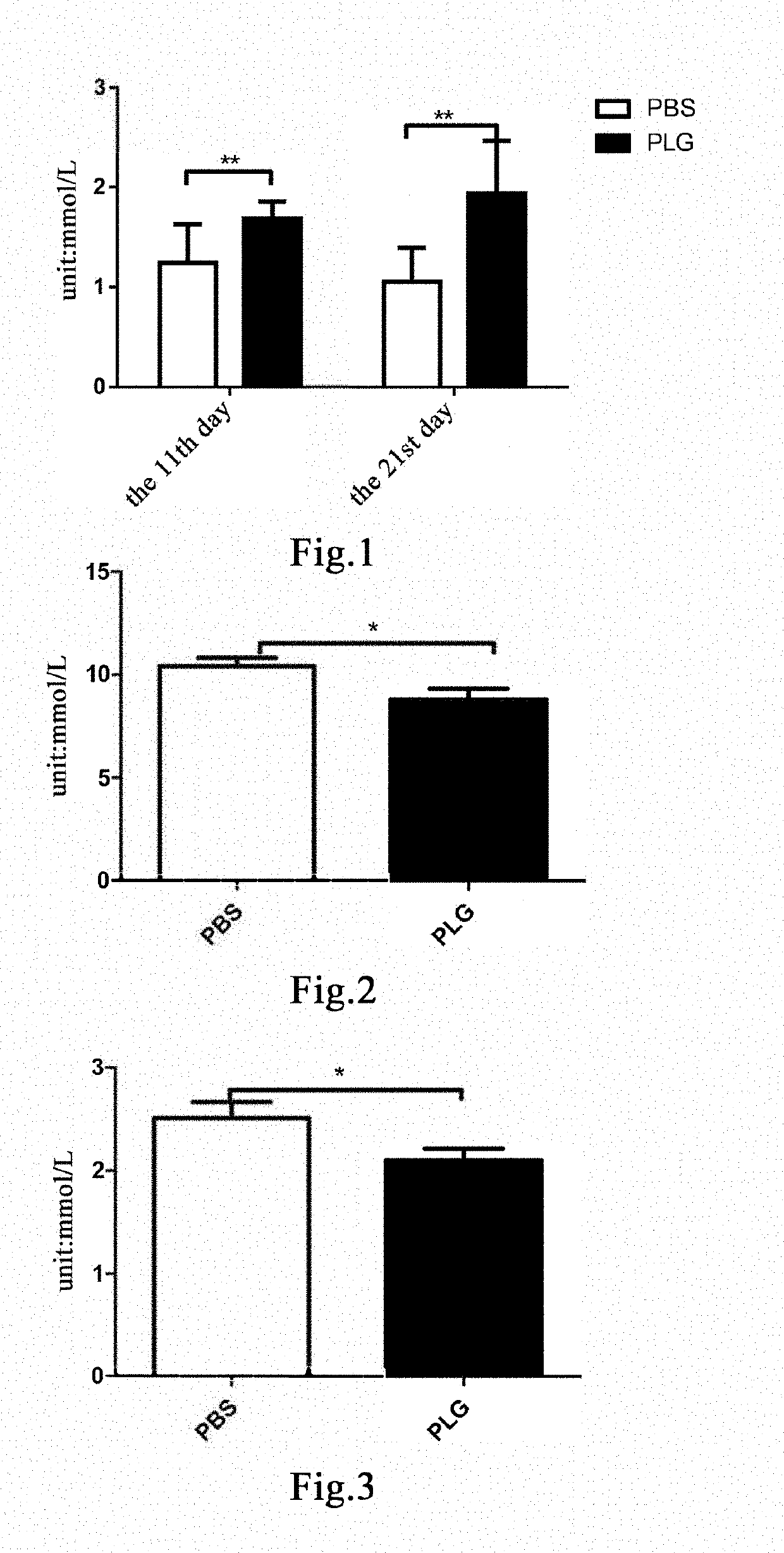
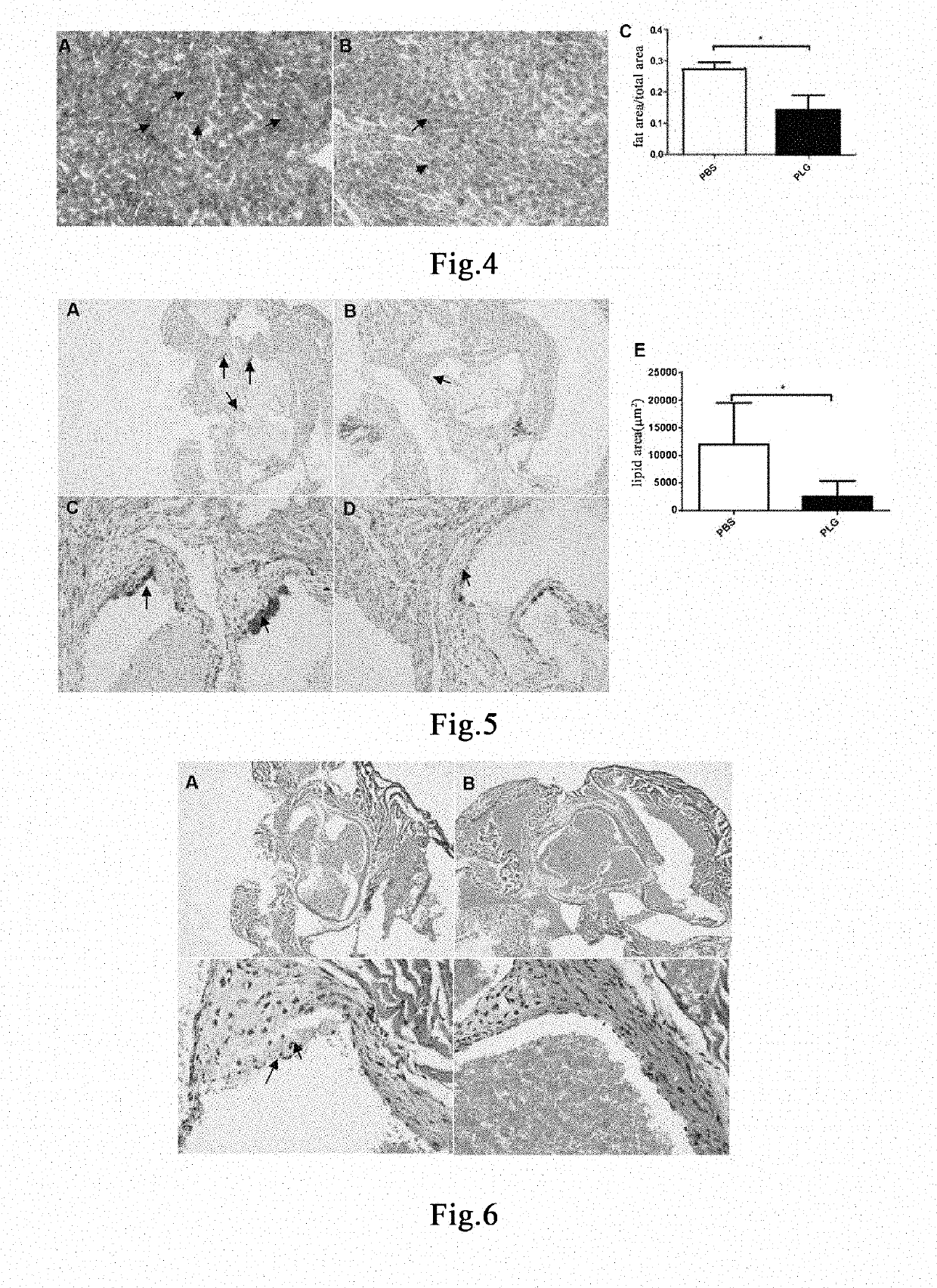
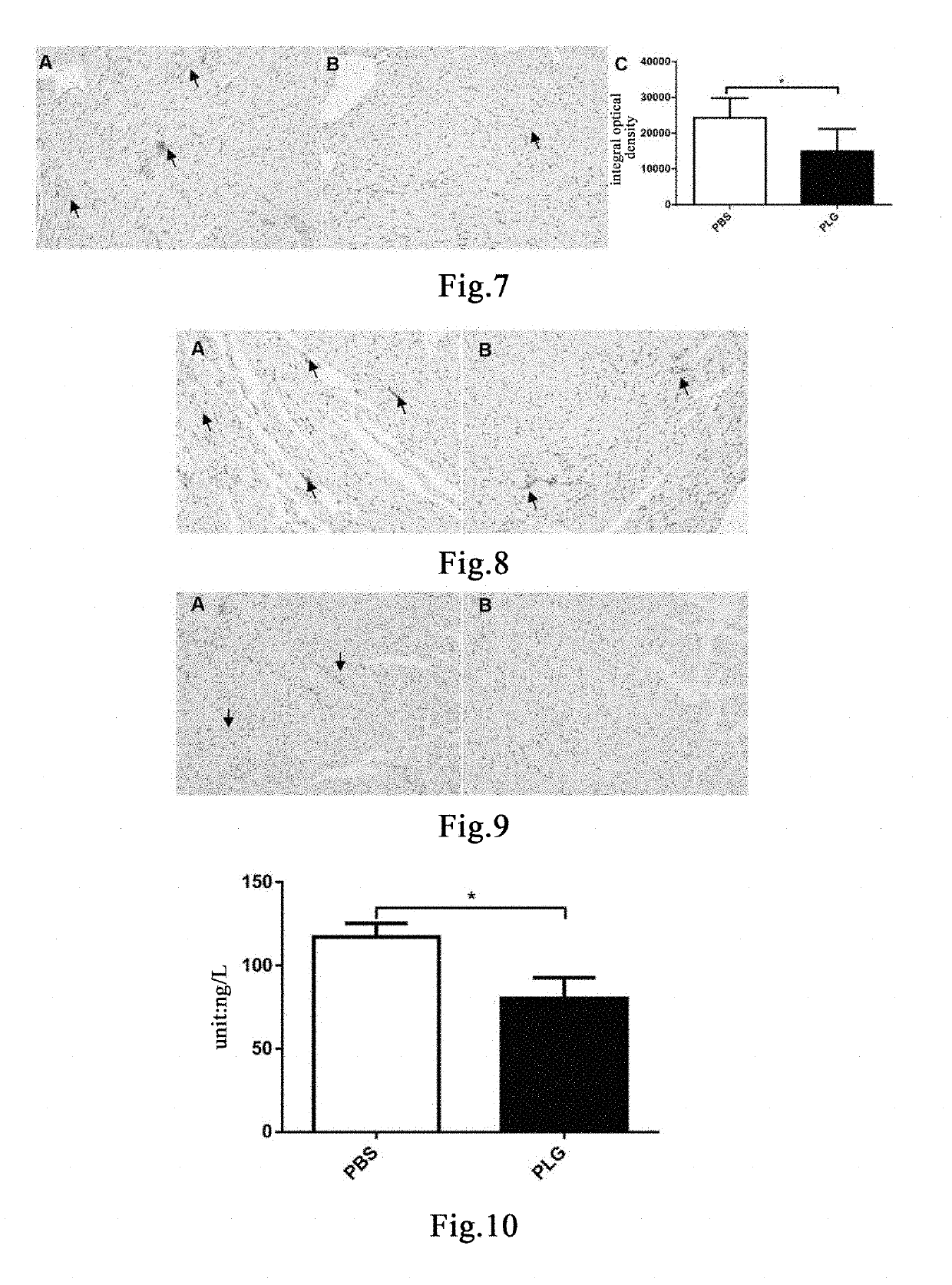
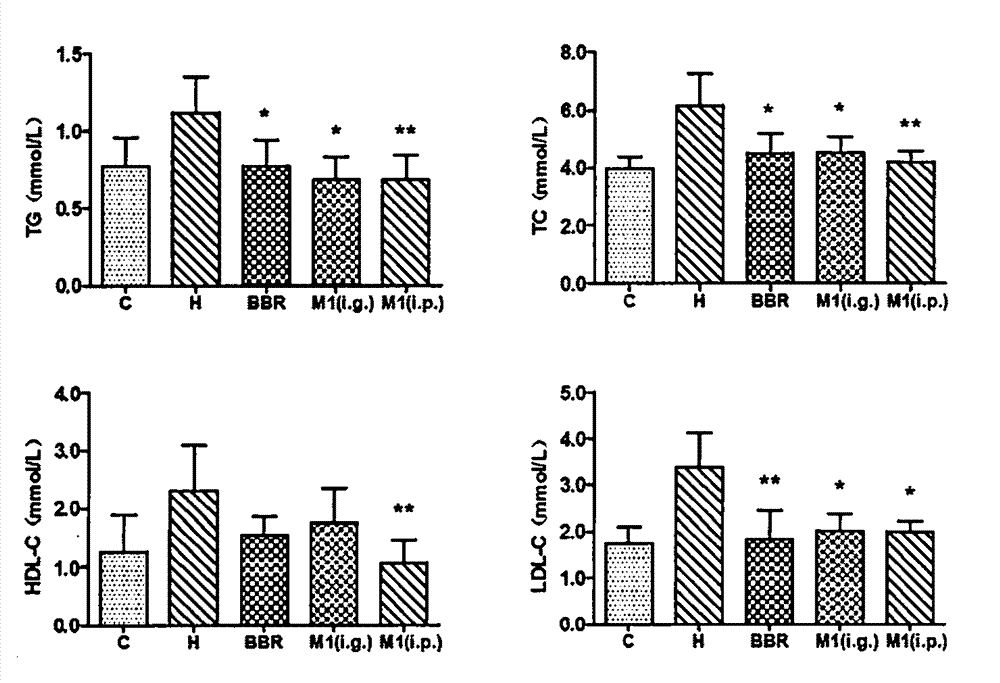
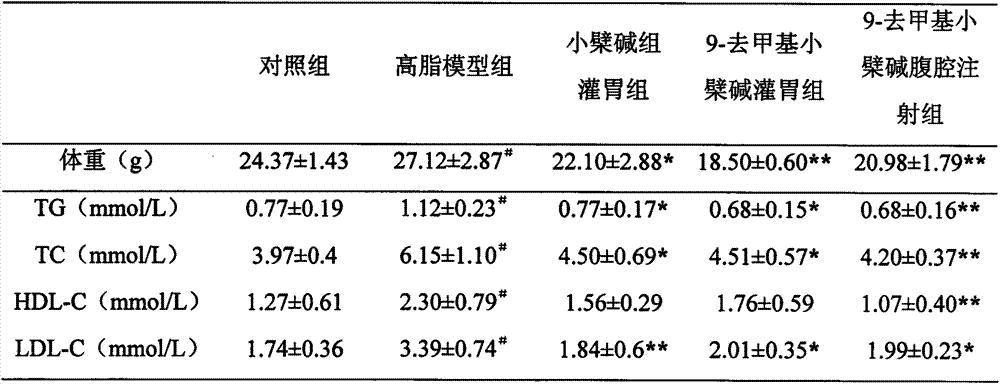
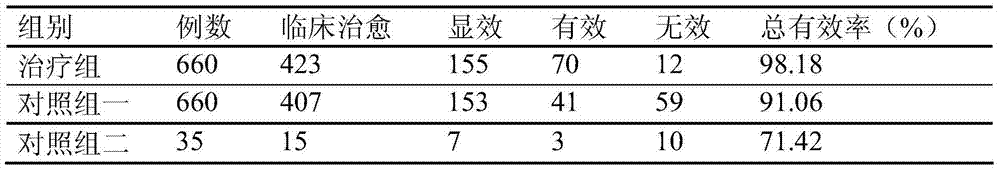
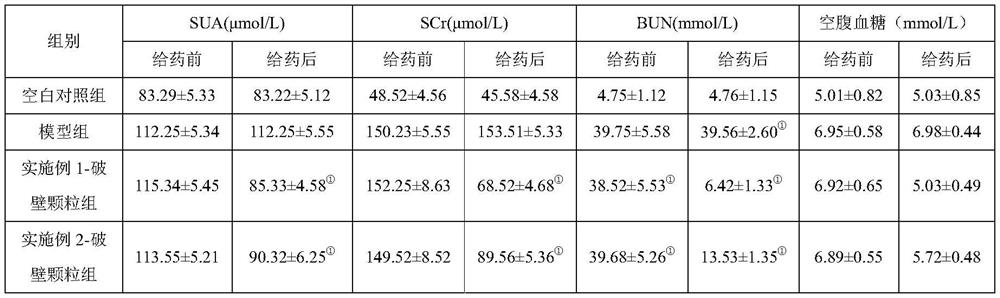
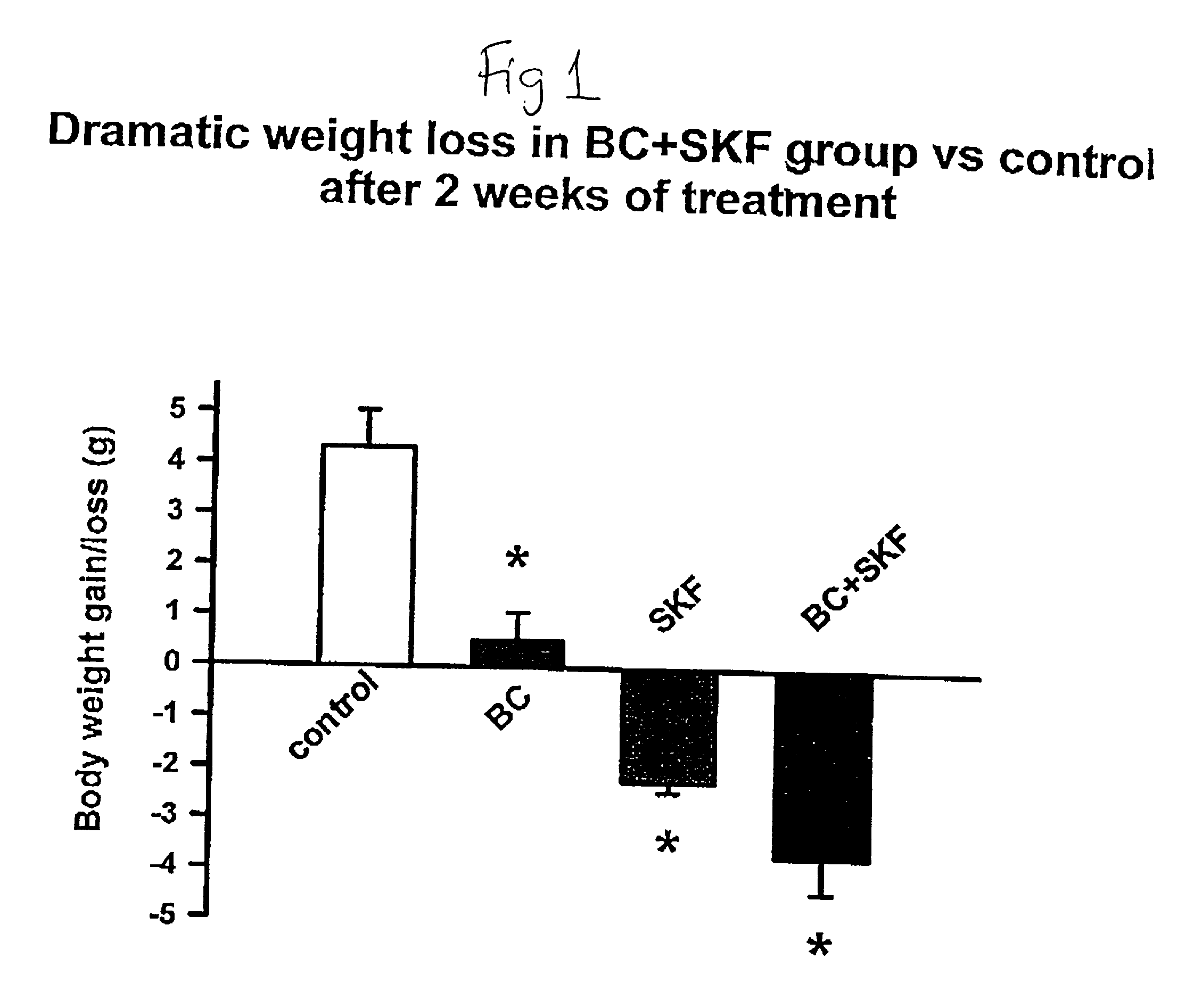Patents
Literature
264 results about "Lipid Metabolism Disorder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
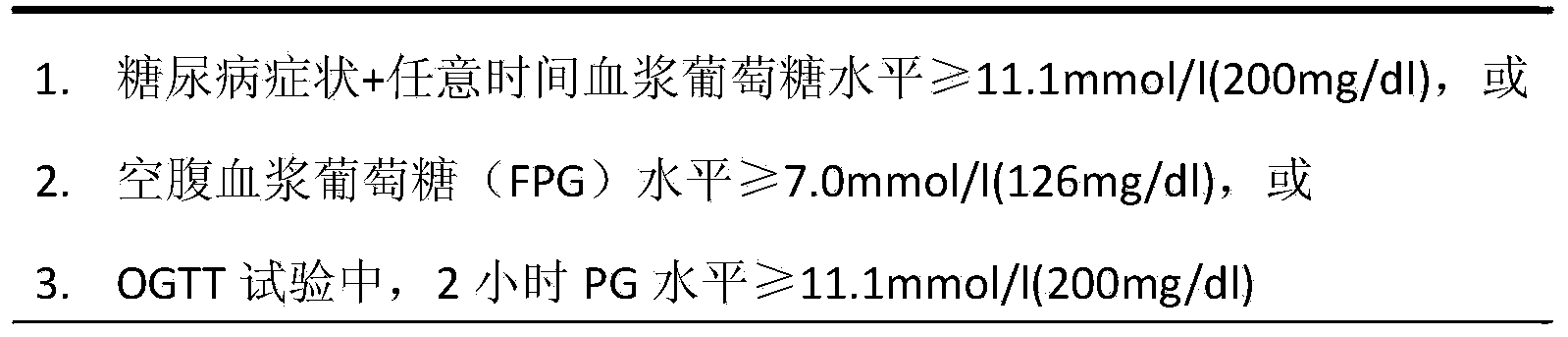
An inherited metabolic disorder caused by an enzyme deficiency, resulting in an inability to oxidize fatty acids for energy production.
Treating pain, diabetes, and disorders of lipid metabolism
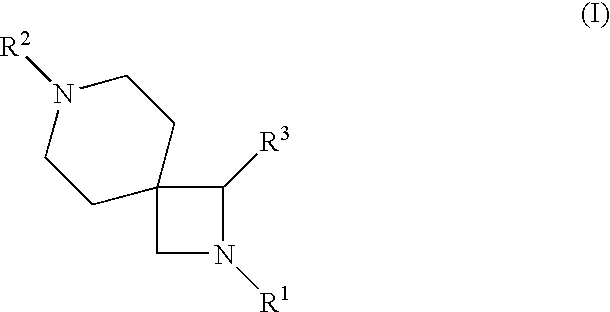
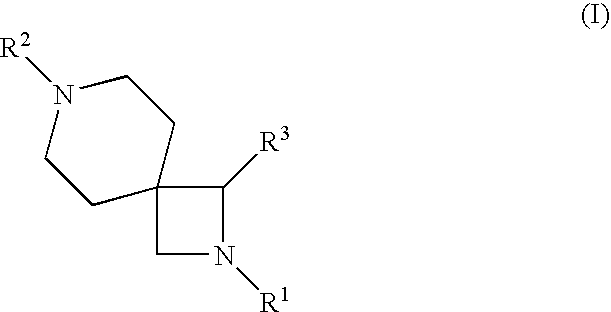
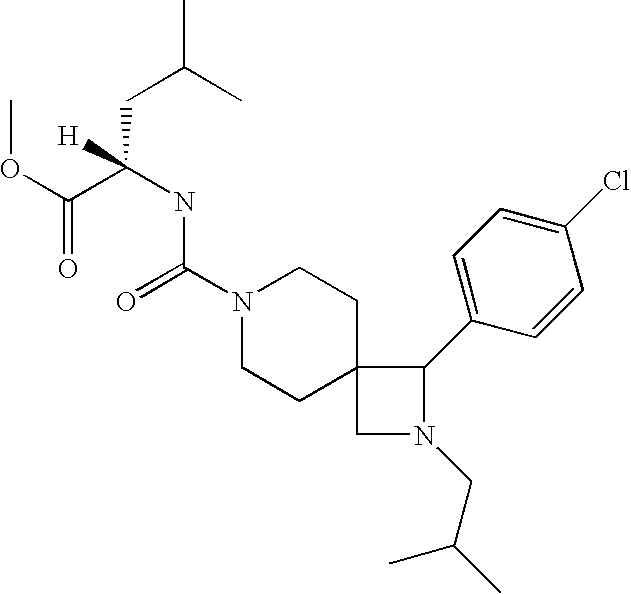
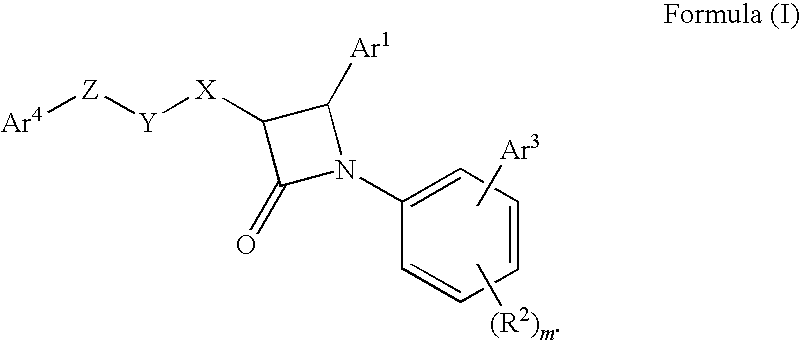
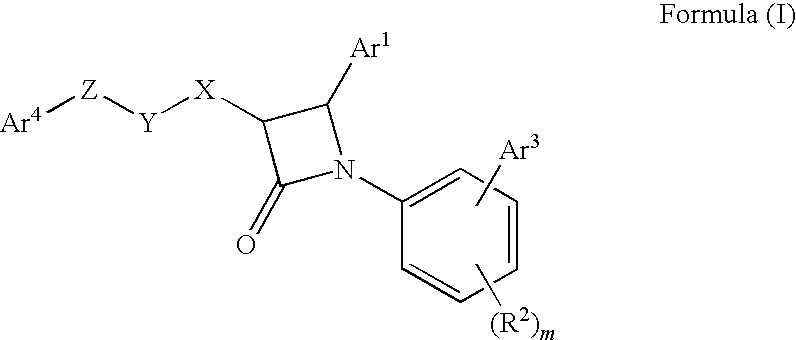
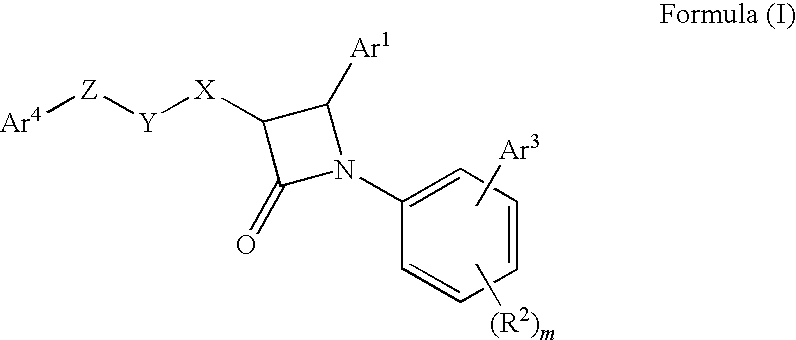
Disclosed is a method of treating a disease or condition (e.g., pain, diabetes or disorders of lipid metabolism) comprising administering an azetidine derivative of the formula I selected from the group consisting of the compounds defined by Tables 1, 2, 3a, 3b, 3c, 3d and 4a.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Agonists of guanylate cyclase useful for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, gallstone, obesity and other cardiovascular diseases
ActiveUS20100152118A1Widen the optionsOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderCyclaseCoronary artery disease
This invention also provides a method to prevent, control, and treata lipid metabolism disorder, a billary disorder, cardiovascular disease, obesity or an endocrine disorder by administering at least one agonist of guanalyte cyclase receptor either alone or in combination with a compound typically used to treat the disorder and or with an inhibitor of cGMP-dependent phosphodieasterases.
Owner:BAUSCH HEALTH IRELAND LTD
Method and composition for the treatment of lipid and glucose metabolism disorders
InactiveUS20020187985A1Improved modification and regulationImprovement of one or more metabolic indicesBiocideAnimal repellantsBlood plasmaPlasma insulin
Disclosed are methods for modifying or regulating at least one of glucose or lipid metabolism disorders which comprises administering to a human or vertebrate subject a D1 dopamine agonist in conjunction with a dopamine D2 agonist where the conjoined administration is effective to improve at least one of the following lipid and glucose metabolic indices: body weight, body fat, plasma insulin, plasma glucose and plasma lipid, and plasma lipoprotein. In preferred embodiments, the administration of the D1 dopamine agonist and the D2 dopamine agonist is conducted at a predetermined time.
Owner:VEROSCI
Method and composition for the treatment of lipid and glucose metabolism disorders
InactiveUS20010016582A1Improved modification and regulationImprovement of one or more metabolic indicesBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsBlood plasmaPlasma insulin
Disclosed are methods for modifying or regulating at least one of glucose or lipid metabolism disorders which comprises administering to a human or vertebrate subject a D1 dopamine agonist in conjunction with a dopamine D2 agonist where the conjoined administration is effective to improve at least one of the following lipid and glucose metabolic indices: body weight, body fat, plasma insulin, plasma glucose and plasma lipid, and plasma lipoprotein. In preferred embodiments, the administration of the D1 dopamine agonist and the D2 dopamine agonist is conducted at a predetermined time.
Owner:CINCOTTA ANTHONY H
Agonists of Guanylate Cyclase Useful for the Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia, Atherosclerosis, Coronary Heart Disease, Gallstone, Obesity and Other Cardiovascular Diseases
This invention also provides a method to prevent, control, and treata lipid metabolism disorder, a biliary disorder, cardiovascular disease, obesity or an endocrine disorder by administering at least one agonist of guanalyte cyclase receptor either alone or in combination with a compound typically used to treat the disorder and or with an inhibitor of cGMP-dependent phosphodieasterases.
Owner:BAUSCH HEALTH IRELAND LTD
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating diabetes and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN103520586AIndications for hyperglycemiaIndications for high blood pressureAnthropod material medical ingredientsMetabolism disorderBlood sugarKidney
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine composition. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared form 46 kinds of raw material medicines of fructus corni, wolfberry, mulberry, radix polygoni multiflori preparata, black sesame, ligustrum lucidum, prepared rehmannia root, herba epimedii, black ants, eucommia and the like. The traditional Chinese medicine composition starts with liver nourishing and kidney tonifying, and focuses on effecting a permanent cure. The traditional Chinese medicine composition removes heat, cools blood, adjusts human body, corrects glucose and lipid metabolism disorder, improves microcirculation, acts on pancreas islet directly, strengthens internal organs, activates pancreas cells in body, repairs and promotes pancreas islet functions, controls and eliminates complications rapidly, decreases blood sugar steadily until human body keeps balance of yin and yang, and eradicates diabetes thoroughly. The invention also provides a preparation method for the traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating diabetes.
Owner:王伏春
Agonists of guanylate cyclase useful for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, gallstone, obesity and other cardiovascular diseases
This invention also provides a method to prevent, control, and treat a lipid metabolism disorder, a billary disorder, cardiovascular disease, obesity or an endocrine disorder by administering at least one agonist of guanalyte cyclase receptor either alone or in combination with a compound typically used to treat the disorder and or with an inhibitor of cGMP-dependent phosphodieasterases.
Owner:BAUSCH HEALTH IRELAND LTD
FXR agonist
PendingCN107021957AExcellent FXR receptor agonistic activityGood biological stabilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPrimary biliary cirrhosisFarnesoid X receptor
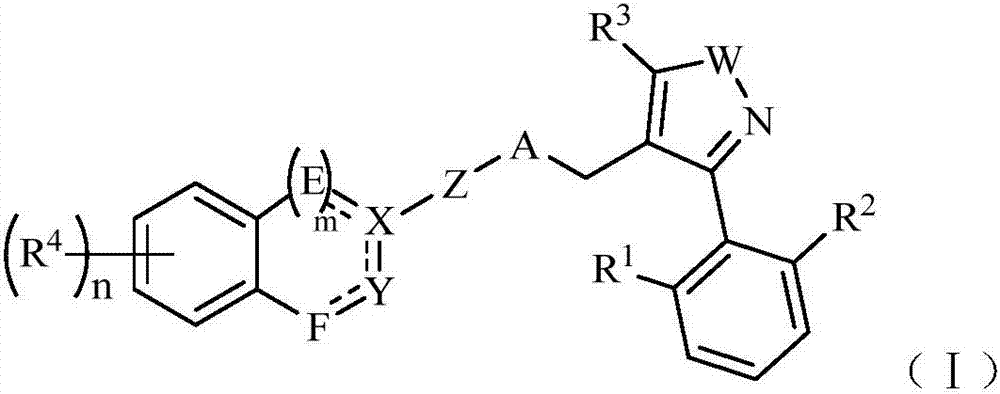
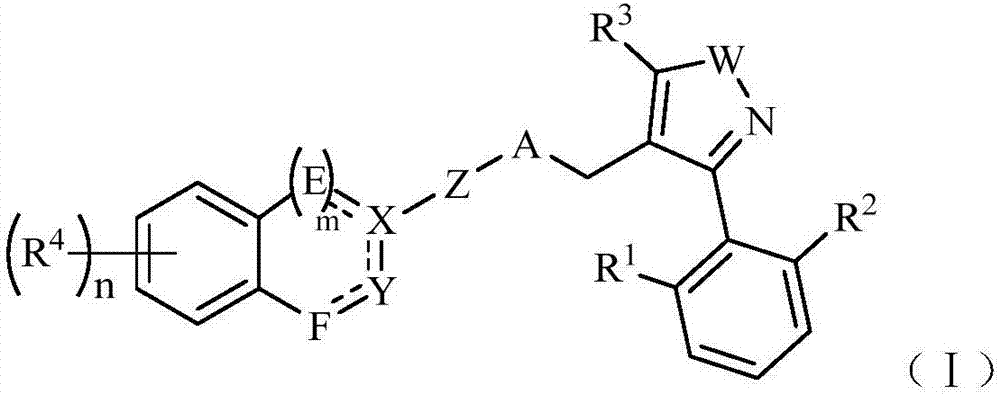
The invention relates to a compound shown as formula (I), a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or stereoisomer thereof. R1, R2, R3, R4, m, n, W, A, Z, E, F, X and Y are defined as the specification. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the compounds, pharmaceutical preparations and application in drugs for treatment and / or prevention of FXR (farnesoid X receptor) mediated nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases, primary biliary cirrhosis, lipid metabolism disorders, diabetic complications, malignant tumors and other related diseases. (formula (I)).
Owner:XUANZHU BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
FXR agonist
PendingCN107021958AExcellent FXR receptor agonistic activityGood biological stabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPrimary biliary cirrhosisFarnesoid X receptor
The invention relates to a compound shown as formula (I), a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or stereoisomer thereof. R1, R2, R3, R4, m, n, W, A, Z, E, F, X and Y are defined as the specification. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the compounds, pharmaceutical preparations and application in drugs for treatment and / or prevention of FXR (farnesoid X receptor) mediated nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases, primary biliary cirrhosis, lipid metabolism disorders, diabetic complications, malignant tumors and other related diseases. (formula (I)).
Owner:XUANZHU BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Composition for amelioration of body lipid
InactiveUS20100190708A1Growth inhibitionPrevent and treat and ameliorate hyperlipemiaPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSecondary hyperlipidemiaAllergy
An object of the present invention is to obtain a composition, which is excellent in amelioration of a lipid metabolism disorder and has a preventive or ameliorating effect on hyperlipemia, obesity or type II diabetes induced by the lipid metabolism disorder, and is also economical and safe with respect to allergy, by extracting a rice bran extract containing a rice bran protein, followed by separation.Disclosed is a composition for amelioration of a lipid metabolism disorder, containing a rice bran protein.
Owner:CHIKUNO SHOKUHIN INDS
Synergistic bifunctional protein for regulating blood sugar and lipid
The invention relates to a synergistic bifunctional protein for regulating blood sugar and lipid. The synergistic bifunctional protein comprises a human GLP-1 analog and human FGF21. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for preparing the synergistic bifunctional protein, and on the other hand, the invention also provides an application of the synergistic bifunctional protein for treatment of type 2 diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, fatty liver disease and / or metabolism syndrome drugs. The synergistic bifunctional protein provided by the invention can synergistically regulate blood sugar and lipid levels in vivo, and meet the multiple needs of hypoglycemia, alleviation of liver fatty degeneration, weight reduction and improvement of circulating lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetic patients.
Owner:AMPSOURCE BIOPHARMA (SHANGHAI) INC
Method of treating or preventing obeisity and lipid metabolism disorders and compositions for use therein
InactiveUS20060105938A1Lose weightUndesired impactBiocideHydrolysed protein ingredientsComplete proteinIntact protein
The present invention provides a method of preventing or treating human obesity, said method comprising ingesting a composition containing, calculated on dry matter: 10-100 wt. % protein hydrolysate; 0-90 wt. % intact protein; 0-50 wt. % carbohydrate; and wherein hydrolysed protein and intact protein together are present in a concentration (w / w) that exceeds the carbohydrate concentration (w / w). The invention also encompasses the use of the same composition in a method of preventing or treating lipid metabolism disorders and in a method for improving body appearance. Other aspects of the invention relate to nutritional beverages, snacks and soups that can advantageously be employed in accordance with the aforementioned methods.
Owner:KERRY GROUP SERVICES
Medicine containing liver-targeting specific ligand and thyroxine receptor agonist
ActiveCN109331185AAvoid side effectsMaintain treatment of lipid metabolism disordersDigestive systemPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNervous systemTherapeutic effect
The invention provides a medicine structurally containing a liver-targeting specific ligand and a thyroxine receptor agonist. The liver-targeting specific ligand and the thyroxine receptor agonist areconnected by branched chains, connectors and connecting chains to form a novel medicine structure. Thyroxine receptors (TRs) are divided into two subtypes, namely TR-alpha and TR-beta, wherein the TR-beta is mainly expressed in the liver, and the TR-alpha is mainly expressed in the heart, the nervous system and the like. In some embodiments, the medicine provided by the invention is expected to have a liver-targeting effect and can specifically bring the thyroxine receptor agonist into the liver so as to prevent the thyroxine receptor agonist from entering the heart and other tissues, so thatside effects triggered by the effect of the thyroxine receptor agonist on the other tissues can be avoided and the therapeutic effect of the medicine on treatment of lipid metabolism disorders and related complications is maintained.
Owner:KYLONOVA (XIAMEN) BIOPHARMA CO LTD
Mutant fibroblast growth factor and use thereof in treating endocrine diseases
ActiveCN102603886AImprove stabilityQuick effectBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsArginineCell membrane
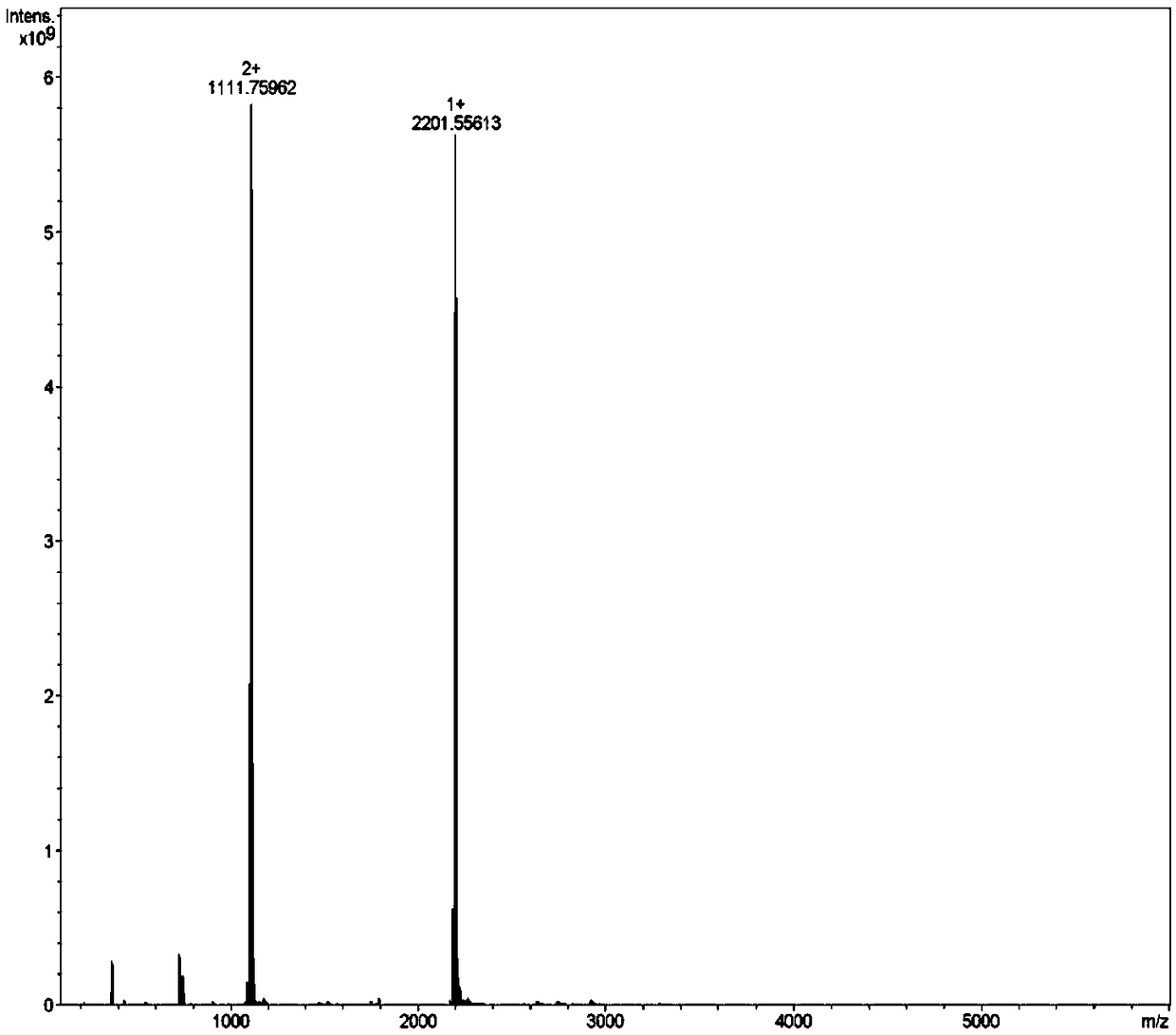
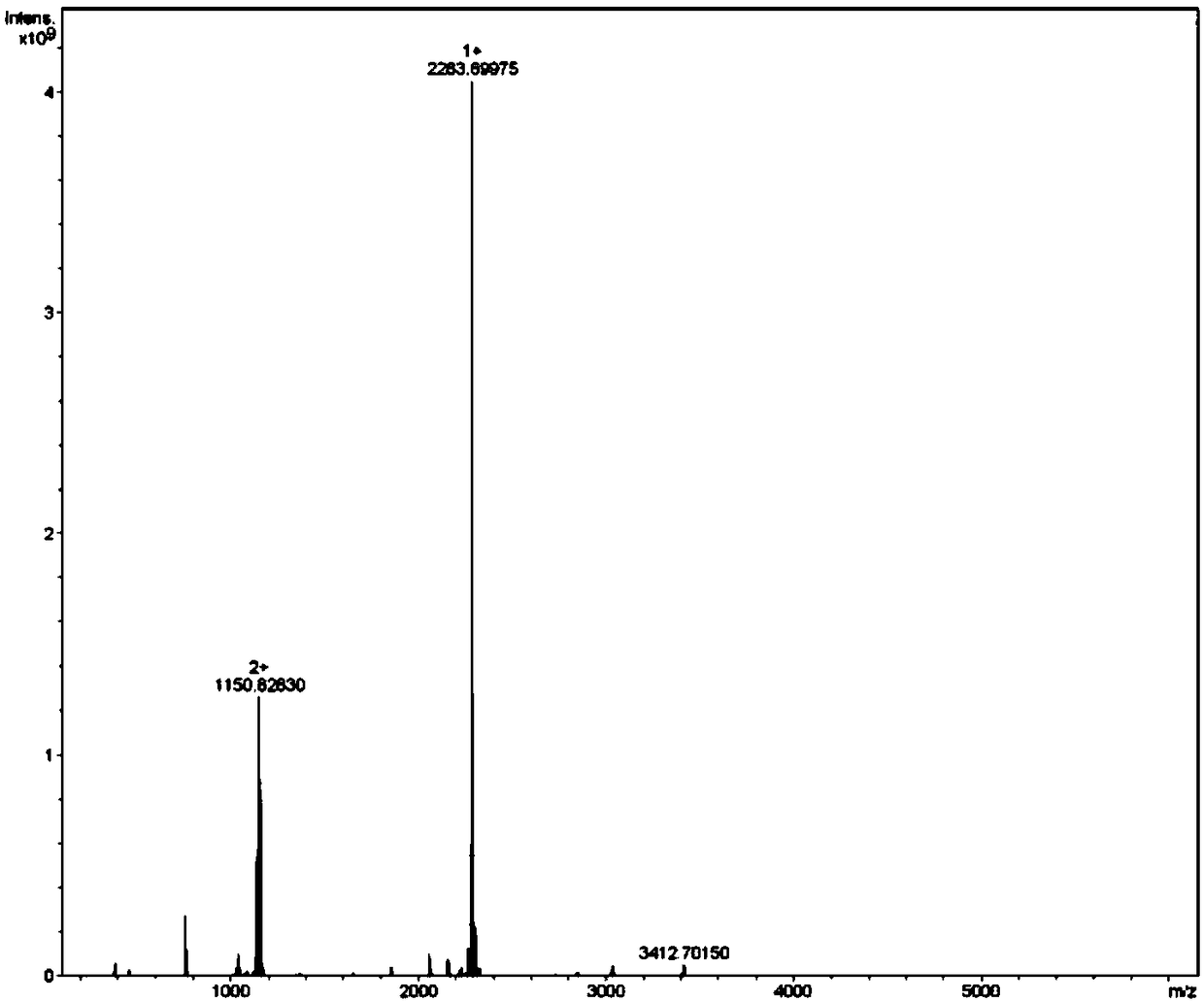
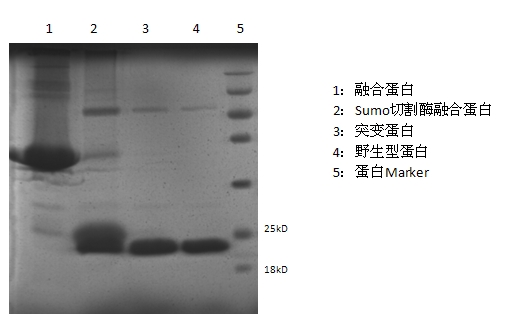
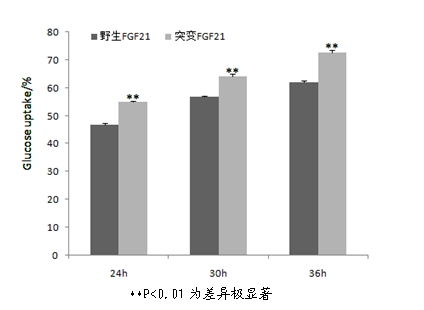
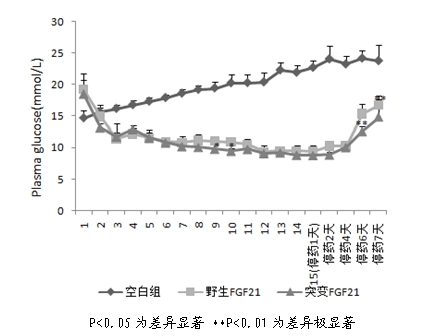
The invention discloses a mutant fibroblast growth factor (FGF-21) and use of the mutant fibroblast growth factor in treating endocrine diseases. The amino acid sequence of the fibroblast growth factor-21 disclosed by the invention is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2, and the sequence of a gene for encoding the mutant fibroblast growth factor is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. According to the invention, a wild typeFGF-21 is used as a template, two arginine (Arg) residues are introduced through a downstream primer, and a mutant is obtained through polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The strong basicity and positive charges in the physiological condition of Arg are mainly utilized so that the isoelectric point of FGF-21 is up-regulated, and FGF-21 binding to the surfaces of cell membranes is facilitated. The results of an animal experiment show that the mutant FGF-21 disclosed by the invention can more effectively reduce the blood glucose level in an animal, and furthermore, the mutant disclosed by the invention has the advantages of fast onset of drug action, lasting drug effect and the like in reducing the blood glucose level. The mutant GF-21 disclosed by the invention can be used as a medicine to treat endocrine diseases such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome, lipid metabolism disorder and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN TASLY PHARMA CO LTD
Compositions and Methods for Treating Disease
InactiveUS20080206231A1Significant positive effectIncreasing IR-mediated ERK pathway activationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiabetic heartDyslipidemia
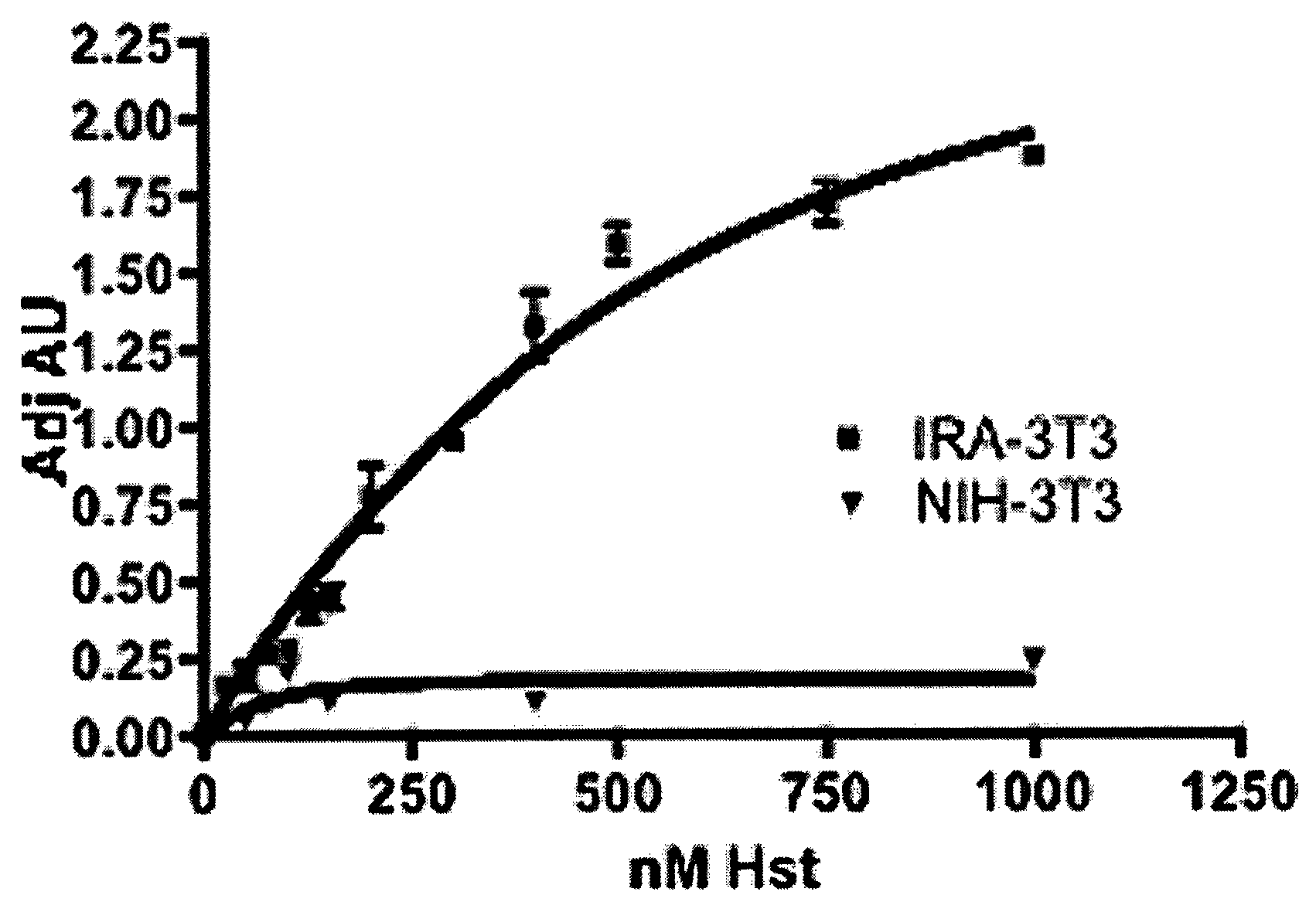
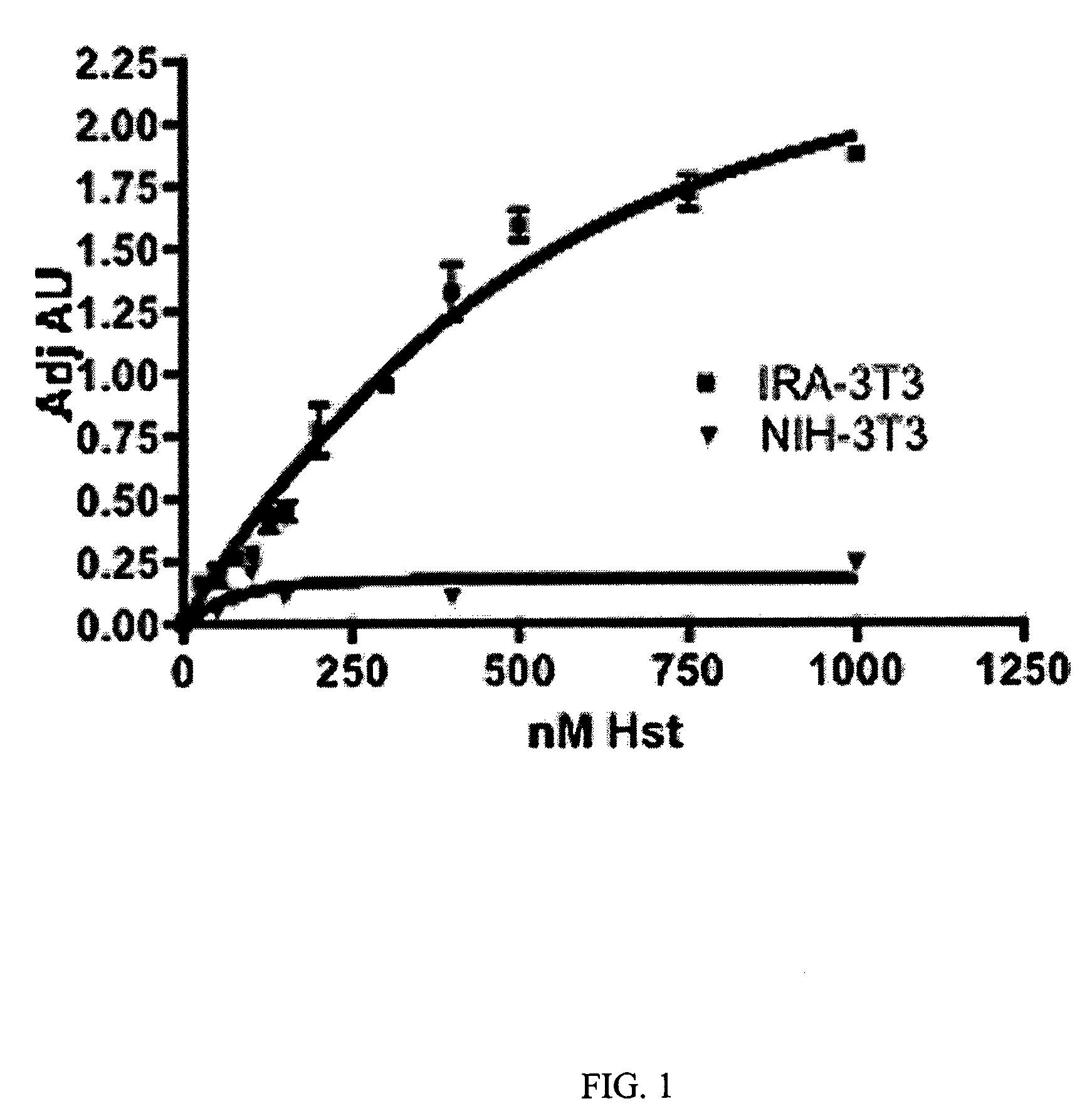
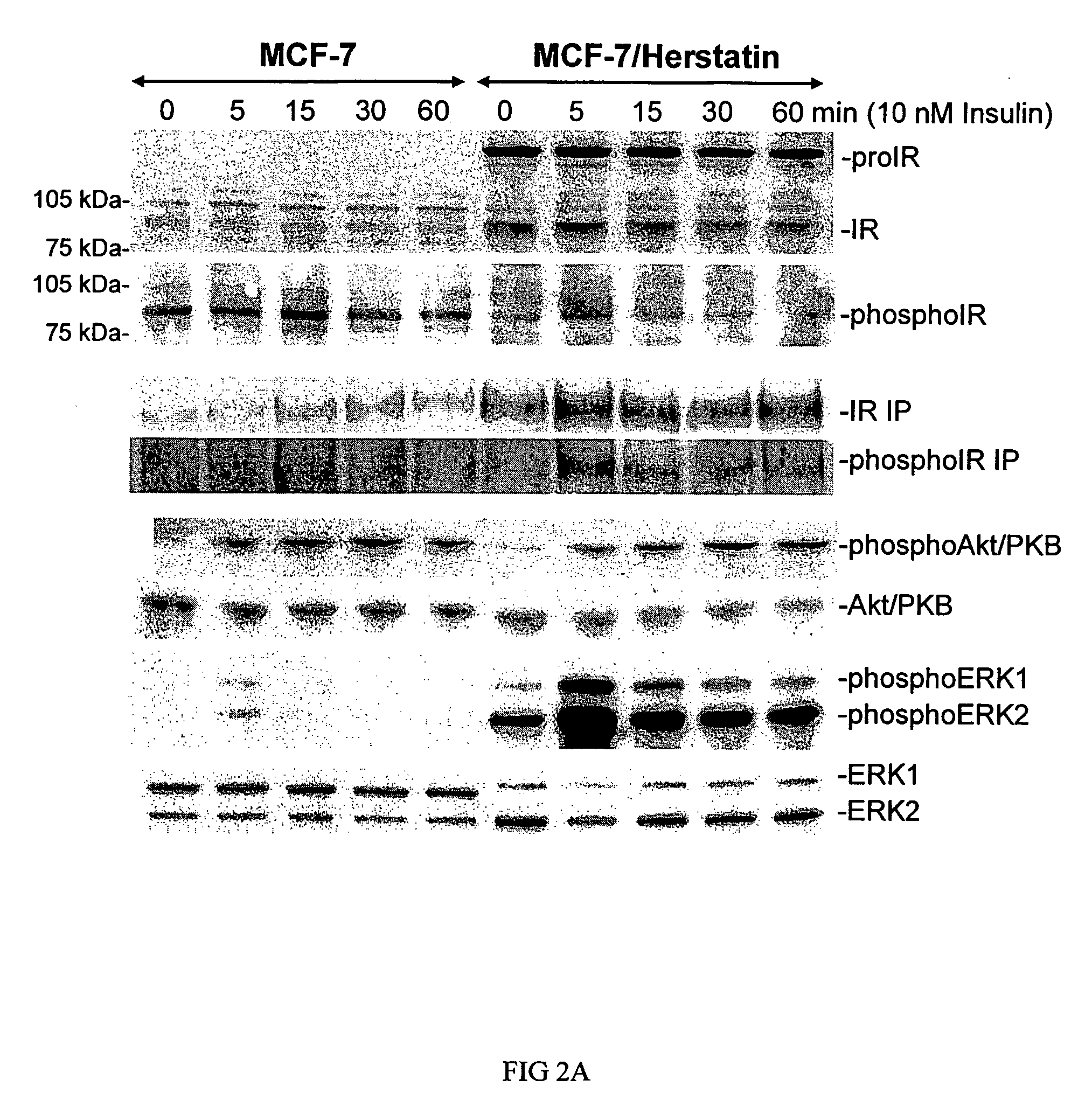
The present invention discloses for the first time that the insulin receptor (IR) is a target of Herstatin, which modulates IR and IR-mediated intracellular signaling. In preferred aspects, Herstatin binds at nM concentrations to cell-surface IR, up-regulates basal IR expression by several-fold, induces the accumulation of pro-IR, and stimulates insulin activation of the ERK pathway. Moreover, these changes in insulin signaling are accompanied by alterations in IGF-IR expression, IRS-2 levels, and the serine phosphorylation state of both IRS-1 and IRS-2. Preferred aspects provide novel therapeutic methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of conditions associated with altered IR expression or IR-mediated signaling, including but not limited to insulin resistance syndrome, pre-diabetic conditions, metabolic syndrome, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, cardiac disease, diabetes-associated vascular disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes-associated lipid metabolism disorders (dyslipidemia), obesity, critical illness, neurodegenerative disorders, and combinations thereof, and cancer.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
1-biarylazetidinone derivative
InactiveUS20100125059A1Excellent cholesterol-lowering effectInhibit progressBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSecondary hyperlipidemiaCholesterol
The object of the present invention is to provide a compound having an excellent cholesterol-lowering effect and to provide a drug for the treatment, prevention of onset, or prevention of progress of lipid metabolism disorder, hyperlipidemia, or atherosclerosis.A compound represented by formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; or a medicament or a pharmaceutical composition, which contain the compound or the salt as an active ingredient.
Owner:TEIJIN PHARMA CO LTD
Preparation method and application of spirulina whole active substances
InactiveCN106923337AReliable workmanshipGood repeatabilityNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsLow density lipoprotein cholesterolFiltration
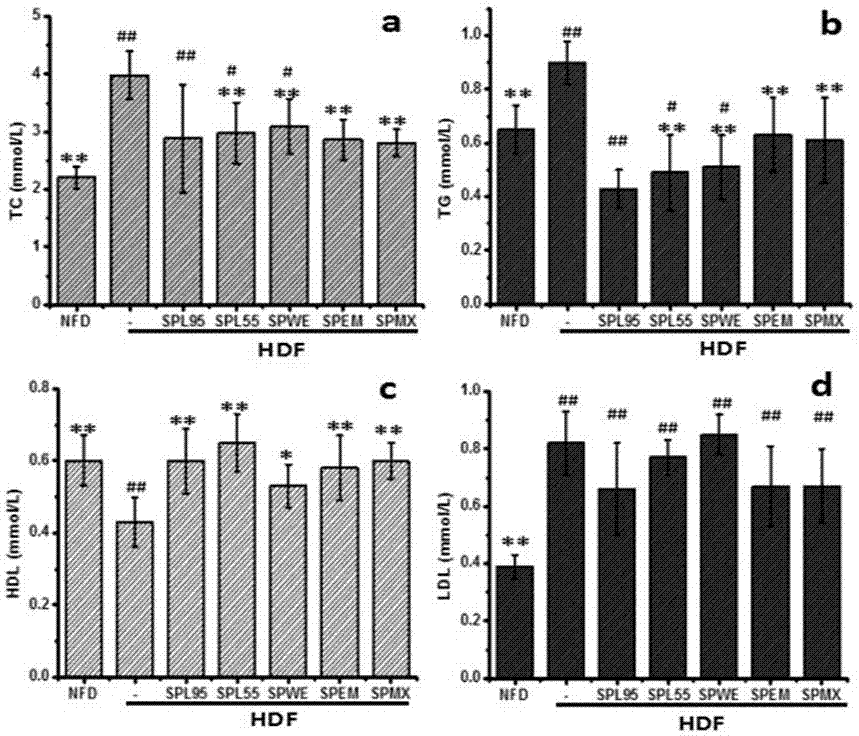
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of spirulina whole active substances. Spirulina is used as a raw material. The spirulina whole active substances are extracted and prepared by the method of performing extraction with solvents of different polarities (from small to large), performing enzymolysis with compound proteinases and the like, and are prepared through the following steps of firstly performing extraction with 85-95wt% ethanol, then performing extraction with 55-65wt% ethanol, then performing water extraction, finally performing enzymolysis on water extraction residues, then performing centrifuging, performing filtration, performing decompression, performing concentration, and performing drying so as to obtain a spirulina 85-95wt% ethanol extract, a spirulina 55-65wt% ethanol extract, a spirulina water extract and a spirulina zymolyte, namely the spirulina whole active substances. Pharmacodynamics experiments verify that the whole active substances can significantly improve lipid metabolism disorder induced by high fat diet, and specifically, can significantly reduce the level of total cholesterol (TC), the level of triglyceride (TG) and the level of low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in serum.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Construction method and application of diet-induced insulin resistance model
ActiveCN104705258AAvoid the problems of instability and low molding rateEliminate adverse reactionsAnimal husbandryHigh fatIn vivo
The invention discloses a construction method of a diet-induced insulin resistance model. Male Kunming mice are induced to generate insulin resistance by being fed with high fat and high glucose food and drinking fructose solutions of a certain concentration, and the insulin resistance model is obtained. The insulin resistance disease process of human beings is simulated in the method, a manufactured animal model has hyperinsulinemia, glucose and lipid metabolism disorders and other insulin resistance classical symptoms, and the method can be suitable for mechanism research of the disease and screening of relevant medicine. Model induction is carried out through the high fat and high glucose food and low-concentration fructose drinking water, the insulin resistance disease process of the human beings can be greatly simulated, result reliability is high, the bad reaction generated by chemical reagents is removed, and the problems that when the mice are only fed with food, the model is unstable, and the model construction success rate is low are solved. Energy intake is larger than consumption through feeding of the high fat and high glucose food, in-vivo energy disequilibrium is caused, and central obesity and fat accumulation are caused, and the aim of enabling an organism to generate insulin resistance is achieved.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Officinal composition for lowering blood fat
InactiveCN101766594AMetabolism disorderSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsImpaired liver functionSide effect
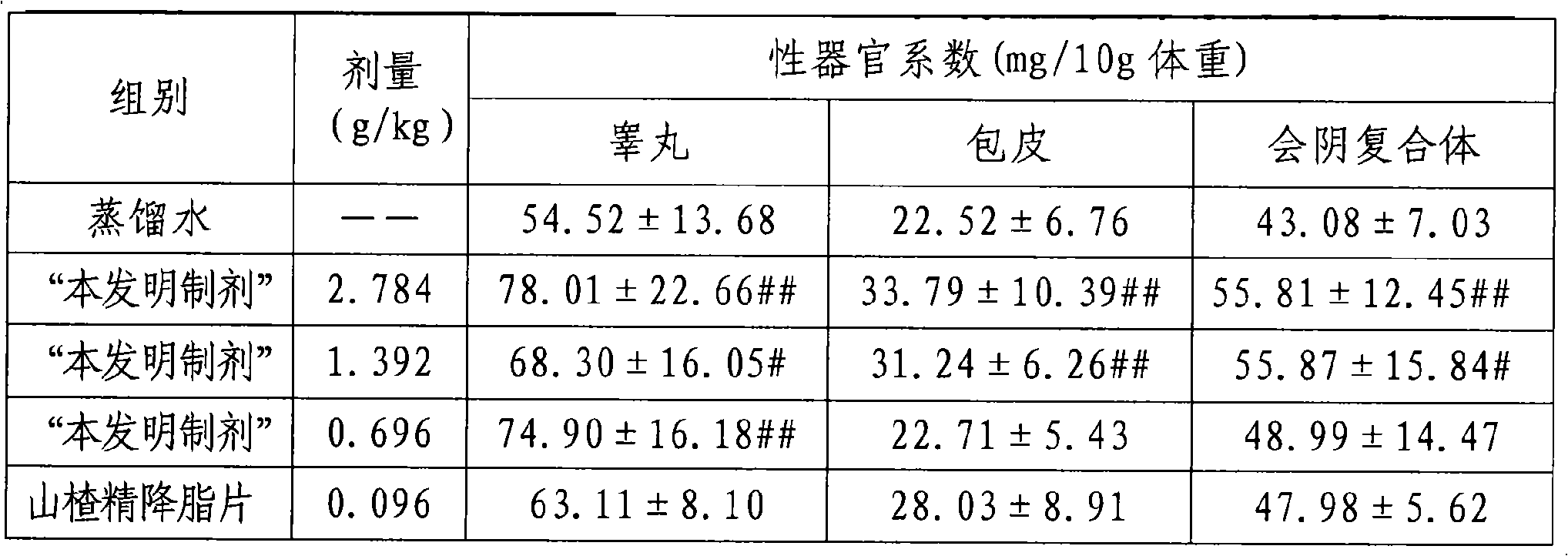
The invention discloses an officinal composition for lowering blood fat. Active ingredients are atorvastatin and probucol. The invention provides a better fat regulating drug for patients clinically suffering from severe lipid metabolism disorders and especially has favorable synergistic effect on patients at high liver function damaging risk level by drug combination; two kinds of drugs complement advantages so as to obviously lower the possibility of side effect occurrence because of increased amount of atorvastatin. The officinal composition for lowering blood fat is prepared from active ingredients and pharmaceutically acceptable supplementary materials, but is not limited in preparations, such as tablets, dispersible tablets, sustained release tablets and the like.
Owner:BEIJING HOPE HUGE PHARM SCI
Chinese medicinal composition for treating hyperlipemia and preparation thereof
The invention provides a Chinese medicine composition for curing hyperlipemia and a preparation method thereof. The Chinese medicine composition is prepared by the following ingredients according to parts by weight: 80 to 640 portions of red sage root, 30 to 240 portions of Sanchi, 60 to 480 portions of polygonum multiflorum, 20 to 160 portions of ginseng, 40 to 320 portions of rhizoma ligustici wallichii, 50 to 400 portions of rhizoma alismatis, 60 to 480 portions of angelica, 40 to 320 portions of rhizoma polygonati, 1 to 8 portions of cinnamon, 20 to 160 portions of herba epimedii and 40 to 320 portions of slenderstyle acanthopanax bark. The Chinese medicine composition of the invention has the effects of correcting the disturbance of lipid metabolism, lowering blood fat, softening blood vessels, improving the microcirculation, inhibiting platelet aggregation and reducing blood viscosity, stimulating the blood circulation and speeding up the removal of lipid residue particles.
Owner:广东宏兴集团股份有限公司宏兴制药厂
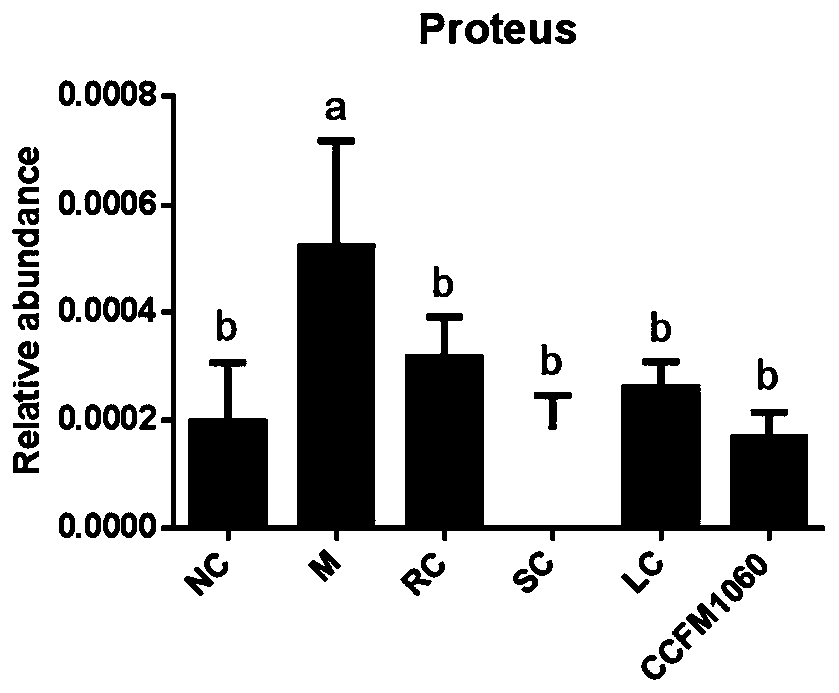
Lactobacillus rhamnosus CCFM1060, fermented food and preparation method of bacterial agent
PendingCN110468070AImprove toleranceReduce concentrationMilk preparationBacteriaBacteroidesLow density lipoprotein cholesterol
The invention discloses lactobacillus rhamnosus CCFM1060, a fermented food and a preparation method of a bacterial agent; increase of the abundance of Proteus induced by high lipid and high cholesterol diet is significantly reduced, and the occurrence of diseases such as urinary tract blockage, intestinal bacterial migration and enteritis is reduced; the lipid metabolism disorder of NAFLD patientsis significantly improved; insulin resistance of NAFLD mice is significantly improved; increase of glutamic-pyruvic transaminase and glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase in serum can be re-adjusted; theconcentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is significantly reduced, and the risk of cardiovascular disease is reduced; the level of SOD in liver of NAFLD patients can be significantly improved; the inflammation of liver can be significantly improved; the damage of liver tissues of the NAFLD patients can be significantly improved; the expression of an Nrf2 gene in fatty liver cells can be significantly improved; the ability to absorb perfluorooctanoic acid in vitro is strong.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nitric oxide-donating chrysin derivatives, preparation method thereof, medical use thereof
InactiveCN101768145APromote generationFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryVascular endotheliumNitric oxide
The invention relates to the fields of pharmaceutical chemistry and particularly provides a series of nitric oxide-donating chrysin derivatives, which are prepared by modifying the chrysin at position 5 and position 7. The nitric oxide-donating chrysin derivatives release nitric oxide and chrysin derivatives in vivo and therefore can conduct functions of reducing blood sugar and blood pressure, promoting angiogenesis, improving a vascular endothelial function and lipid metabolism disorders and can be used in the preparation of medicaments for treating diabetes, diabetic cardiovascular complications, metabolic syndrome and endothelial dysfunction.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Application of galactooligosaccharides and derivatives of galactooligosaccharides as SGLT inhibitor
PendingCN110812364AInhibition of transport functionReduce resistanceOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderGalactooligosaccharideOligosaccharide
The invention belongs to the field of marine medicine, and particularly relates to an application of oligosaccharides containing D-galactose and L-galactose and derivatives of the oligosaccharides asa sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitor. The galactooligosaccharides and derivatives are prepared by the following steps: by using red algae polysaccharide containing the D- / L-galactose as a raw material, performing degradation by using a physical method, a chemical method, a bioenzyme method or any combination of the above methods to prepare the galactooligosaccharides and the derivativesof the galactooligosaccharides with different degrees of polymerization, wherein the molecular skeleton contains the D-galactose and the L-galactose and derivatives thereof. The raw material of the product provided by the invention is from the red algae polysaccharide, and has the advantages of rich resources, a simple preparation process, high safety, clear targets and easy industrialization, the oligosaccharides and the derivatives are used as the SGLT1 and 2 inhibitor, and has broad application prospects in the development of medicines for treating diseases such as diabetes mellitus, obesity, diabetic nephropathy and glucose and lipid metabolism disorder and functional foods for improving non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Corydalis edulis extract, pharmaceutical composition containing same and uses thereof
ActiveCN105560390ALower levelLower plasma cholesterolMetabolism disorderDigestive systemDiseaseAlkaloid
The invention provides Corydalis edulis extract, prepared by a method comprising the following steps: (1), after crushing a Corydalis edulis plant, and extracting with alkaline ethyl alcohol or methyl alcohol to obtain an extract; (2), subjecting the extract obtained in step (1) to normal pressure or vacuum concentration to obtain concrete, or spray drying to obtain powder; (3), adding an acid solution into the concrete or powder obtained in step (2), filtering to obtain an acid aqueous solution, adding an alkaline solution to the acid aqueous solution to obtain an alkali treated solution; (4), adding an organic solvent to the alkali treated solution obtained in step (3), vacuum recycling the organic solvent after extracting to obtain Corydalis edulis total alkaloids crude extract. The Corydalis edulis extract or a pharmaceutical composition containing the extract can be used to prepare pharmaceuticals for preventing and / or treating diseases caused by glucose and lipid metabolism disorder.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Lignum aquilariae resinatum extract, pharmaceutical composition with same and application thereof
ActiveCN105560612ALower levelPromote secretionMetabolism disorderDigestive systemSpray driedLipid Metabolism Disorder
The invention provides lignum aquilariae resinatum extract. The lignum aquilariae resinatum extract is characterized in that the lignum aquilariae resinatum extract is prepared by the aid of a method including steps of (1), smashing lignum aquilariae resinatum and extracting the lignum aquilariae resinatum by the aid of methanol or ethanol aqueous solution to obtain extract liquid; (2), concentrating and drying the extract liquid obtained in the step (1) under normal pressures or reduced pressures to obtain extract cream, or carrying out spray-drying on the extract liquid to obtain powder, then dissolving the extract cream or the powder in water to obtain solution, extracting the solution by the aid of petroleum ether to obtain petroleum ether extract liquid, and extracting aqueous layers by the aid of ethyl acetate to obtain ethyl acetate extract liquid; (3), concentrating and drying the ethyl acetate extract liquid obtained in the step (2) under reduced pressures to obtain extract cream, or carrying out spray-drying on the ethyl acetate extract liquid to obtain powder. The lignum aquilariae resinatum extract and the method have the advantage that the lignum aquilariae resinatum extract or a pharmaceutical composition with the lignum aquilariae resinatum extract can be used for preparing medicines for preventing and / or treating diseases due to glucose and lipid metabolism disorder.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Application of neohesperidin in preparing of diabetes preventive treatment medicines
InactiveCN102772424AImprovement of glucose and lipid metabolismImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseNaringin
The invention provides application of neohesperidin in preparing of diabetes preventive treatment compound medicines or health care products. Neohesperidin is extracted and separated from citrus grape fruit tengyuch euonymus bark layers and is subjected to glucose and lipid metabolism biological activity research, and just as naringin, neohesperidin can obviously increase hepatic cell glucose consumption, improve phosphorylation levels of glucose and lipid metabolism related protein adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK) and lipid synthesized key protein activated calcium carbonate (ACC) and cooperate to reduce triglyceride level in lipopexia hepatic cells molded by free fatty acid, has effects of prompting reduction of blood sugar and blood lipid levels, and effect concentration of neohesperidin is far lower than that of positive medicine metformin. Neohesperidin can serve as ancillary drugs or health care products to be used for preventive treatment of diseases related to glucose and lipid metabolism disorder.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preventing and treating lipid metabolism disorders and related diseases thereof
InactiveUS20190328850A1Reduce riskLow-density lipoprotein levelPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseLipid Metabolism Disorder
The present invention relates to a method for preventing and / or treating a fat metabolism disorder and its related conditions, comprising administering an effective amount of plasminogen to a subject susceptible to or suffering from a fat metabolism disorder and its related conditions, to reduce an abnormal fat deposition at various sites of the body, thereby achieving the purpose of preventing and / or treating a fat metabolism disorder and its related conditions or complications.
Owner:TALENGEN INTERNATIONAL LIMITED
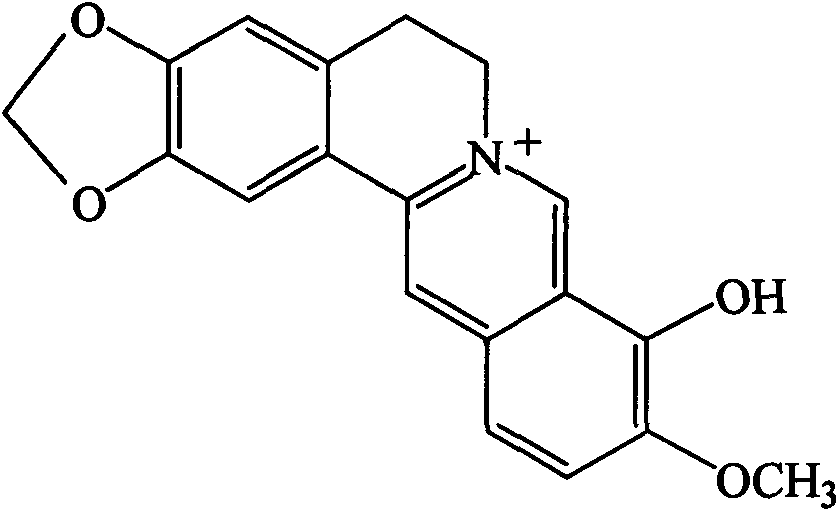
Application of 9-demethylberberine in preparation of hypolipidemic drug
InactiveCN103919773AFat-lowering effect is goodOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide effectMetabolite
The invention provides a hypolipidemic compound 9-demethylberberine. The 9-demethylberberine is derived from a main in-vivo metabolite of natural medicine berberine, and is also named as berberrubine. The researches on model animals with hyperlipidemia find that the 9-demethylberberine has good drug effects of reducing cholesterol, triglyceride, low density lipoprotein (LDL) and the like, and has no obvious side effects for 6 weeks of continuous medication. The discovery can lead to discovery of a new hypolipidemic drug, and provides another alternative medicine for clinic treatment of hyperlipidemia, lipid metabolism disorder and high fat and obese patients and related people wanting to lose weight.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Lipid-decreasing liver protection traditional Chinese medicine composition
ActiveCN103479691AGood effect of lowering blood fatLittle side effectsMetabolism disorderDigestive systemSalvia miltiorrhizaFatty liver
The invention discloses a lipid-decreasing liver protection traditional Chinese medicine composition, and belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine compositions. The lipid-decreasing liver protection traditional Chinese medicine composition is an agent, a health care product or food and is prepared by raw materials of stems and leaves of radix bupleuri, white peony roots, liquorice, hawthorn, salvia miltiorrhiza and rhizoma alismatis. Clinical verifications show that the traditional Chinese medicine composition can protect the liver, soften blood vessels and decrease lipid through long-time use; and the traditional Chinese medicine composition has remarkable prevention and treatment effects on symptoms and diseases such as fatty liver, hyperlipidemia, angiosclerosis and the like which are caused by glucose and lipid metabolism disorder of middle-aged and aged people.
Owner:SICHUAN DE PEI YUAN TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE SCI & TECH DEV CO LTD
Ampelopsis grossedentata leaf and herba cichorii composition and preparation method thereof and application of composition
InactiveCN111973704ANo side effectsEasy to takePowder deliveryDispersion deliveryMedicinal herbsCichorium
The invention relates to an ampelopsis grossedentata leaf and herba cichorii composition and a preparation method thereof and application of the composition. The ampelopsis grossedentata leaf and herba cichorii composition consists of ampelopsis grossedentata leaves, herba cichorii, fructus gardeniae, folium mori, radix puerariae and bulbus lilii. The composition of the invention takes medicinal and edible medicinal materials as raw materials; according to the theory of traditional Chinese medicine, medicine properties and dosage, the composition is reasonably proportioned, keeps pathogenesis,and performs treatment based on syndrome differentiation, and has a significant treatment effect on damp-heat blockage type uricemia (symptoms including proteinuria, hematuresis, edema, uric acid calculus, glucose and lipid metabolism disorder and the like). In addition, the prescription of the invention has no toxic and side effects, is safe and reliable, and is convenient to take.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN ZHONGZHI PHARMA GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com