Method for separating plasmodiophora brassicae monospore on basis of methylene blue agarose method
A technique for the separation of Plasmodium brassicae and its isolation method, which is applied in the field of single-spore isolation of Plasmodium brassicae, can solve problems such as difficult picking and fuzzy targets of Pyrophylla brassicae single-spore, and improve efficiency, speed and The effect of accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
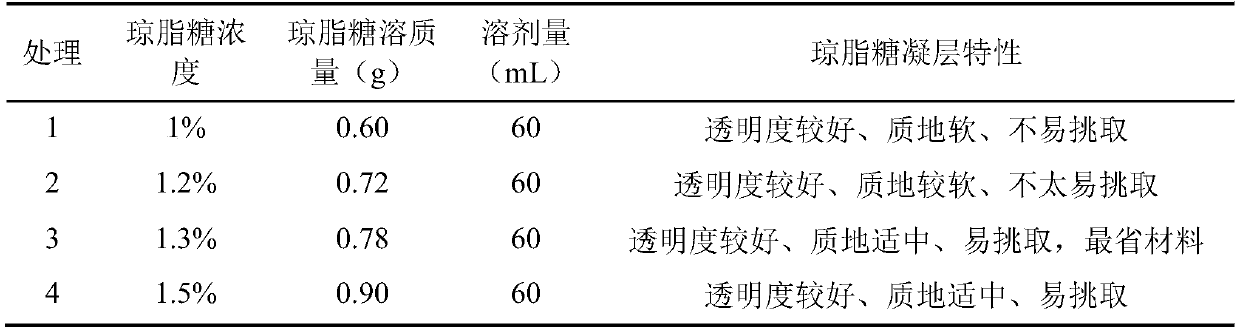
[0034] Embodiment 1, the screening of optimal concentration of agarose
[0035] Dip the sterilized glass slide in different concentrations of agarose solution to form a gel on the surface of the slide. Then take 5 μL of the diluted dormant spore suspension and drop it on the surface of the agarose gel layer. Observe under a microscope, cut about 1 mm agarose gel layer containing the staining solution of single spore with a scalpel. Screen out the optimal agar block concentration. The concentration of the agarose solution was set as 1%, 1.2%, 1.3%, 1.5%, 1.8%, 2%, 2.5% and 3% for a total of 8 treatments, and the transparency, texture hardness, and individuality of the agarose gel layer were analyzed at different concentrations. The difficulty of spore picking.
[0036] Table 1 Analysis table of results of different concentrations of agarose
[0037]
[0038]
[0039] The results showed that when the concentration was 1.3%, the agarose layer had good transparency, mode...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2, the screening of optimal dyeing agent and dyeing solution concentration
[0041] Staining solution configuration: Weigh 0.05g acid fuchsin, 0.01g Congo red, 0.01g eosin Y sodium, 0.05g neutral red, 0.01g safranin, 0.005g methylene blue, 0.01g methylene blue, 0.02g methylene blue, 0.03 g methylene blue, 0.04g methylene blue, 0.02g bromophenol blue, 0.01g methyl green, add 100mL sterile water. The mass and volume percent concentrations are prepared to be 0.05% acid fuchsin, 0.01% Congo red, 0.01% eosin Y sodium, 0.05% neutral red, 0.01% safranin, 0.005% methylene blue, 0.01% methylene blue, 0.02% methylene blue, The staining solution of 0.03% methylene blue, 0.04% methylene blue, 0.02% bromophenol blue and 0.01% methyl green was stored in a brown bottle at 4°C for later use.
[0042] Preparation of staining solution agarose gel layer: Take 50 μL of each of the above 12 different staining solutions, add 15 mL of 1.3% agarose solution that has been melted and...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3, the comparison of methylene blue agarose block method and traditional water agar method single spore separation effect
[0051] The methylene blue agarose block method established by the present invention and the reported water agar method (method 1 mentioned in the background technology) were used to inoculate P. brassica monospore, and the results of P. brassica monospore isolation were compared. The chrysanthemum Chinese cabbage seedlings (purchased from Zhongshu Seed Industry Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.) seedlings that had been germinated for 24 hours were inoculated with two different methods, transplanted to sterile seedling trays with a diameter of 5 cm × 5 cm, and placed in a greenhouse for cultivation. 200 plants were treated with 3 repetitions. Place it in a greenhouse environment, keep the daily temperature at 20-25°C, night temperature at 11-16°C, and light at 16h·d -1 , the humidity is 100% for the first two weeks, and then watered as need...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com