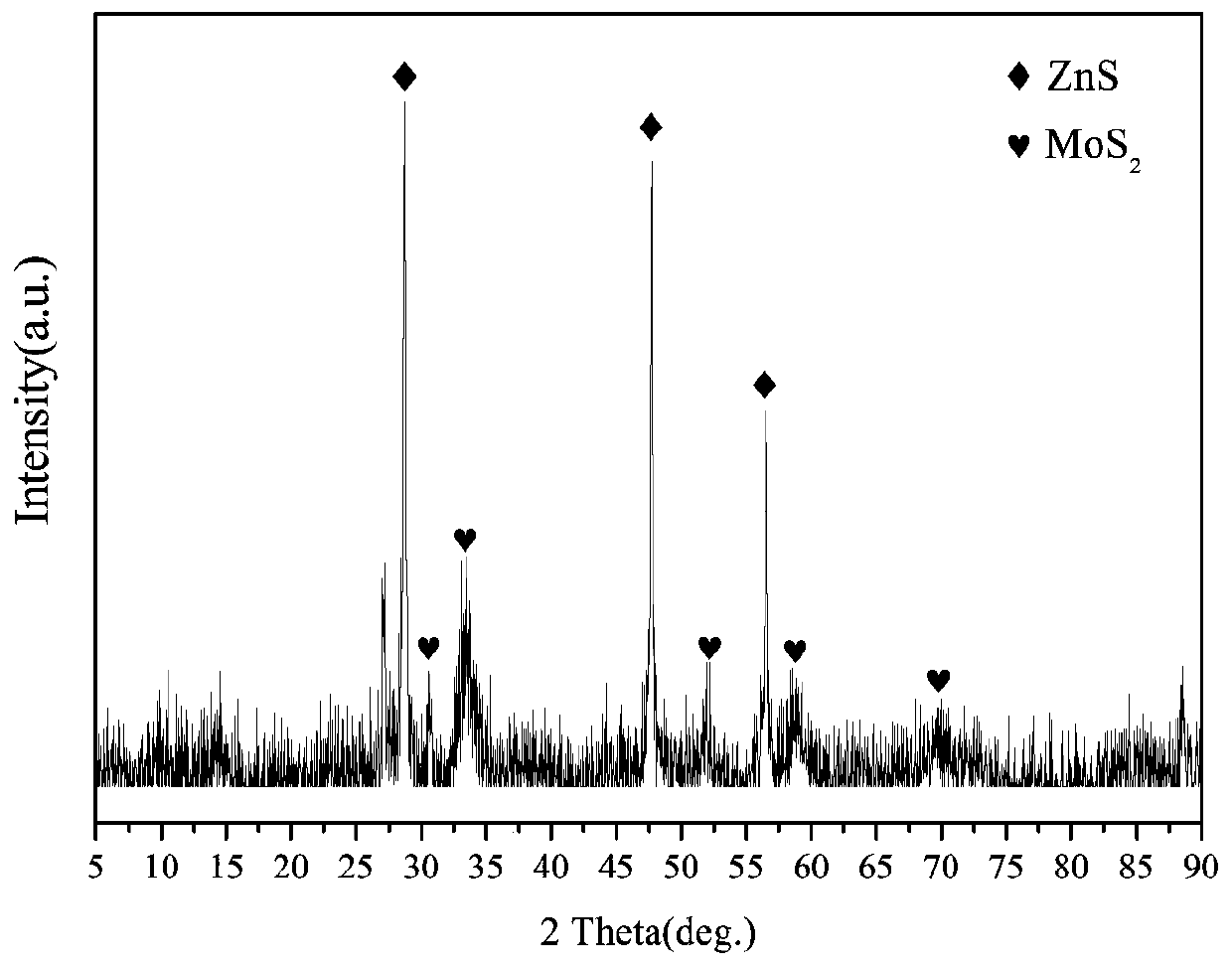
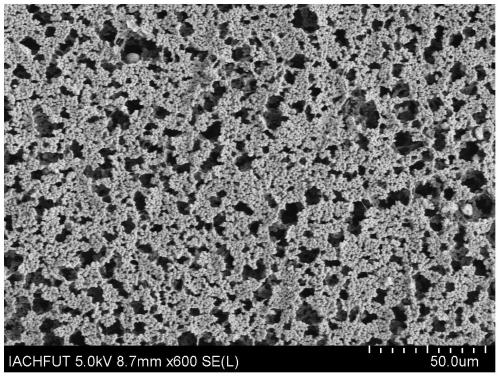
Preparation and application of polymer carrier coated transition metal doped molybdenum sulfide nanoparticle composite catalytic material
A high-molecular polymer, transition metal technology, applied in organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalyst, physical/chemical process catalyst, chemical/physical process, etc. Cumbersome process, secondary pollution of water and other problems, to achieve the effect of increasing catalytic active sites, solving easy aggregation and efficient reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] In this example, the polymer carrier-coated zinc-doped molybdenum sulfide nanoparticle composite catalytic material was first prepared according to the following steps:
[0043] (1) Preparation of zinc-doped molybdenum sulfide nanoparticles:
[0044] 12.4mmol ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and 0.16mol ZnCl 2 Place in a beaker containing 1L of deionized water, stir at room temperature for 2h, then add 200mmol thiourea and continue stirring for 1h at room temperature, the resulting mixed solution is hydrothermally reacted at 180°C for 18h; tube furnace, at N 2 In the atmosphere, the temperature was raised to 700°C at a constant rate of 10°C / min, and the constant temperature was reacted for 2 hours; after the reaction, the N 2 Cool to room temperature in the atmosphere, and the obtained black powder is zinc-doped molybdenum sulfide nanoparticles, which are fully ground and bottled for use;
[0045] (2) Coating of polyvinylidene fluoride carrier
[0046] Add 4g of zinc...
Embodiment 2
[0061] In this example, first, the polymer carrier-coated zinc-doped molybdenum sulfide nanoparticle composite catalytic material was prepared according to the same method as in Example 1, the only difference being that ferric chloride was used instead of zinc salt.
[0062] With the composite membrane material obtained in this example, the same structure and method as in Example 1 were used to reduce the heavy metal hexavalent chromium, and the final reduction rate of hexavalent chromium was 90%.
Embodiment 3
[0064] In this example, first, the polymer carrier-coated zinc-doped molybdenum sulfide nanoparticle composite catalytic material was prepared according to the same method as in Example 1, the only difference being that cobalt chloride was used instead of zinc salt.
[0065] With the composite membrane material obtained in this example, the same structure and method as in Example 1 were used to reduce the heavy metal hexavalent chromium, and the final reduction rate of hexavalent chromium was 80%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com