Method for improving xylose utilization capacity of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and mutant strain of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae stain
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains and recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of no work proof Tec1p, etc., and achieve the effect of shortening the fermentation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: Construction and acquisition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain BSGX001
[0027] The main process of construction is as follows:
[0028] (1) Overexpressing the xylulokinase gene XKS1 of strain CEN.PK113-5D.
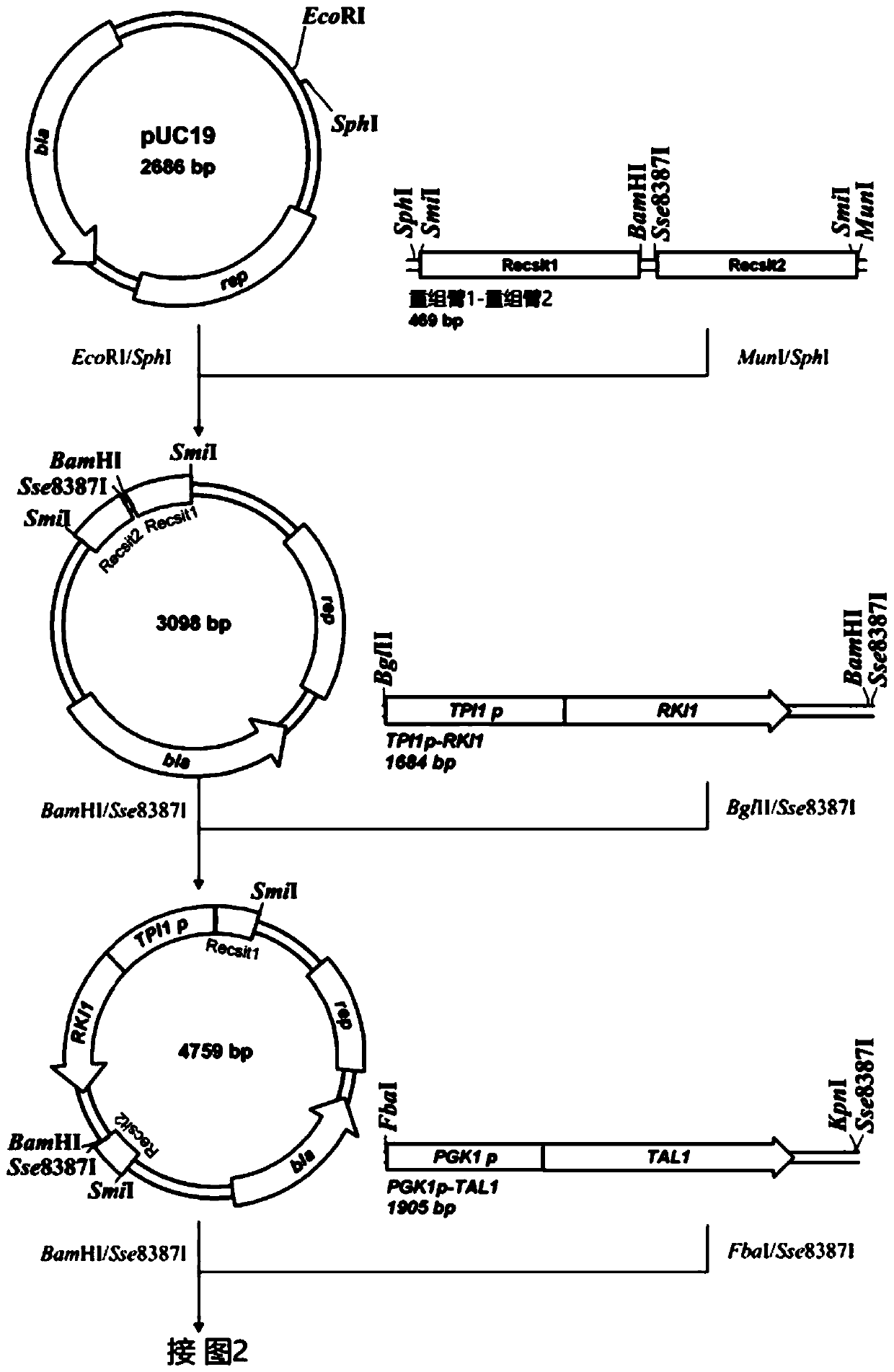
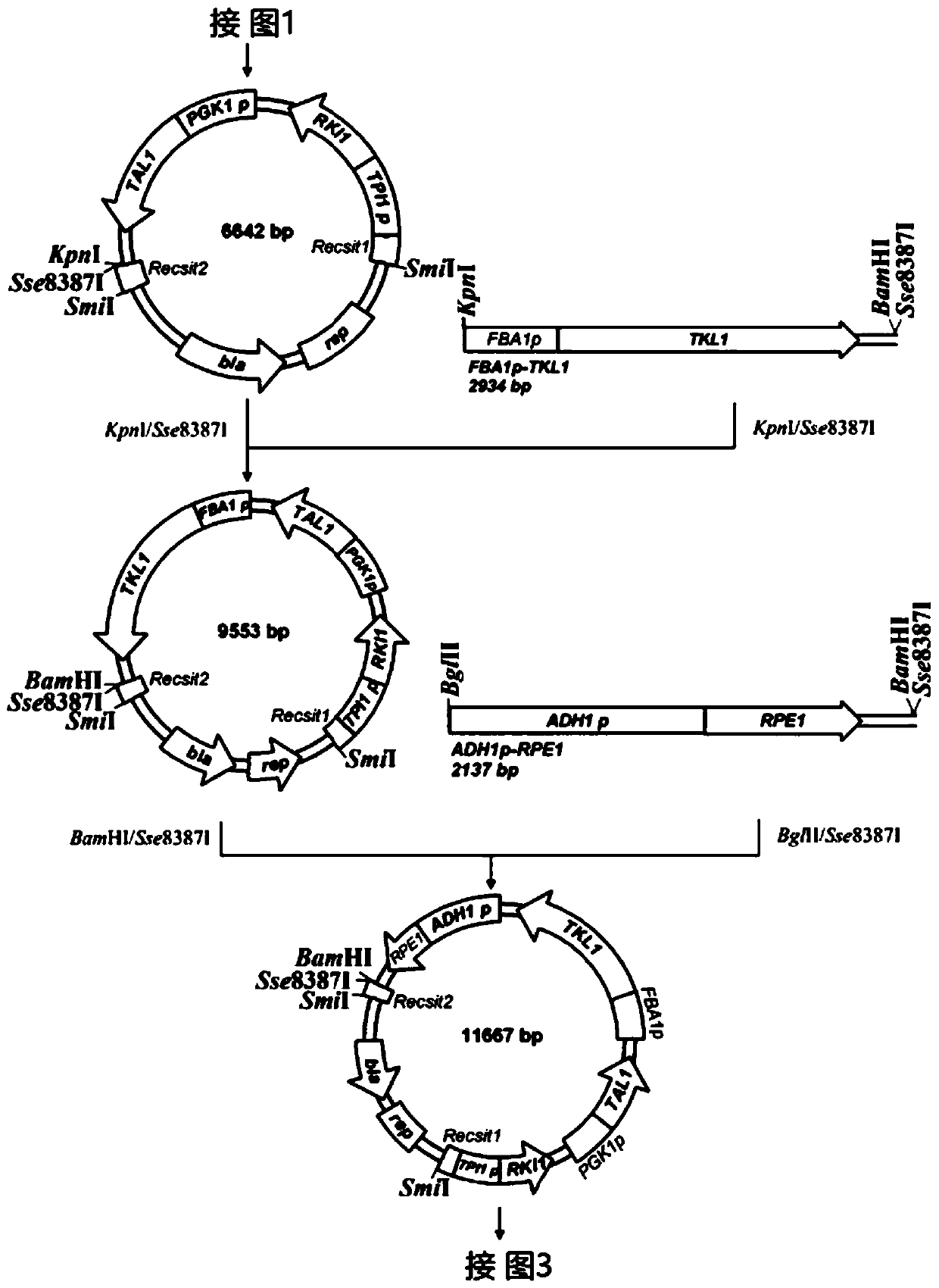
[0029] Using the plasmid pUG6 (GenBank: AF298793.1) as a template, primers XKKans and Kana were used to amplify the G418 resistance gene KanMX4 fragment LoxP-KanMX4-LoxP with LoxP sites at both ends.
[0030] Using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome as a template, primers XKTEF1ps and XKTEF1pa were used to amplify the fragment containing promoter TEFp. Then, fusion amplification of the promoter and the DNA fragment LoxP-KanMX4-LoxP was carried out by fusion PCR to obtain the integrated fragment of LoxP-KanMX4-LoxP-TEF1p.
[0031] The integrated fragment was transformed into Saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK113-5D (MATa SUC2MAL2-8cura3-52) using the lithium acetate transformation method. For details, see the literature [25 Yeast Genetic Strain and Plasm...
Embodiment 2
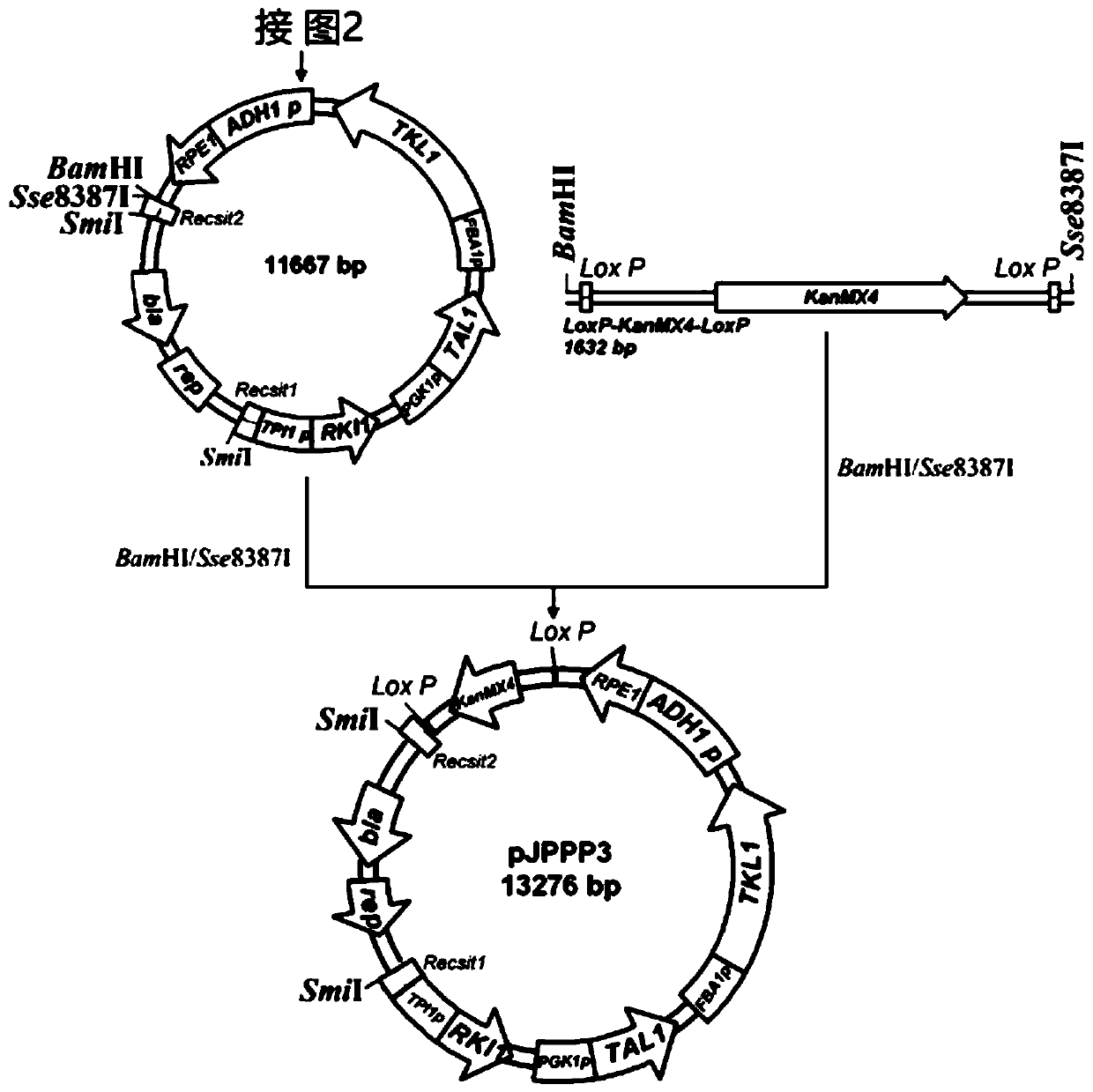
[0048] Example 2: Acquisition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cre-LoxP Genetic Operating System Tool Plasmid YEp-CH
[0049] When the Cre enzyme is expressed in the cell environment, the Cre enzyme recognizes the specific DNA sequence LoxP and catalyzes site-specific recombination. This recombination process will cause the sequence between the two homologous LoxP site sequences to be deleted from the DNA. . YEp-CH is a tool plasmid with Cre-LoxP genetic operating system used in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and its Cre enzyme gene is expressed under galactose-induced conditions. The construction method of the YEp-CH plasmid is obtained by methods such as cloning construction and DNA sequence synthesis known in the art.
[0050] Specifically, the source of each sequence of YEp-CH is: the backbone is YEp24 (GenBank: L09156.1), the Cre expression frame is cloned from the 2066 to 4256 bp of the plasmid pSH47 (GenBank: AF298782.1), the length is 2019 bp, and inserted into YEp24 At the Nc...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: Mutation of the TEC1 gene in situ on the chromosome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0053] The DNA fragment used for in situ mutation of the TEC1 gene on the chromosome is obtained by fusion PCR technology, and the annealing temperature in the amplification conditions is 52°C, and the operation refers to Figure 4 As shown, the specific steps are as follows:
[0054] Using the chromosomal DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae BSGX001 as a template, primer tec1-1 (SEQ ID NO:39) and primer tec1-2 (SEQ ID NO:40) were used to amplify to obtain DNA fragment 1: TEC1-T273M-1 (839bp); Use primers tec1-3 (SEQ ID NO: 41) and tec1-4 (SEQ ID NO: 42) as primers to obtain DNA fragment 2: TEC1-T273M-2 (687bp), fragment 2 and the downstream of fragment 1 and the upstream of KanMX4 respectively There are homologous parts.
[0055] Using plasmid pUG6 (GenBank: AF298793.1) as a template, amplified with primer tec1-5 (SEQ ID NO: 43) and primer tec1-6 (SEQ ID NO: 44) to obtain DNA frag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com