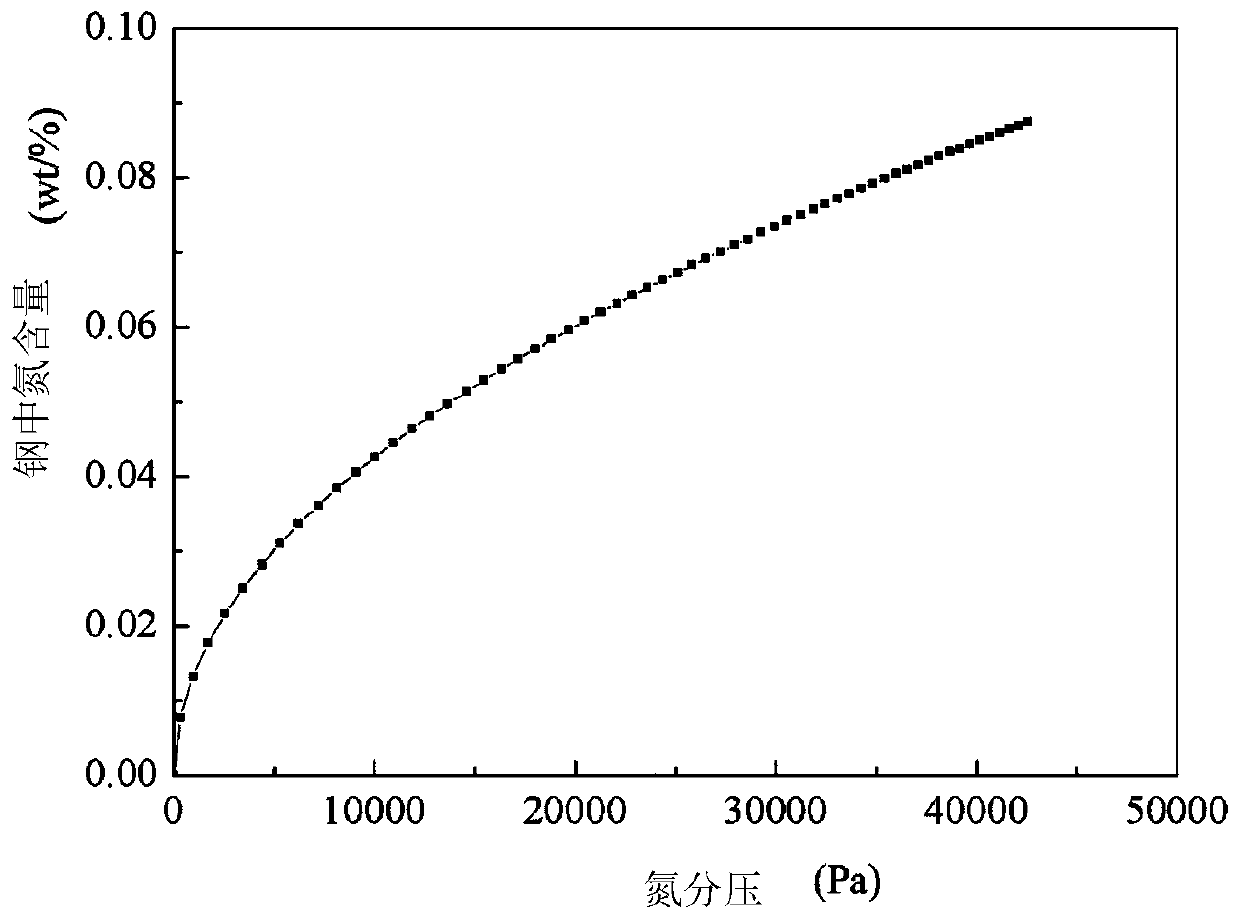
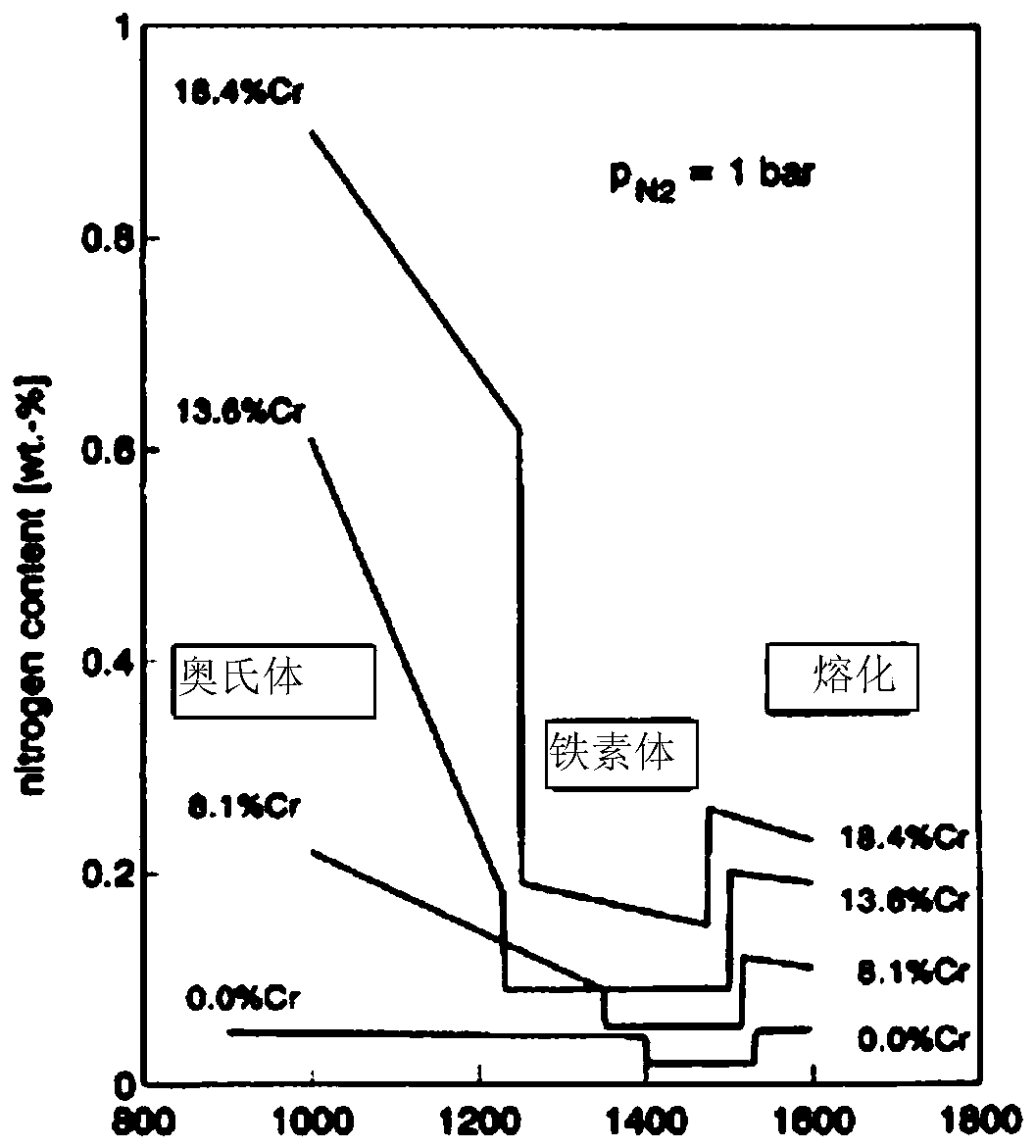
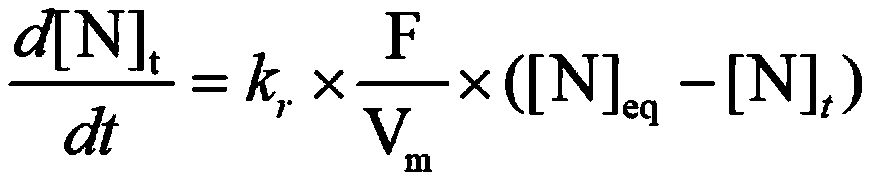Method for smelting COST-FB2 steel through gas-phase nitriding under negative pressure condition
A COST-FB2, gas-phase nitriding technology, applied in the direction of coating, metal material coating process, solid-state diffusion coating, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Present embodiment adopts 30kg vacuum induction furnace to smelt target steel type COST-FB2, and its target composition is as table 4. The quality of this smelting is 22kg, and the nitrogen content is controlled at 0.02%. The ultimate vacuum of the furnace is 0.01Pa, and the maximum power is 100kW. The smelting process uses a magnesium-aluminum crucible with an inner diameter of 140mm and an inner depth of 300mm.
[0075] Table 4: Composition requirements of FB2 steel (wt / %)
[0076]
[0077] The smelting steps are as follows:
[0078] 1, determine the quality of every kind of alloy material according to table 4 and table 3, and carry out weighing batching, the required graphite carbon is equally divided into two parts.
[0079] 2. Distributing the alloy materials weighed above, including chromium, nickel, molybdenum, cobalt, industrial pure iron and half of carbon, which are added with the furnace, while the other half of carbon, silicon, vanadium, niobium, ferro...
Embodiment 2
[0088] In this embodiment, a 30kg vacuum induction furnace is used to smelt the target steel grade with a quality of 22kg, and the nitrogen content is controlled at 0.03%. The rest of the ingredients are shown in Table 4. Determine according to table 4 and table 3 the quality that needs every kind of alloy material, and carry out weighing batching, the required graphite carbon is equally divided into two parts.
[0089] The smelting steps are as follows:
[0090] 1. Distribute the alloy material weighed above, among which chromium, nickel, molybdenum, cobalt, industrial pure iron and half of carbon are added with the furnace, while the other half of carbon, silicon, vanadium, niobium, ferroboron and manganese are put in order In the silo.
[0091] 2. Slowly increase the power to about 52kW during the melting process and turn on the three-stage vacuum pump step by step until the vacuum degree is about 0.1Pa to ensure dehydrogenation, denitrification and deoxidation during the ...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Present embodiment adopts 100kg vacuum induction furnace smelting quality to be the target steel grade of 76kg, and nitrogen content is controlled at 0.02%, and all the other compositions are shown in Table 3. The magnesium-aluminum crucible used has an inner diameter of 210mm, an inner depth of 560mm, a nominal smelting mass of 85kg, a furnace limit vacuum of 1.2Pa, and a maximum power of 200kW. According to formula (8), the nitriding pressure is 2200Pa, and the nitriding time is 24min.
[0100] The smelting steps are as follows:
[0101] 1. According to Table 4 and Table 3, determine the quality of each alloy material required, and weigh the ingredients, and divide the required carbon equally into two parts.
[0102] 2. Distributing the alloy materials weighed above, including chromium, nickel, molybdenum, cobalt, industrial pure iron and half of carbon, which are added with the furnace, while the other half of carbon, silicon, vanadium, niobium, ferroboron and manga...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com