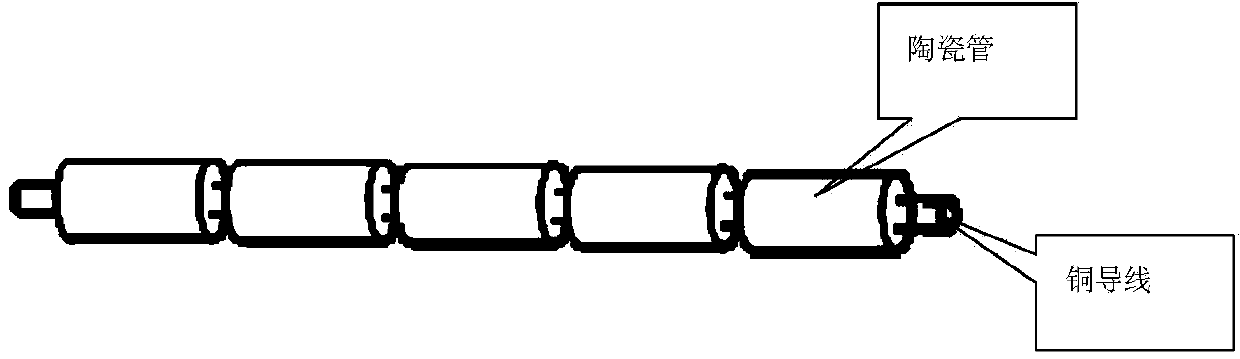
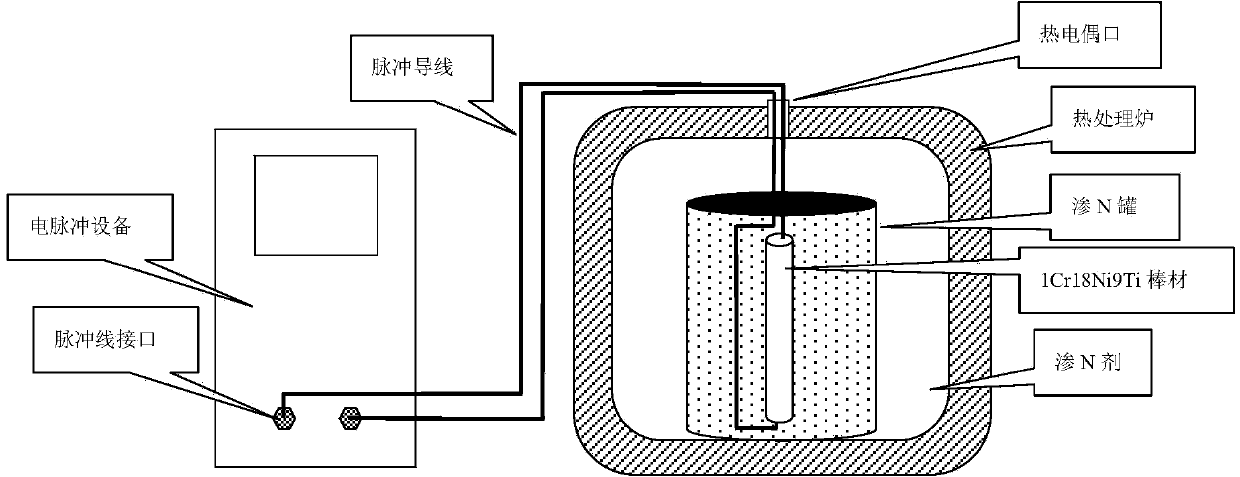
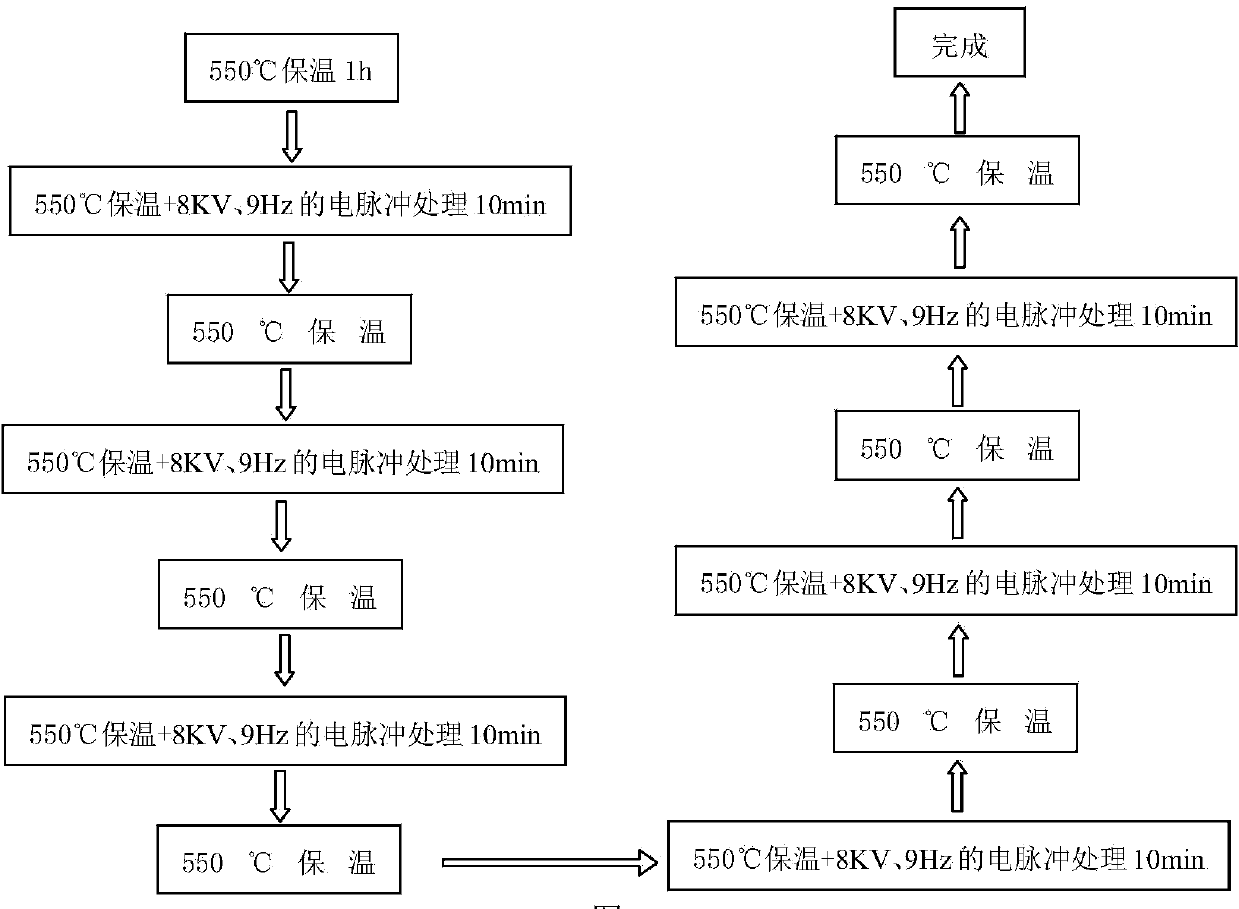
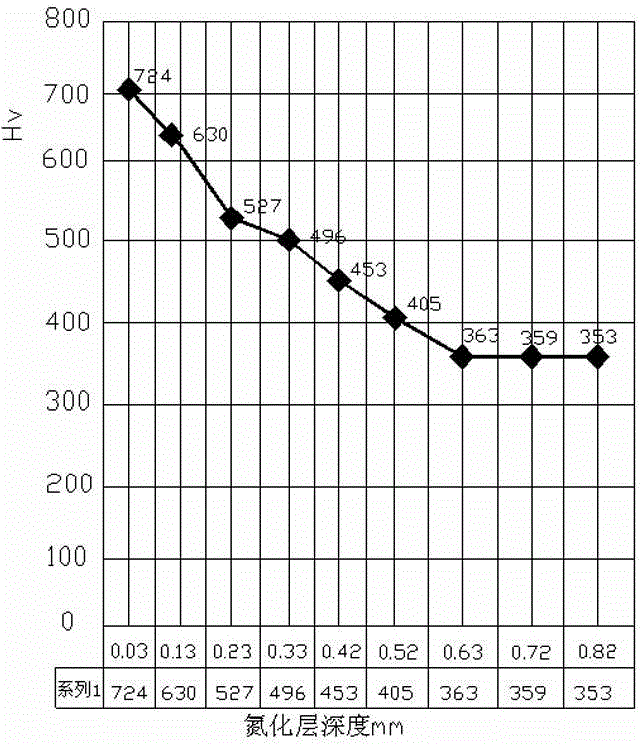
Patents
Literature
107results about How to "High nitriding efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Orientating silicon steel, manufacturing process and equipment
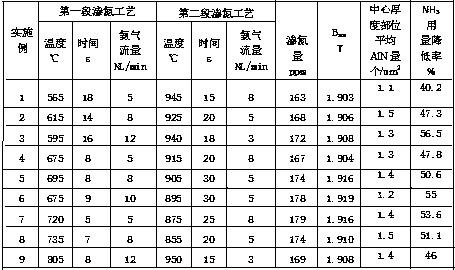
ActiveCN1796587AReduce energy consumptionReduce manufacturing costSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesSiliconHot rolled
This invention relates to an oriented silicon steel and its processing method and equipment. It comprises of 0.035~0.060% of C, 2.5~3.5% of Si, 0.08~1.8% of Mn, 0.005~0.010% of S, 0.015~0.035% of Al, 0.0050~0.0090% of N, 0.01~0.15% of Sn, 0.010~0.030% of P and 0.05~0.12% of Cu, with the rest iron. The processing method includes: a) smelting; b) hot rolling. Billets are heated to 1100~1200 deg.C and rolling temperature is lower than 1200 deg.C with a finishing temperature of above 850 deg.C and a coiling temperature of below 650 deg.C; c) normalizing. Hot-rolled boards are normalizing annealed at 1050~1180 deg.C for 1~20 seconds and 850~950 deg.C for 30~200 seconds and then cooled quickly; d) cold rolling. Boards are rolled to product thickness by one-off cold rolling or repetitious cold rolling with intermediate annealing; e) nitriding, decarbonization and high-temperature and hot-leveling annealing with boards coated with high-temperature annealing isolation agents mainly made of MgO.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for producing high magnetic induction grain-oriented silicon steel
The invention relates to a method for producing high magnetic induction grain-oriented silicon steel, and belongs to the technical field of silicon steel production. The process comprises the following steps of: smelting, refining, and performing continuous casting to obtain a casting blank; performing hot rolling; normalizing, namely performing normalizing annealing and cooling; performing cold rolling at one time, wherein the cold rolling reduction ratio is 85 to 90 percent; nitriding by using a nitriding medium, namely dry NH3 at the temperature of between 600 and 740 DEG C for 5 to 40 seconds; decarburizing at the temperature of between 750 and 850 DEG C for 60 to 360 seconds, wherein the dew-point temperature is 25 DEG C; and annealing at a high temperature, and coating a stress coating. The method has the advantages that: a plate blank low-temperature heating process of nitriding at the temperature of between 600 and 740 DEG C and decarburizing annealing is adopted, the nitriding of a steel plate is not influenced by an oxidation film, the steel plate is uniformly nitrided, and efficiency is high; by controlling the nitriding and decarburizing processes, an appropriate amount of effective (Al, Si) N inhibitor is formed, and high magnetic property is achieved; and nitriding is performed at a low temperature, so energy consumption is low, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Glass-film-free oriented silicon steel manufacture method and annealing isolation agent
ActiveCN102952931AGuaranteed decarbonization efficiencyImprove nitriding efficiencyNitrogen gasOxide
The invention discloses a glass-film-free oriented silicon steel manufacture method. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) smelting; (2) hot rolling and normalizing; (3) cold rolling; (4) decarburization and nitriding, wherein a cold-rolled sheet is subjected to decarburization annealing treatment in wet N2+H2 protective gas at 800 to 860 DEG C, and oxidation energy is controlled within 0.16 to 0.40; carbon in the steel sheet can be reduced to below 30ppm by the decarburization annealing treatment while an oxide layer mainly containing SiO2 is formed on the surface of the steel sheet, and the single-side oxygen content of the steel sheet is controlled to below 0.7g / m<2>; and continuous nitriding treatment is carried out on the steel sheet in ammonia-contained N2+H2 protective gas with oxidation energy of 0.05 to 0.15 to control the nitrogen content of the steel sheet within 180ppm to 280ppm; (5) application of an isolation agent; (6) high-temperature annealing and temperature rising and maintenance, wherein the steel sheet is heated to 1150 to 1250 DEG C in dry N2+H2 mixed atmosphere containing 50% to 90% of N2 and H2, is maintained at the 1150 to 1250 DEG C in pure hydrogen atmosphere for above 15 hours; and (7) coating of an insulation coating, stretching, leveling and annealing, thus obtaining the grain-oriented silicon steel product with an excellent magnetic property.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
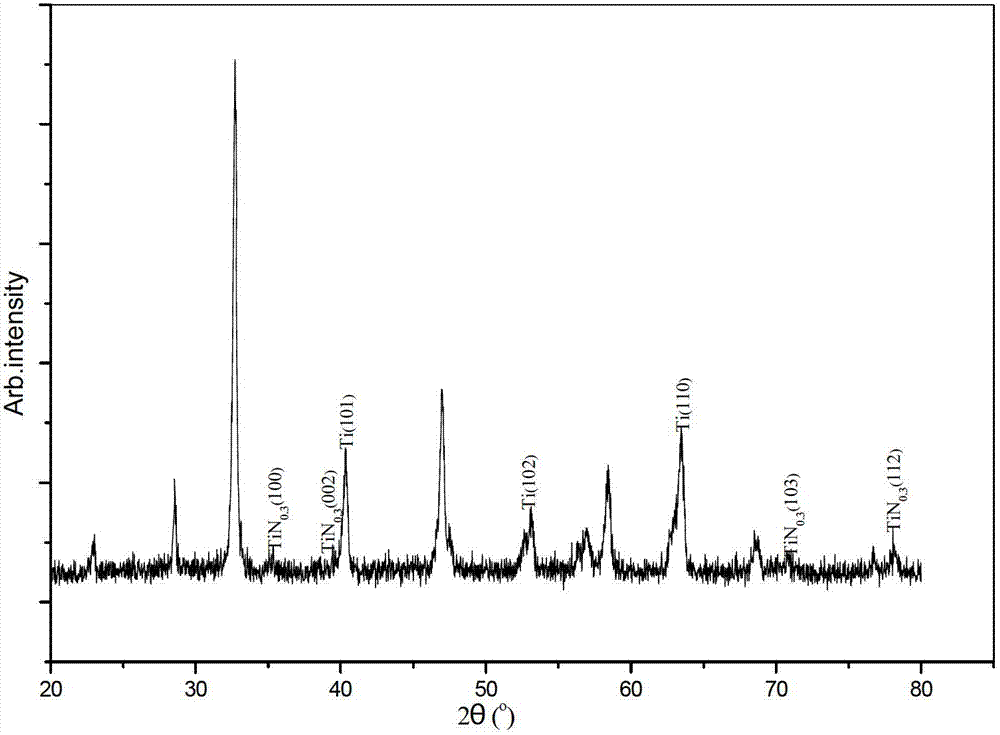
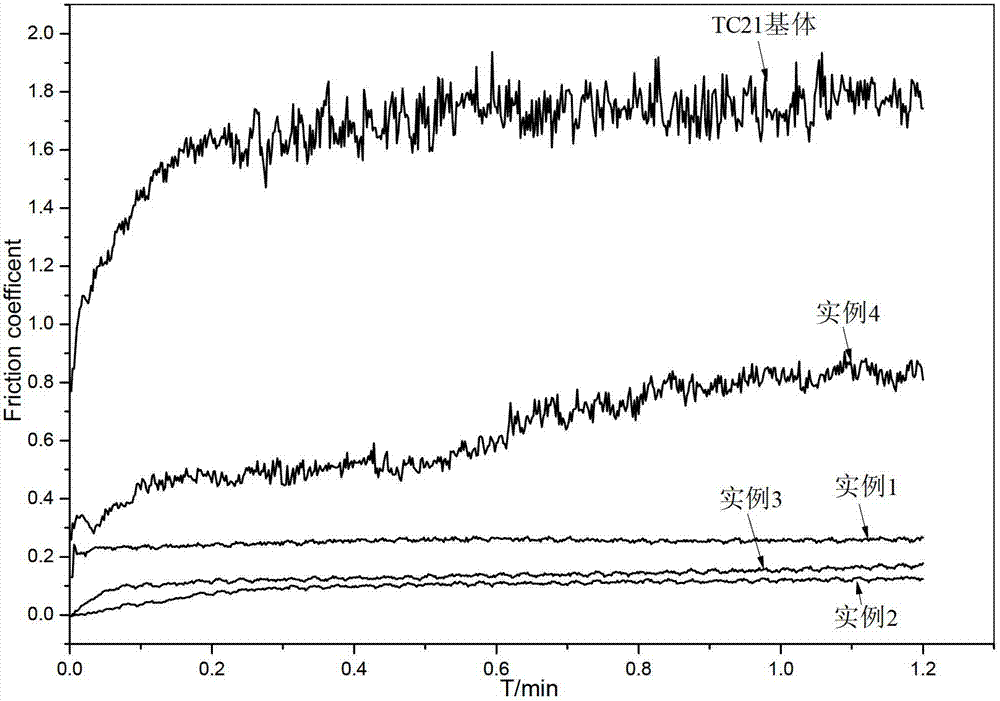
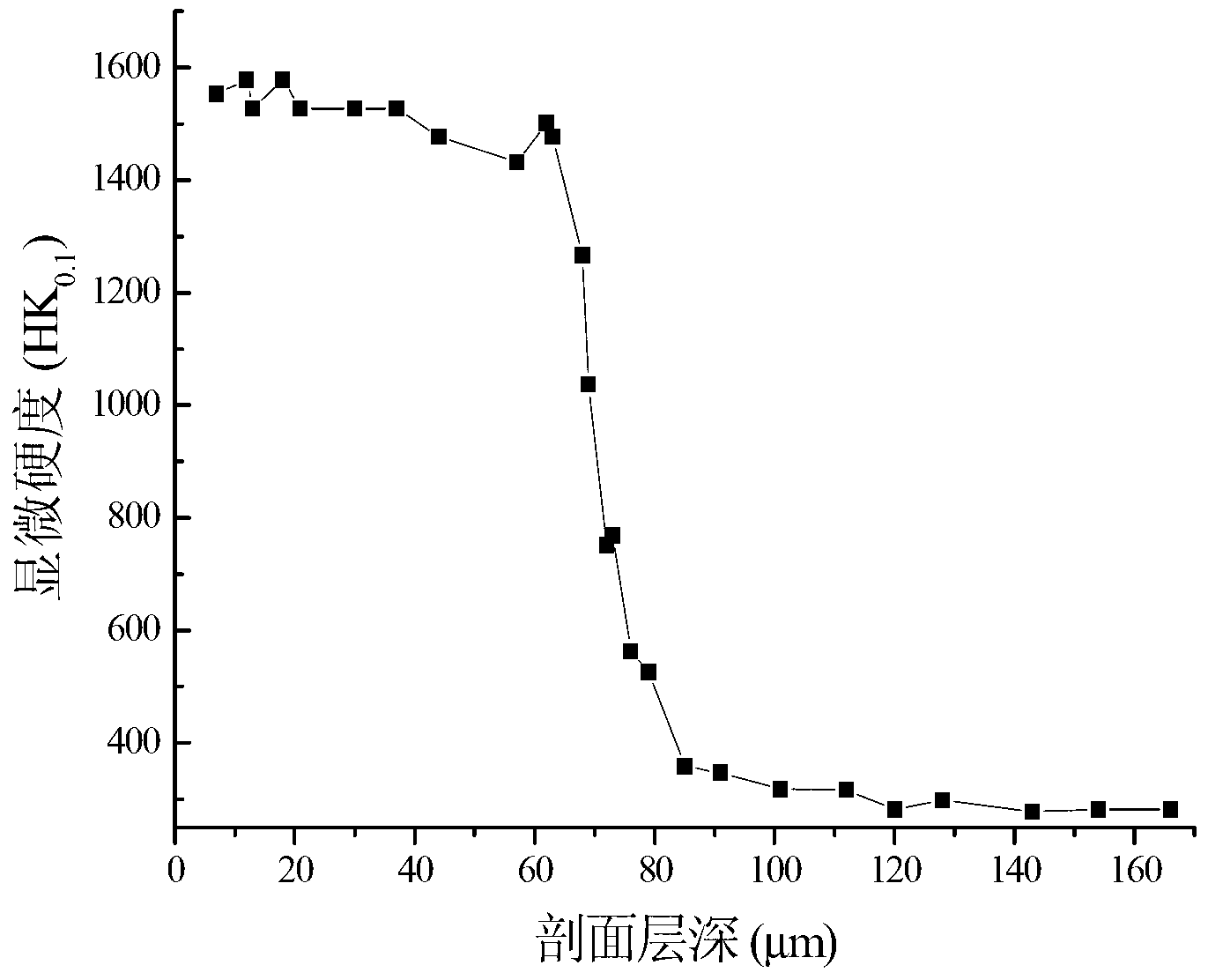
Low-temperature surface nitriding method of titanium alloy
ActiveCN102965613ASimple processImprove controllabilitySolid state diffusion coatingPtru catalystSand blasting
The invention discloses a low-temperature surface nitriding method of a titanium alloy, and belongs to the technical field of metal surface heat treatment and modification. The low-temperature surface nitriding method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, carrying out sand blasting cleaning on the surface of the titanium alloy, then carrying out chemical mechanical lapping and polishing, then mixing powder crystal sodium cyanate (NaCNO) and granular crystal potassium cyanate (KCNO) and rare earth CeO2 powder in a certain proportion so as to obtain a nitriding reagent, placing the nitriding reagent and the treated titanium alloy in a crucible for compacting and sealing, then drying, and placing the crucible in a high-temperature furnace for heating, wherein NaCNO and KCNO are used as nitriding sources, and rare earth CeO2 is used as a catalyst. According to the low-temperature surface nitriding method, a TiN 0.3-1 nitriding layer is formed on the surface of the titanium alloy TC21, the friction coefficient of the surface of the titanium alloy is remarkably reduced, the surface hardness is increased, and the surface property is enhanced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
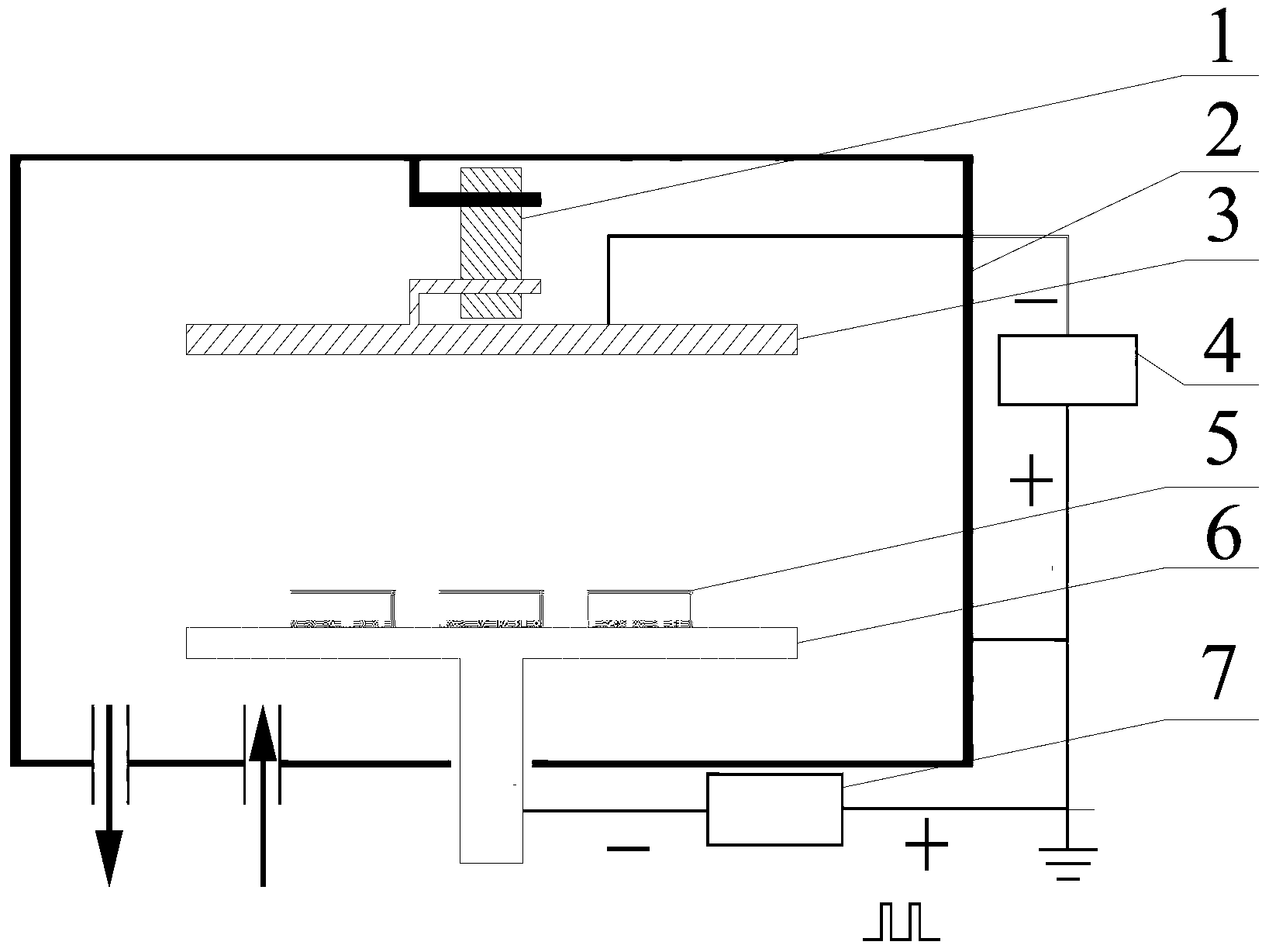
Low-temperature and low-pressure ion nitriding method and device for stainless steel workpiece
InactiveCN103305786AIncrease ionization rateRealize nitriding treatmentSolid state diffusion coatingPulse power supplyVacuum chamber
The invention discloses a low-temperature and low-pressure ion nitriding method and a low-temperature and low-pressure ion nitriding device for a stainless steel workpiece. A nitriding vacuum chamber of the low-temperature and low-pressure ion nitriding device for the stainless steel workpiece can be vacuumized to keep constant air pressure; nitrided stainless steel can be placed on a sample platform; a negative electrode of a pulse power supply is connected with the sample platform; a negative electrode of a direct current power supply is connected with an auxiliary cathode titanium plate; the auxiliary cathode titanium plate is suspended in the nitriding vacuum chamber through an insulating ceramic suspension rod; the nitrided stainless steel is placed on the sample platform; and an appropriate distance is formed between the auxiliary cathode titanium plate and the nitrided stainless steel. In the nitriding process, the stainless steel workpiece subjected to low-temperature and low-pressure ion nitriding is obtained by controlling process parameters. According to the method and the device, the corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance and fatigue resistance of stainless steel are improved, and the nitriding surface of the obtained stainless steel workpiece is clean and bright.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Low-temperature rapid ion nitriding method of austenitic stainless steel
InactiveCN103233197AImprove diffusion abilityHigh energySolid state diffusion coatingVacuum pumpAustenite
The invention relates to a surface treatment method and particularly relates to a low-temperature rapid ion nitriding method of austenitic stainless steel. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a thicker ion nitriding layer can be obtained by changing gas pressure in an ion nitriding furnace and performing heat preservation for a period of time at the ion nitriding temperature of 350-370 DEG C. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly removing oil stains on the austenitic stainless steel, performing pre-grinding treatment on a test sample, and then performing ultrasonic cleaning and drying in an organic solvent; then placing the well prepared test sample into a vacuum chamber of an ion nitriding device, performing vacuum-pumping operation to the required vacuum degree, and then introducing hydrogen to perform ion bombard cleaning; and finally adjusting ion nitriding pressure and heat preservation time during the low-temperature ion nitriding process to obtain the thicker nitriding layer so as to solve the problems of thin ion nitriding layer and poor wear resistance under low-temperature conditions. By using the method disclosed by the invention to perform ion nitriding and respectively perform heat preservation for 4h, 6h and 8h, the maximum thickness of the nitriding layer can respectively achieve 22.2 mu m, 29.6 mu m and 51.7 mu m.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for producing high magnetic induction grain-oriented silicon steel by low temperature heating
ActiveCN101748259AImprove nitriding efficiencyUniform surfaceSolid state diffusion coatingSteel platesLubrication
The invention discloses a method for producing high magnetic induction grain-oriented silicon steel by low temperature heating, which comprises the following steps: heating a grain-oriented silicon steel plate blank produced by a common process; performing hot rolling; annealing or normalizing the hot-rolled plate, performing one-pass cold rolling with heavy reduction rate, and rolling the plate into the thickness approximate to that of a finished product; decarburizing in wet atmosphere; nitriding and coating a parting agent; and finally performing high temperature annealing. The method is characterized in that: the heating temperature for the plate blank is controlled to below 1,280 DEG C; before the nitriding, the decarburized plate is subjected to 1.5 to 3 percent critical deformation cold rolling to damage a SiO2 film under the condition of no lubrication; and the parting agent is Al2O3 fine particles with the size less than 10 mu m, and 5 to 30 weight percent of TiO2 is added into the Al2O3 fine particles. The method solves the problem that the SiO2 film is formed on the surface of the decarburized plate to barrier the nitriding; and a glass film underlayer with good performance is obtained simultaneously.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
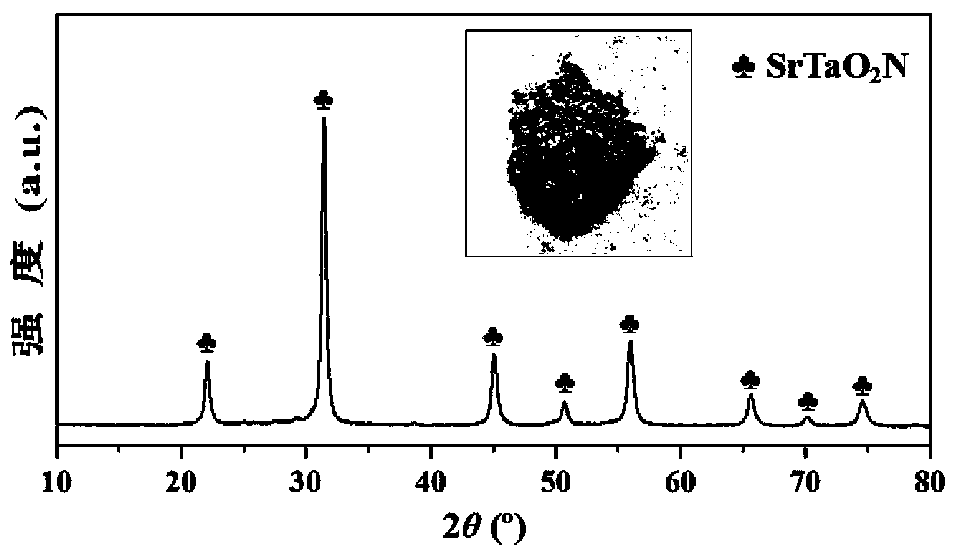
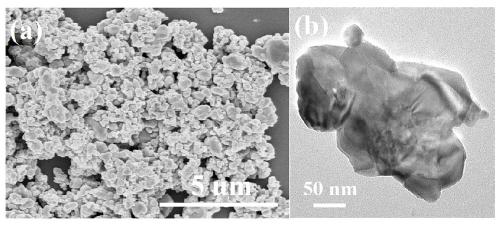
SrTaO2N oxynitride nano powder and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109928761AHigh purityEfficient removalMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen and non-metal compoundsAlcoholAlkaline earth metal
The invention discloses a preparation method of SrTaO2N oxynitride nanopowder, the preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, dissolving an alkaline earth metal salt, a tantalum salt and anitrogen source I in an alcohol, and drying after ball milling to obtain a mixed precursor; and S2, putting the mixed precursor obtained in the step S1 and a nitrogen source II in a reaction vessel and calcining in a protective atmosphere to obtain the SrTaO2N oxynitride nanopowder; the mixed precursor is spaced apart from the nitrogen source II. The product prepared by the preparation method hashigh purity and good dielectric properties.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Induction heating nitriding method for oriented silicon steel
InactiveCN107858633AReduce consumptionEvenly distributedSolid state diffusion coatingDecarburizationSteel plates
Disclosed is an induction heating nitriding method for oriented silicon steel. The method comprises the steps that smelting and continuous casting are carried out, then a casting blank is heated, andthen subjected to hot rolling, normalizing, cold rolling and decarburization; and in an induction nitriding furnace, two stages of nitriding treatment are carried out: natural cooling to room temperature under dry N2 atmosphere, applying isolating agent, and high temperature purification annealing for standby use. Nitrides obtained by the nitriding method are numerous and evenly distributed, and the depth of a nitriding layer can reach the central part of the steel plate thickness, AlN particles on the central part of the steel plate thickness reach 1-1.5 per square micron, and the final magnetic performance is stable, and the deviation is small, that is, the fluctuation between batches does not exceed 0.02 T; at the same time, the consumption of ammonia gas is reduced by not less than 40%, and the operation is simple, the implementation is easy, and mass production is easy to realize.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Method for preparing iron nitride magnetic powder through low-temperature plasma nitriding
ActiveCN106086776ASolve the bottleneck problem of decomposition inefficiencyHigh nitriding efficiencyTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusHydrogenIron powder
The invention relates to a method for preparing iron nitride magnetic powder through low-temperature plasma nitriding. The method comprises the following steps that atomized iron powder, hydroxy iron powder or reduced iron powder of which the average particle size is 2-80 microns is used as a raw material; O2 is introduced, and the raw material is oxidized for 1-10 h at 300-400 DEG C to obtain ferric oxide powder; hydrogen is introduced, the ferric oxide powder is reduced for 4-20 h at 300-400 DEG C to obtain iron powder; the low-temperature plasma nitriding temperature is controlled to 120-200 DEG C, and the low-temperature plasma nitriding time is 1-30 h; and the nitrided iron powder is cooled to room temperature in a furnace, and a sample is taken out. Low-temperature plasma nitriding is conducted, the bottleneck problem that the ammonia dissolving efficiency in the ammonia nitriding method is low is solved, and the nitriding efficiency is effectively improved.
Owner:东阳市顶峰磁材有限公司
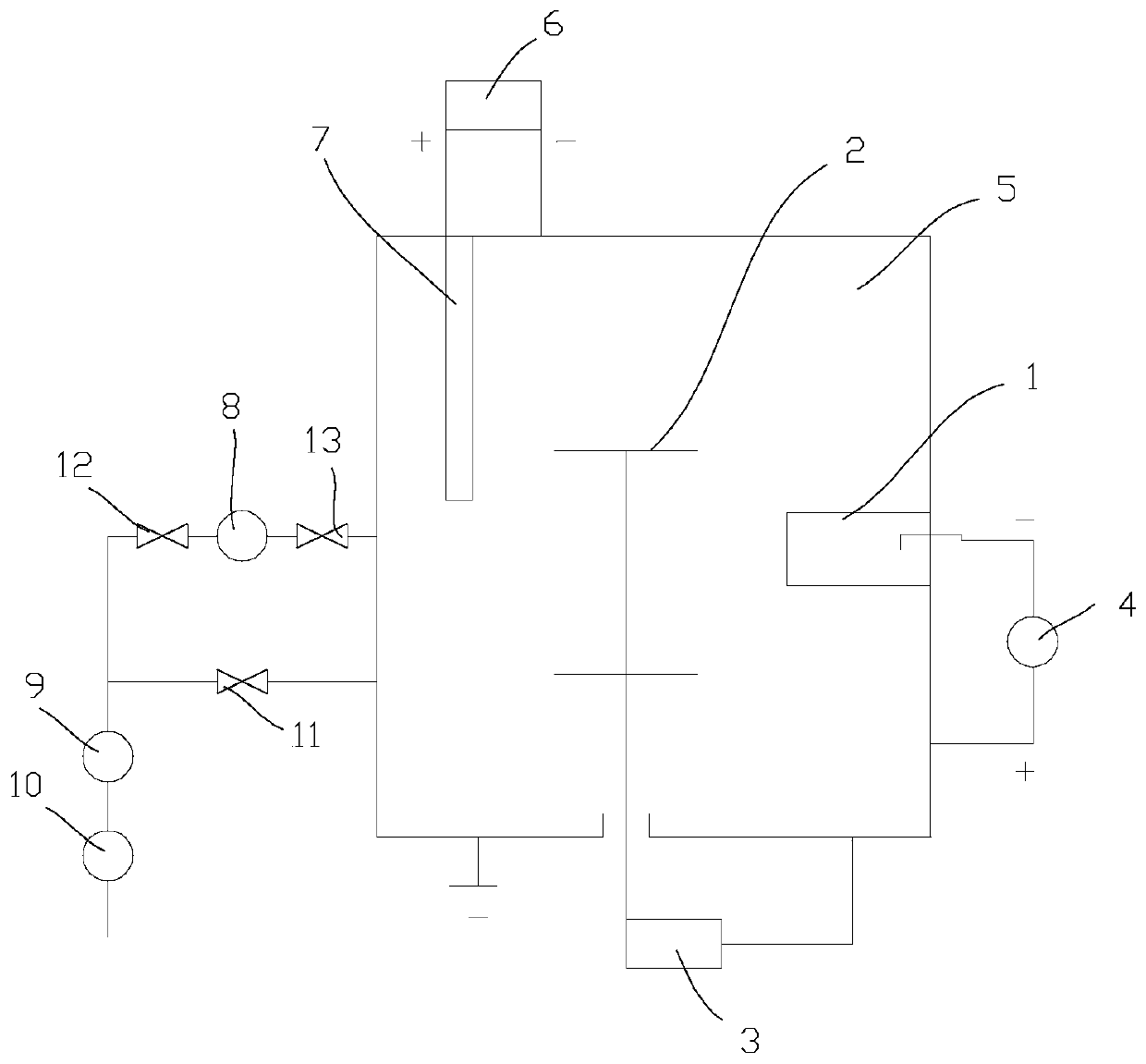
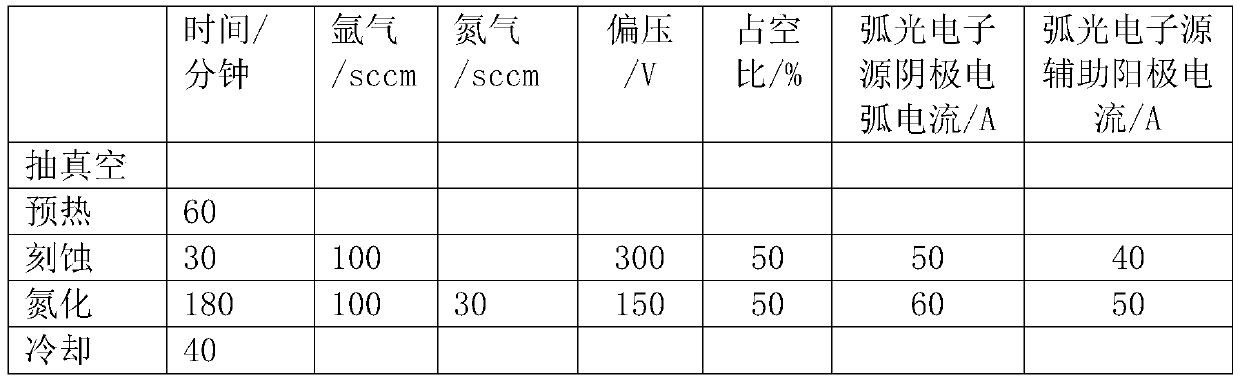
Ionic nitriding technology assisted by arc electron source
ActiveCN109797363AReduce consumptionIncrease ionization rateSolid state diffusion coatingNitrogen gasSupply current
The invention provides an ionic nitriding technology assisted by an arc electron source. The ionic nitriding technology assisted by the arc electron source comprises the steps that S1, vacuumizing iscarried out; S2, preheating is carried out; S3, mechanical corrosion is carried out, specifically, argon is pumped to keep vacuum of 0.1-1Pa, the temperature is 200-600 DEG C, a bias voltage is applied between a workpiece and a cavity body, meanwhile, a furnace inner arc electron source is started, a main power supply current is 40-150 A, and arc discharge plasma is generated; an auxiliary anode electrode power supply is turned on, a current is 10-100 A, an electron current in the arc discharge plasma is led to enter a nitriding chamber space, and ironic bombardment mechanical corrosion is carried out on the workpiece for 5-30mins; S4, nitriding is carried out, the furnace inner temperature is kept 200-600 DEG C, the argon and nitrogen are pumped, the vacuum degree is kept at 0.1-1Pa, a voltage is applied between the workpiece and the cavity by a direct current bias voltage power supply, the arc electron source main power supply is turned on, the current is 40-150 A, and the arc discharge plasma is generated; the auxiliary anode electrode power supply is turned on, the current is 10-100A, the electron current of the arc discharge plasma is led to enter the nitriding chamber space,and ironic nitriding is carried out for 0.5-6 hours; and S5, cooling is carried out below 250 DEG C. According to the ionic nitriding technology assisted by the arc electron source, a glow discharge plasma can be enhanced, the reactivity is improved, time is shortened, and gas and energy consumption are reduced.
Owner:DONGGUAN HUICHENG VACUUM TECH
Preparation method of low-oxygen vanadium-nitrogen alloy
Provided is a preparation method of a low-oxygen vanadium-nitrogen alloy. According to the method, powder-like vanadium compound and carbonaceous powder are added into a vacuum induction heating furnace according to a certain proportion to be subjected to a carbonization reaction; then a forming agent and wet milling media are mixed and added into a wet mill to be subjected to wet milling treatment, and then spraying drying is performed so that vanadium carbide particles can be manufactured; then a forming agent desorption process, a pre-sintering process and a nitriding process are sequentially performed in a vacuum dewaxing and sintering integrated furnace; and finally the low-oxygen vanadium-nitrogen alloy is made. By adopting the preparation method of the low-oxygen vanadium-nitrogen alloy, temperatures of the carbonization reaction and a nitridation reaction can be effectively lowered, and the oxygen content of the finished vanadium-nitrogen alloy is substantially lowered.
Owner:HUNAN ZHONGXIN NEW MATERIALS TECH
45 steel transmission shaft quick ion nitriding method
InactiveCN106086777AFast nitridingLower activation energySolid state diffusion coatingOrganic solventHydrogen
The invention relates to a 45 steel transmission shaft quick ion nitriding method. A 45 steel transmission shaft is sampled to machine and cut as a sample; oil stains on the surface of the sample are removed; the thermal refining and the polishing are performed for the sample in sequence, and the polished sample is ultrasonically cleaned and dried in organic solvent; the sand blasting is performed for the sample, and then, the sample is ultrasonically cleaned and dried in the organic solvent after sand blasting; the sample in positioned in an ion nitriding furnace, hydrogen is sputtered, and dry air is introduced for ion preoxidizing; and the ion nitriding surface treatment is performed to cool the sample to reach the room temperature. The 45 steel transmission shaft quick ion nitriding method has the following beneficial effects: the operation flow is simple and convenient; gas adopted by the ion preoxidizing is air, so that the acquisition is easy, the cost is low, and the nitriding speed and the nitriding layer thickness can be increased in a short time; and the 45 steel transmission shaft quick ion nitriding method has the advantages of high efficiency and energy conservation, and can realize large-area industrial production.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Gas soft nitriding process for stainless steel part
ActiveCN106011731AUniform Depth ControlDepth control is stable and evenSolid state diffusion coatingNitrogenQuality performance
The invention discloses a gas soft nitriding process for a stainless steel part. According to the gas soft nitriding process for the stainless steel part, a nitriding carburized layer of gas nitrocarburizing of the stainless steel part is uniform; the consumption of gas raw materials is low; the single charging quantity is large; the nitriding efficiency is high; the nitriding time is short; and meanwhile, the advantages that pollution to the environment is little, corrosion of the production process to equipment is little, and product quality performance is high are achieved.
Owner:XINAN TOOLS GUIZHOU PROV
Large-deformation enhanced rapid ion nitriding method
ActiveCN109371212AImproves strength and hardnessHigh chemical activitySolid state diffusion coatingDislocationIon
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal surface treatment, and relates to a large-deformation enhanced rapid ion nitriding method. The large-deformation enhanced rapid ion nitriding method comprises the specific steps that original steel is machined and cut into a plate shape; plate-shaped to-be-nitrided steel is subjected to solution treatment; solid-solution-state to-be-nitrided steel is placed in a cold rolling machine to be subjected to cold rolling treatment; and the large-plastic-deformation to-be-nitrided steel obtained after cold rolling treatment is machined and cut intoa sample, and then ion nitriding treatment is conducted. According to the method, the large plastic deformation treatment is conducted before ion nitriding, the dislocation density in a microstructure is obviously increased, grains are obviously refined, in the nitriding process, a rapid diffusion channel is provided for nitrogen atoms through high-density dislocation and other defects, the ion nitriding efficiency is obviously improved, and the thickness of a nitriding layer is improved; and under the situation that the same nitriding layer depth is obtained, the nitriding time can be greatly shortened, accordingly, the energy is saved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of samarium-iron-nitrogen series permanent magnet material
ActiveCN107557551AIncrease the amount of nitridingImprove uniformitySolid state diffusion coatingMagnetic materialsDecompositionShear band
The invention discloses a preparation method of a samarium-iron-nitrogen series permanent magnet material. The method comprises the steps that metastable state samarium-iron alloy is subjected to severe plastic deformation and then is subjected to nitrogen treatment and annealing crystallization treatment, and therefore the samarium-iron-nitrogen series permanent magnet material can be obtained. In the method, when the deformed samarium-iron-nitrogen series permanent magnet material is subjected to nitrogen treatment, since the free volume 'defect' content in the metastable state alloy can beincreased through multiple shear bands produced in the severe plastic deformation process, entering and diffusion of nitrogen atoms are facilitated, and the nitriding amount and nitriding uniformity of the alloy can be remarkably improved; since the multiple shear bands are produced through the severe plastic deformation, the follow-up crystallization annealing temperature can also be reduced, andnitride is reduced or prevented from being produced; and generation of the metastable phase is restrained, grains are refined, and coercive force is improved. By means of the method, the nitriding speed can be improved, the nitriding temperature can be reduced, decomposition of a samarium-iron-nitrogen compound is restrained, the microstructure is refined, and the nitriding efficiency of samarium-iron alloy for preparing the samarium-iron-nitrogen magnetic material is improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Electric pulse-assisted nitriding method of austenitic stainless steel
InactiveCN103741092AFacilitated DiffusionHigh energySolid state diffusion coatingPulse parameterElectrical impulse
An electric pulse-assisted nitriding method of austenitic stainless steel comprises the following steps: preparing a nitriding medium, uniformly mixing wood chips, urea, sodium carbonate and ammonium chloride according to a mass ratio of 10:6:3:1; turning on a heat treatment furnace power supply to increase the temperature in the furnace to 500-700 DEG C, performing heat preservation for 1 hour, then performing electric pulse treatment for 10 minutes with pulse parameters of 6.5-9 KV of voltage and 7-10 Hz of frequency, stopping electric pulse, waiting for 50 minutes, then performing electric pulse treatment for 10 minutes with the same parameters, and repeating the above treatment for more than four times. The method of the invention improves the nitriding efficiency, shortens the nitriding time, and greatly reduces the energy consumption.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Rapid nitriding process
InactiveCN103981480AShorten nitriding timeHigh nitriding efficiencySolid state diffusion coatingElectricityElectrolysis
The invention provides a rapid nitriding process, and belongs to the technical field of heat treatment. The rapid nitriding process includes: a step A that an electrolyte is added to an electrolysis container, the electrolysis container is then sealed, an electric heating device is arranged on the side portion of the electrolysis container, and a natural gas heating device is arranged at the bottom of the electrolysis container; a step B that external ammonia gas is sent to a gas outlet pipe through a valve, the whole electrolysis container and a whole nitrogenation oven are filled with the ammonia gas in a circulating mode, and then the valve is closed; a step C that a controller controls the natural gas heating device to heat the electrolyte to the boiling point, and then the controller drives an electrolysis rod to work and conduct electrolysis; a step D that the controller controls the natural gas heating device and the electric heating device to conduct alternative heating so that the concentration of nitrogen atoms can be increased; and a step E that an air blower is started so that the ammonia gas and the generated nitrogen atoms can be mixed in water vapor and unceasingly sent to the nitrogenation oven, and closed type circulation is achieved through cooperation of the gas outlet pipe and a gas inlet pipe. Thus, the nitrogen atoms in the nitrogenation oven can be unceasingly supplemented, the nitridation time can be shortened by half, and the defect that the cost is high due to the fact that ammonia gas is unceasingly conveyed in the conventional process is overcome.
Owner:浙江省舟山中学
Method for smelting COST-FB2 steel through gas-phase nitriding under negative pressure condition
ActiveCN110093582APrecise temperature controlUniform compositionSolid state diffusion coatingGas phaseManganese
The invention relates to a method for smelting COST-FB2 steel through gas-phase nitriding under a negative pressure condition. The method comprises the following steps that firstly carbon deep deoxidation is performed under the condition of high vacuum degree, deoxidation is completed after the surface of molten steel is stable and bubbles do not rush out any longer; then an alloy element for promoting nitrogen dissolution is added and completely molten, and then gas-phase nitriding is started; during gas-phase nitriding, nitriding pressure during gas-phase nitriding is calculated by using thermodynamic calculation software Factsage, the molten steel temperature is accurately controlled, and the nitriding time is calculated and determined through the surface area of the molten steel, the volume of the molten steel and the nitrogen balance content; when gas-phase nitriding is about to be completed, the alloy element boron and the volatile manganese are added, then through argon filling,pressurization is performed until the high pressure is reached, pressurization casting is performed under the condition that the nitrogen partial pressure is kept unchanged, the under-pressure stateis kept in the solidification process, vacuum breaking is performed after complete solidification, and a COST-FB2 steel cast ingot which has the content of N being 0.015%-0.03% and the content of O being less than or equal to 0.0035%, is uniform in component and compact in structure is prepared.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
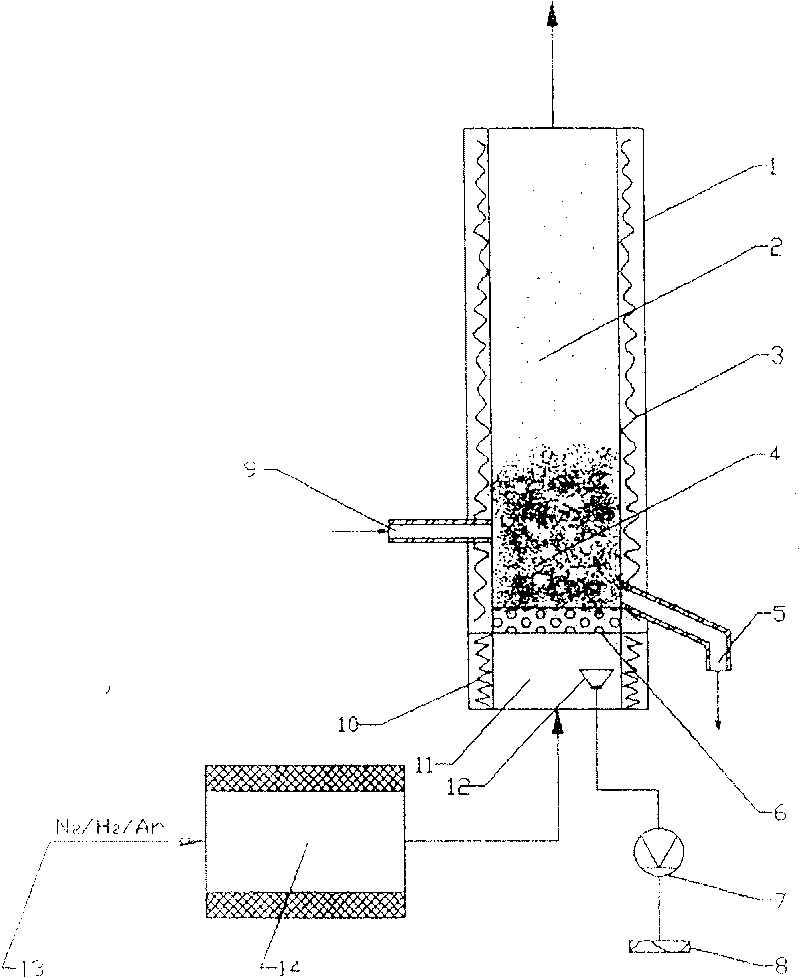
Method for producing zirconium nitride powder
The invention discloses a method for producing zirconium nitride powder, which comprises the following steps of: crushing sponge zirconium into granules with the granularity of less than 3mm, putting the crushed sponge zirconium granules into a vacuum furnace, supplying power for raising the temperature when the vacuum degree is 5 to 40Pa, keeping the temperature at the pre-nitrogenization temperature, stopping vacuumizing, and introducing nitrogen into the furnace for a pre-nitrogenization reaction; after the pre-nitrogenization, cutting off the power for reducing the temperature to 80 DEG C, and discharging; crushing the pre-nitrogenized materials into powder with the granularity of less than 0.075mm, putting the powder into the vacuum furnace, supplying power for raising the temperature to between 500 and 700 DEG C within 2 to 5 hours when the vacuum degree is 5 to 40Pa; stopping vacuumizing, introducing nitrogen into the furnace continuously raising the temperature to the nitrogenization temperature within 3 to 6 hours, and continuously introducing the nitrogen for nitrogenization; after the nitrogenization, cutting off the power for reducing the temperature, continuously introducing the nitrogen in the process of reducing the temperature, and discharging a zirconium nitride clinker when the temperature is reduced to 80 DEG C; and crushing the zirconium nitride clinker so as to prepare the zirconium nitride powder.
Owner:锦州市金属材料研究所
Steel cylinder jacket surface treatment process
InactiveCN101135037AAchieve recyclingImprove wear resistanceSolid state diffusion coatingManufacturing technologyPiston ring
The present invention is surface treatment process for cylinder jacket of steel, and belongs to the field of diesel engine accessory making technology. The surface treatment process for cylinder jacket of steel features the soft gas nitridizing process or carbonitriding process. The present invention has reasonable design, and is smart, simple and feasible. The present invention can form one nitride layer with thickness of 0.1-0.4 mm, hardness up to HV600-700, and capacity of raising the mechanical performance and wear resistance of the cylinder jacket, increasing its service life and raising the piston ring matching performance.
Owner:莱阳市永立精工汽车配件有限公司
Vanadium nitride and ferrovanadium nitride alloy reinforcing agent and preparing method and application thereof
The invention discloses a vanadium nitride and ferrovanadium nitride alloy reinforcing agent and a preparing method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of special alloy materials. The reinforcing agent comprises 23%-66% of Si, 0.1%-17.5% of Mn, 11%-37% of N, 0%-9.6% of Ti, 0%-7.3% of Cr, 0.03%-5.6% of Al, 0.1%-1.9% of C, smaller than or equal to 0.10% of P, smaller than or equal to 0.15% of S and the balance Fe and impurities. Nitrogen fixation alloy elements such as the element Si and the element Mn are preferably selected, and nitride is formed by the N and the nitrogen fixation alloy elements. Preferable selection of the nitrogen fixation alloy elements mainly has the following beneficial effects that the combination rate of the nitrogen fixation alloy elements and the N is high; secondly, the nitrogen fixation alloy elements are beneficial to and harmless to molten steel; and thirdly, the thermodynamics environment of molten steel deoxidization, desulfuration vanadium nitride optimization and vanadium nitride iron microalloying is facilitated, more nitrogen ions can be cured, and the utilization rate of the alloy elements is greatly increased.
Owner:马鞍山市恒兴耐火炉料厂
Orientating silicon steel, manufacturing process and equipment thereof
ActiveCN100381598CHigh nitriding efficiencyNitriding is goodSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesSiliconHot rolled
This invention relates to an oriented silicon steel and its processing method and equipment. It comprises of 0.035~0.060% of C, 2.5~3.5% of Si, 0.08~1.8% of Mn, 0.005~0.010% of S, 0.015~0.035% of Al, 0.0050~0.0090% of N, 0.01~0.15% of Sn, 0.010~0.030% of P and 0.05~0.12% of Cu, with the rest iron. The processing method includes: a) smelting; b) hot rolling. Billets are heated to 1100~1200 deg.C and rolling temperature is lower than 1200 deg.C with a finishing temperature of above 850 deg.C and a coiling temperature of below 650 deg.C; c) normalizing. Hot-rolled boards are normalizing annealed at 1050~1180 deg.C for 1~20 seconds and 850~950 deg.C for 30~200 seconds and then cooled quickly; d) cold rolling. Boards are rolled to product thickness by one-off cold rolling or repetitious cold rolling with intermediate annealing; e) nitriding, decarbonization and high-temperature and hot-leveling annealing with boards coated with high-temperature annealing isolation agents mainly made of MgO.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Zirconium nitride powder and method for producing same
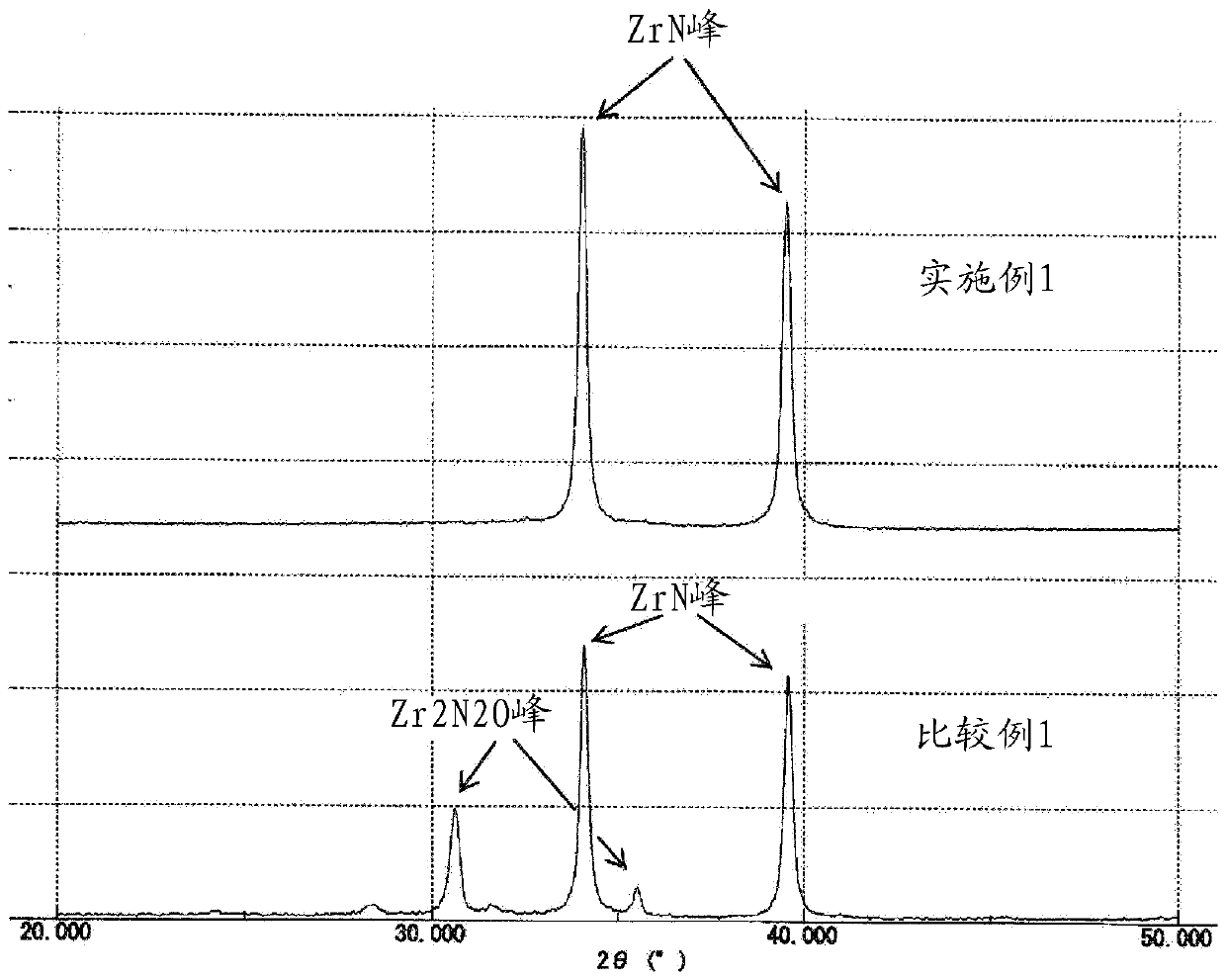
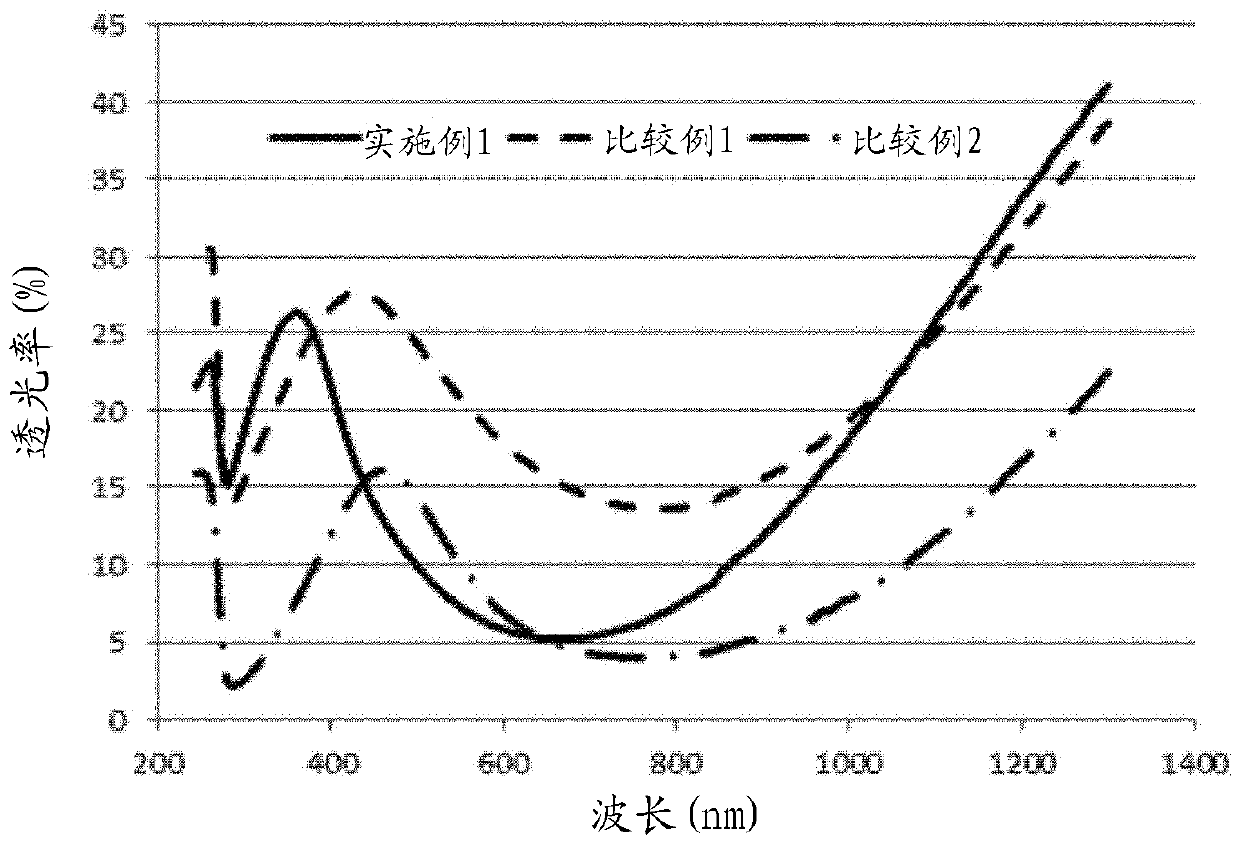
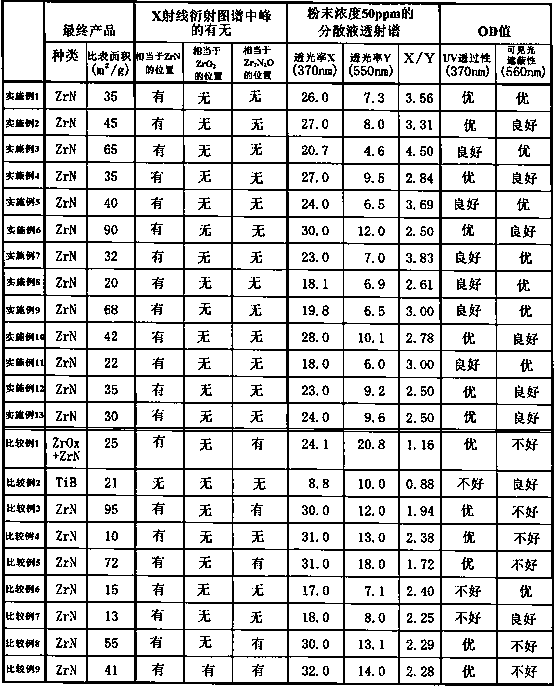
ActiveCN109923062AHigh resolutionGood shading effectPigmenting treatmentNitrogen compoundsPhysical chemistryTransmittance
A zirconium nitride powder which has a specific surface area of 20 to 90 m2 / g as measured by a BET method, has a peak corresponding to zirconium nitride but does not have a peak corresponding to zirconium dioxide, a peak for lower zirconium oxide or a peak corresponding to lower zirconium oxynitride in an X-ray diffraction profile, and the light transmittance X at 370 nm is at least 18%, the lighttransmittance Y at 550 nm is 12% or less and the ratio (X / Y) of the light transmittance X at 370 nm to the light transmittance Y at 550 nm is 2.5 or more in the transmission spectra of a dispersion that contains the powder at a concentration of 50 ppm.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS ELECTRONICS CHEM CO LTD
Apparatus for direct preparing silicon nitride by fluidized bed and process
InactiveCN1974379BStrong gas-solid reactionEnhance heat and mass transferNitrogen compoundsHydrogenFluidized bed
The present invention is fluidized bed apparatus and process for preparing silicon nitride directly. The fluidized bed has the features of strong gas-solid reaction, high heat transfer and mass transfer effect and homogeneous temperature. In a high temperature fluidized bed at 1000-1650 deg.c, silicon powder is nitrided directly to produce silicon nitride powder. The reacted silicon powder of diameter before sintering smaller than 10 micron and average diameter after sintering in 300-500 micron is fed to the fluidized bed directly. The fluidized bed gas consists of nitrogen in 10-100 vol%, hydrogen in 0-60 vol% and Ar in the balanced amount. The silicon powder fluidizing bed is fluidized in sound forced mode. The present invention can produce homogeneous silicon nitride powder of high quality in high efficiency, and has wide industrial application foreground.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for producing oriented silicon steel with good bottom by low-temperature heating
ActiveCN100455702CHigh nitriding efficiencyEfficient formationSolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesMetallurgyHot Temperature
The invention supplies a method used to produce orientation silicon steel by low temperature heating. It includes the following steps: heating the plate blank under 1280 degree centigrade; hot rolling; once or double cold rolling to gain finished product sheet thickness; nitriding treatment; decarburizing annealing; coating insulator; high temperature annealing. In the nitriding technology, heating area dew point is controlled at -15-40 degree centigrade. The invention has the advantages of high nitriding efficiency, no influence from the surface oxide film, excellent MgO coat formula which makes the magnesium silicate substrate have good magnetic property, ensure the implementation for the next hot leveling annealing and insulating coating.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
QPQ salt bath nitriding optimization treatment method and device through laser shock peening
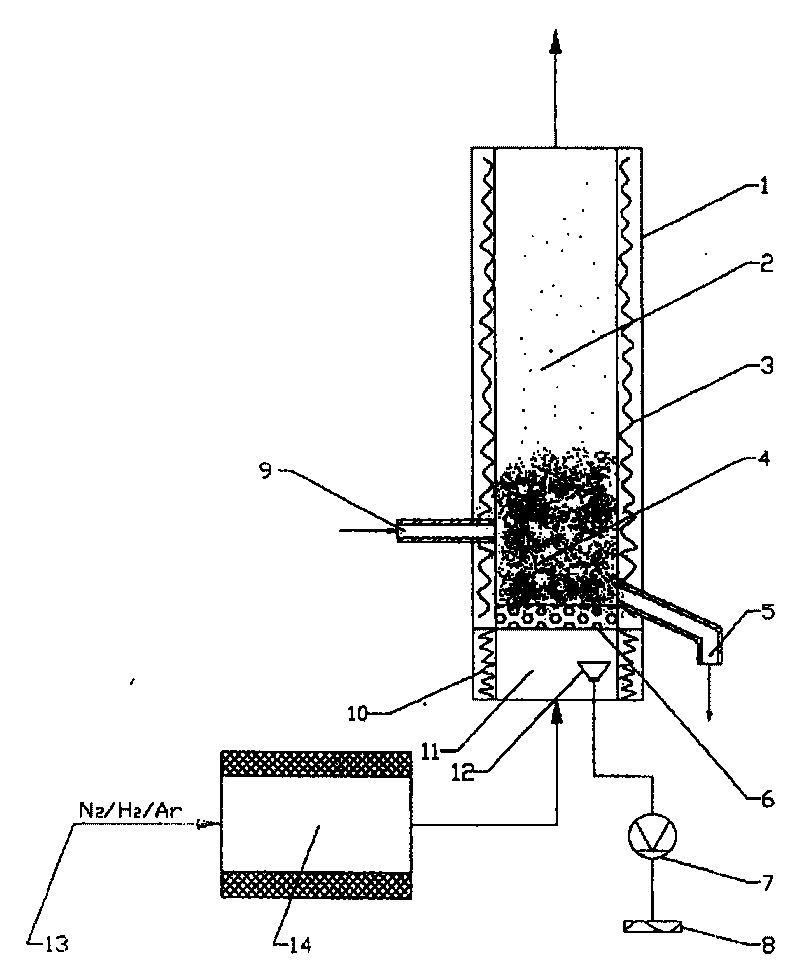
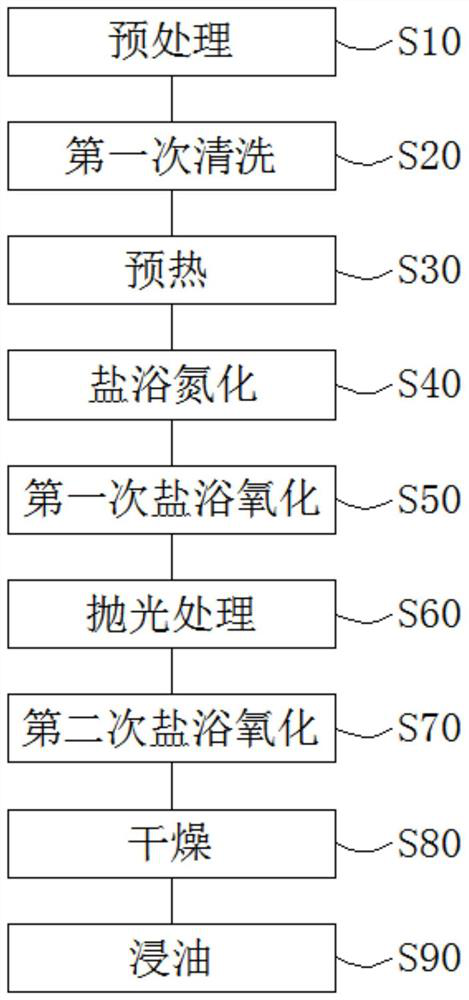
PendingCN111945106AImprove adaptabilityRealize omni-directional scanningSolid state diffusion coatingCurrent electricPeening
The invention discloses a QPQ salt bath nitriding optimization treatment method through laser shock peening. The QPQ salt bath nitriding optimization treatment method comprises the following steps that shock peening treatment is conducted on a workpiece by using a laser device to enable the surface of the workpiece to be dislocated; the workpiece is deoiled, cleaned and dried; the workpiece is putinto a preheating furnace for preheating; the workpiece is put into a direct-current electric field salt bath nitriding furnace, wherein the temperature in the furnace is 500-580 DEG C; the temperature is reduced to 400-450 DEG C for oxidation treatment, and the workpiece is taken out to be cleaned so as to remove CN<-> or CNO<->; the surface of the workpiece is polished; the workpiece is put into the direct-current electric field salt bath nitriding furnace, oxidation treatment is conducted on the workpiece again at the temperature of 300-400 DEG C, and the workpiece is cleaned to remove CN<-> or CNO<->; drying is conducted; and oil immersion is conducted. Compared with the prior art, the QPQ salt bath nitriding optimization treatment method has the advantages that the nitriding efficiency and the nitriding layer thickness are improved, and energy conservation and high efficiency are realized. The invention further provides a QPQ salt bath nitriding optimization treatment device.
Owner:湖南申亿精密零部件股份有限公司
Laser treatment method for raising stress corrosion resistance and abrasive resistance of nuclear power 690 alloy
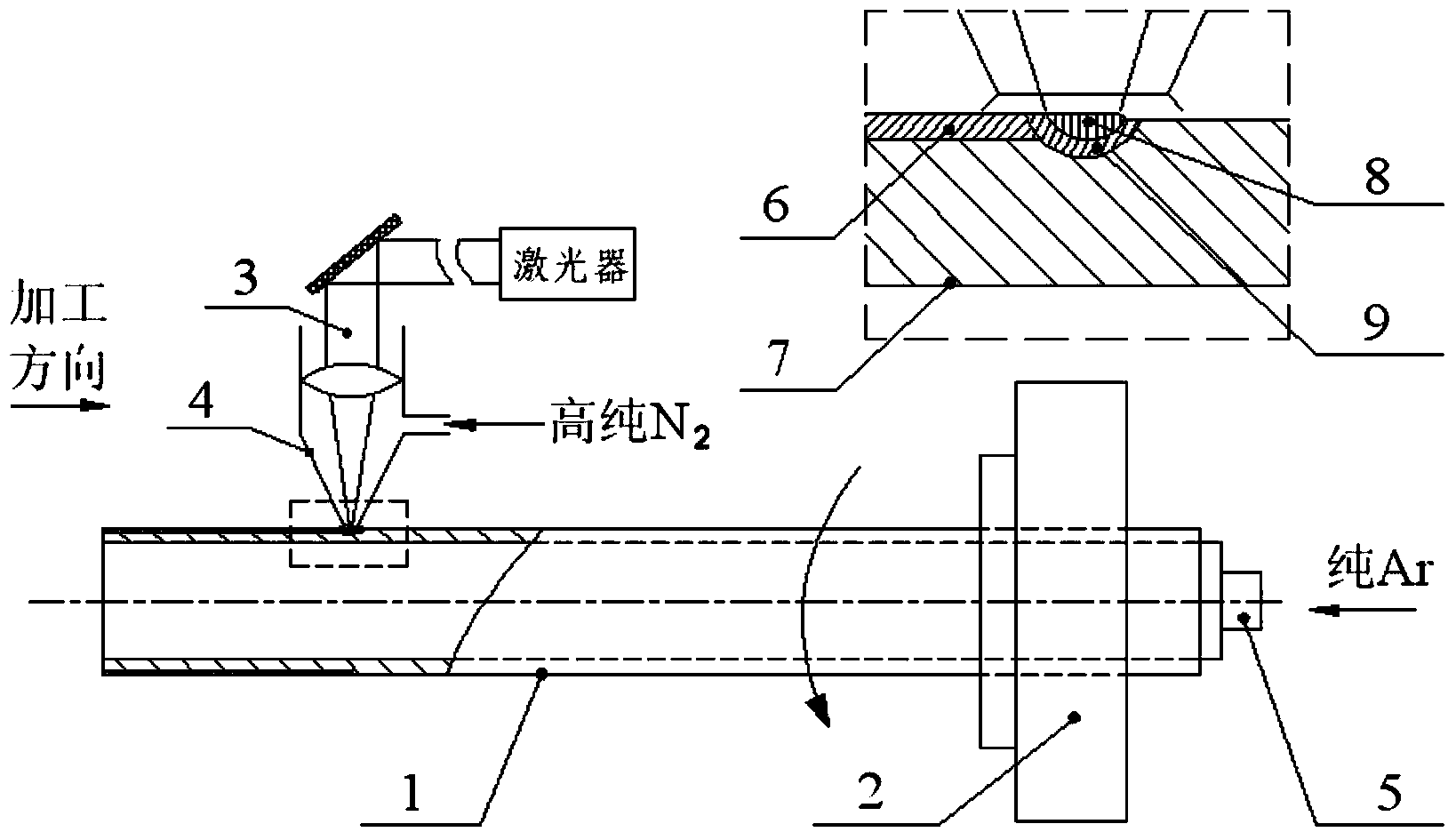
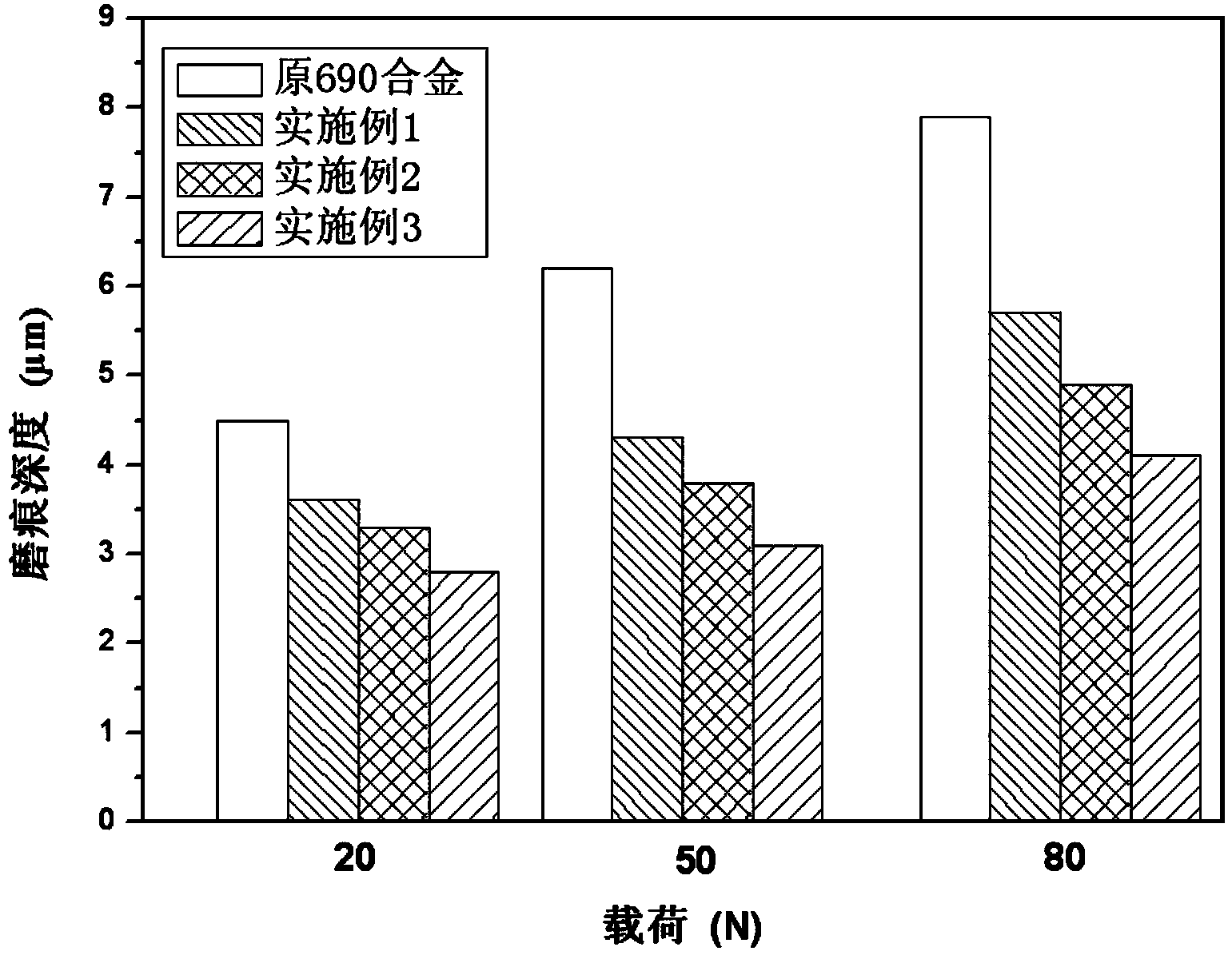
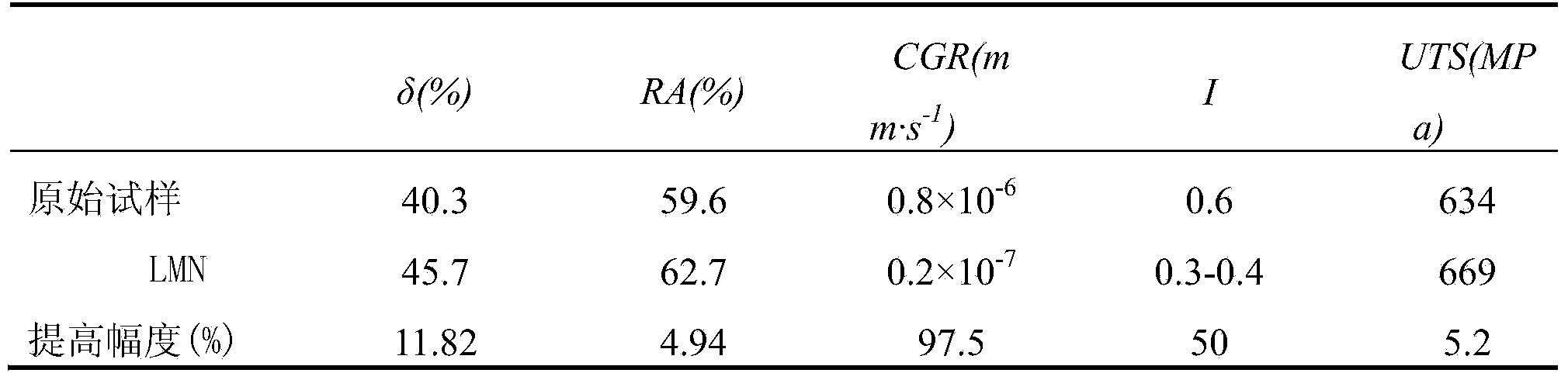
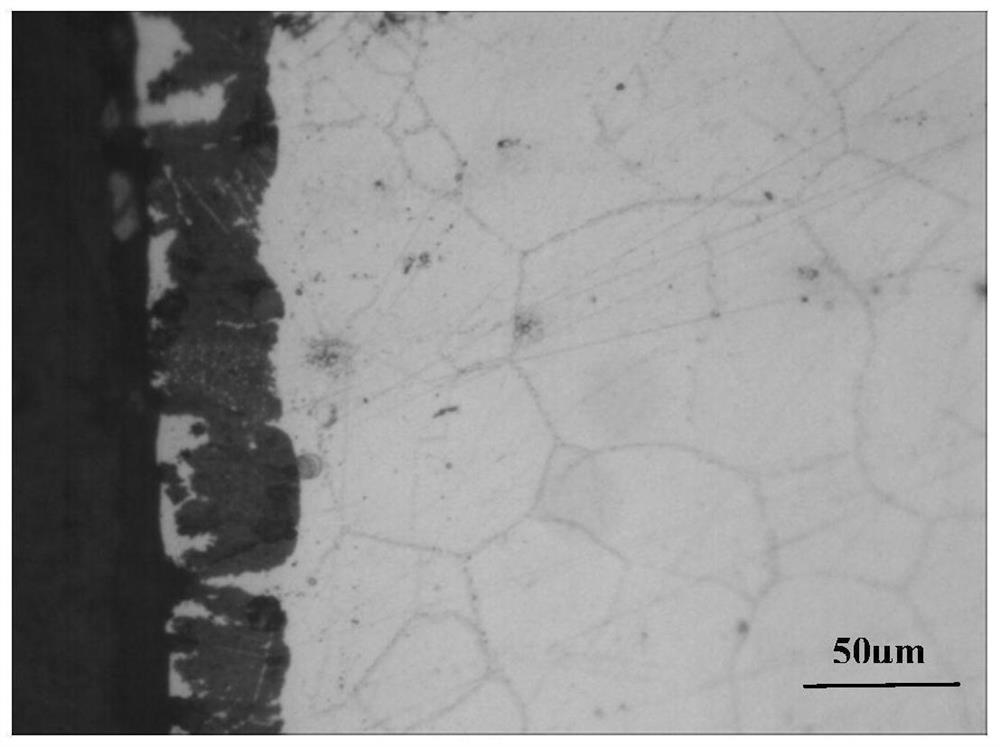
ActiveCN104164539ACompact structureUniform tissueSolid state diffusion coatingCorrosionNitrogen pressure
The invention relates to a laser treatment method for raising stress corrosion resistance and abrasive resistance of nuclear power 690 alloy. According to the invention, a continuous laser thermal source with the wavelength of 800-1070nm is adopted to carry out a melting treatment on the cylindrical surface of a 690 alloy heat-transfer pipe while a nitrogen-assisted nitriding treatment is carried out. Laser power is 300-1000 W; laser scanning linear velocity is 200-800 mm / min; spot diameter is 0.5-3 mm; and overlap rate is 20-60%. When the nitrogen-assisted nitriding treatment is carried out while laser melting of the cylindrical surface of the 690 alloy pipe, flow rate of nitrogen is 20-30L / min; the distance from a nitrogen nozzle to the surface of the heat-transfer pipe is 5-12 mm; nitrogen pressure at an nozzle outlet is 0.5-1 MPa; and argon with auxiliary flow rate of 20-30L / min in a bore of the 690 heat-transfer pipe is used to protect the surface of the bore and cool the pipe wall. Laser melting is adopted and nitrogen is blown to a melting zone to carry out the nitriding treatment on the surface of the 690 alloy heat-transfer pipe. Thus, a compact nitriding layer with the thickness of 20-100 microns is obtained, so as to raise stress corrosion resistance and abrasive resistance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
High-performance low-temperature efficient ion composite permeation surface modification method for austenitic stainless steel
PendingCN114231895AImprove corrosion resistanceCorrosion resistance does not decreaseSolid state diffusion coatingOrganic solventSS - Stainless steel
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal surface treatment, relates to a high-performance low-temperature efficient ion composite nitriding surface modification method for austenitic stainless steel, and aims to solve the problems that CrN can be separated out through high-temperature ion nitriding, solid solution chromium is reduced, and the corrosion resistance of the austenitic stainless steel is reduced. The diffusion speed of active atoms at low temperature is low, so that the nitriding efficiency is low. The method comprises the following steps: cutting original austenitic stainless steel into a sample; grinding the sample, ultrasonically cleaning the sample in an organic solvent, and drying the sample; the sample is put into a vacuum nitriding furnace, and TC4 wires are added around the sample for ion composite nitriding treatment. According to the low-temperature ion composite permeation surface modification method, CrN is prevented from being formed, and the excellent corrosion resistance of the austenitic stainless steel is kept; an S phase and a Ti2N phase are formed on the surface of the austenitic stainless steel, so that the surface hardness of the austenitic stainless steel is greatly improved; and meanwhile, the ion nitriding efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
A kind of low temperature plasma nitriding preparation method of ferronitride magnetic powder
ActiveCN106086776BSolve the bottleneck problem of decomposition inefficiencyHigh nitriding efficiencyTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusNitrogen plasmaDecomposition
The invention relates to a low-temperature plasma nitriding preparation method of iron nitride magnetic powder. The invention uses atomized iron powder, hydroxyl iron powder or reduced iron powder with an average particle size of 2-80 μm as the raw material; feeds O2 and oxidizes at 300-400 °C for 1-10 hours to obtain iron oxide powder; feeds hydrogen, Restore at 300~400°C for 4-20h to regain iron powder; low-temperature plasma nitriding, control temperature at 120~200°C, nitriding for 1~30h; cool down, cool to room temperature with the furnace, and take out the sample. The method uses low-temperature nitrogen plasma for nitriding, which solves the bottleneck problem of low ammonia gas decomposition efficiency in the ammonia gas nitriding method, and effectively improves the nitriding efficiency.
Owner:东阳市顶峰磁材有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com