Detoxification-free ethanol fermentation method of non-enzymatic cellulose hydrolyzed saccharification solution
A technology of ethanol fermentation and cellulose, applied in fermentation, biochemical equipment and methods, bulk chemical production, etc., can solve the problem of no multi-level domestication selection, continuous passage, inhibitors without stable and heritable tolerance, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of industrialized production of cellulosic ethanol, reduction of production costs, and improvement of output and efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] (1) The configuration of the acclimatization medium, specifically: adjust the pH of the non-enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis and saccharification solution to 4.5, and then mix it with the seed medium at a volume ratio of 0-20 to obtain the acclimatization medium. The specific formulation is shown in Table 1.
[0023] The non-enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis and saccharification liquid is furfural slag hydrolysis saccharification liquid: furfural slag and phosphorus pentoxide are mixed and ball milled for 30 minutes at a mass ratio of 20:1, heated to 140° C. for 60 minutes, and solid-liquid ratio is 20%. Hydrolyze at 200°C for 30 minutes to obtain a hydrolyzed saccharification slurry, and perform solid-liquid separation on the saccharified slurry to obtain a hydrolyzed saccharification liquid of furfural slag.
[0024] Its specific components are glucose 29.04g / L, xylose 7.59g / L, 1.6-anhydroglucose 1.12g / L, 5-HMF 1.66g / L, furfural 1.78g / L, cellobiose 0.50g / L, phenol 0.88 g / L...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Configuration of acclimatization medium: the experimental procedure is the same as in Example 1, except that the non-enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis and saccharification solution is concentrated furfural slag hydrolysis and saccharification solution, wherein glucose is 102.94g / L and xylose is 6.07g / L , 1.6-anhydroglucose 3.50g / L, 5-HMF 3.95g / L, cellobiose 2.45g / L, phenol 2.54g / L, guaiacol 2.22g / L, vanillin 2.35g / L, syringaldehyde 2.63g / L, benzoic acid 1.84g / L.
[0036] (2) Then carry out step-by-step acclimatization culture to amylogous Saccharomyces cerevisiae to obtain domesticated strains: the experimental procedure is the same as that in Example 1, and the obtained strains are designated as strain B.
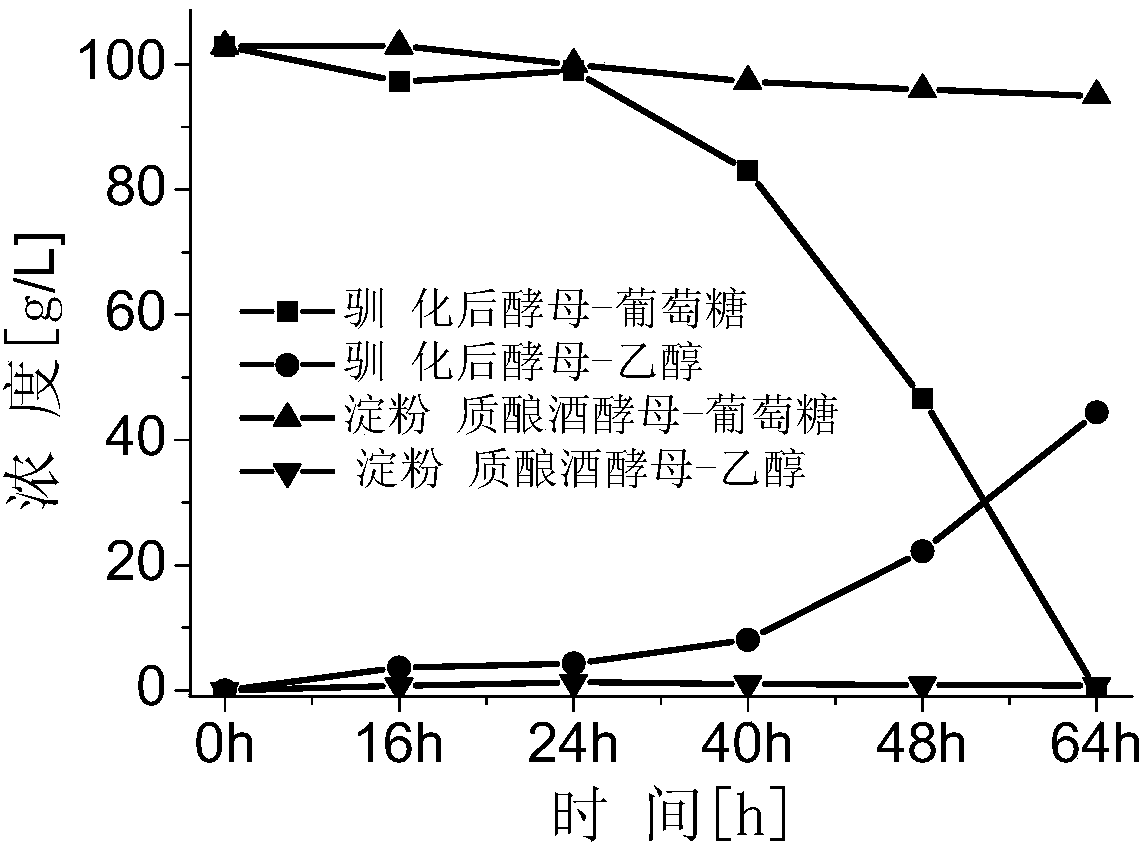
[0037] (3) Concentrate the non-enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis and saccharification solution used for the domesticated strain B to contain 140 g / L of glucose, prepare a fermentation medium, and then inoculate the strain B for ethanol fermentation.
[0038] The ferm...
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) Configuration of domestication medium: the experimental procedure is the same as in Example 1, the difference is the change of the concentration of substances in the furfural residue hydrolyzate, which contains glucose 102.94g / L, xylose 6.07g / L, 1.6 -Anhydroglucose 3.50g / L, 5-HMF 3.95g / L, cellobiose 2.45g / L, phenol 2.54g / L, guaiacol 2.22g / L, vanillin 2.35g / L, syringaldehyde 2.63g / L, benzoic acid 1.84g / L.
[0041] (2) Then carry out step-by-step acclimatization culture to amylogous Saccharomyces cerevisiae to obtain domesticated strains: the experimental procedure is the same as that in Example 1, and the obtained strains are designated as strain B.
[0042] (3) Concentrate the non-enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis and saccharification solution used by the domesticated strain B to contain 180 g / L of glucose, then prepare a fermentation medium, and then inoculate the strain B for ethanol fermentation.
[0043] The fermentation medium is: adding MgSO to the furfural sla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com