A preparation method based on polyelectrolyte-surfactant composite antibacterial nanofibers
A surfactant and polyelectrolyte technology, applied in the direction of one-component synthetic polymer rayon, fiber chemical characteristics, rayon manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of less research on polyelectrolyte-surfactant composites, and reduce the Finishing process, mild reaction conditions, good antibacterial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] (1) Preparation of polyelectrolyte polymer:
[0031] Add 10 g of sodium hydroxide to 200 mL of aqueous solution, stir to dissolve, and then heat to 100°C. Add 10g of PAN high polymer powder, condense and stir for 3h. The resulting solution was precipitated, washed, and dried in an oven at 50° C. to obtain a hydrolyzed PAN polymer, that is, a polyelectrolyte polymer.
[0032] (2) Preparation of polyelectrolyte-surfactant complex:
[0033] Dissolve 4g of polyelectrolyte in 100mL of deionized water, 8g of dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride in 200mL of deionized water, and then slowly add the surfactant solvent into the polyelectrolyte solution dropwise until a white precipitate occurs, at 50°C Stirring was continued for 30 minutes, and the reacted solution was filtered, washed, and vacuum-dried at 50° C. to obtain a polyelectrolyte-surfactant antibacterial complex.
[0034] (3) Preparation of polyelectrolyte-surfactant composite antibacterial nanofibers:
[0035] Dissol...
Embodiment 2
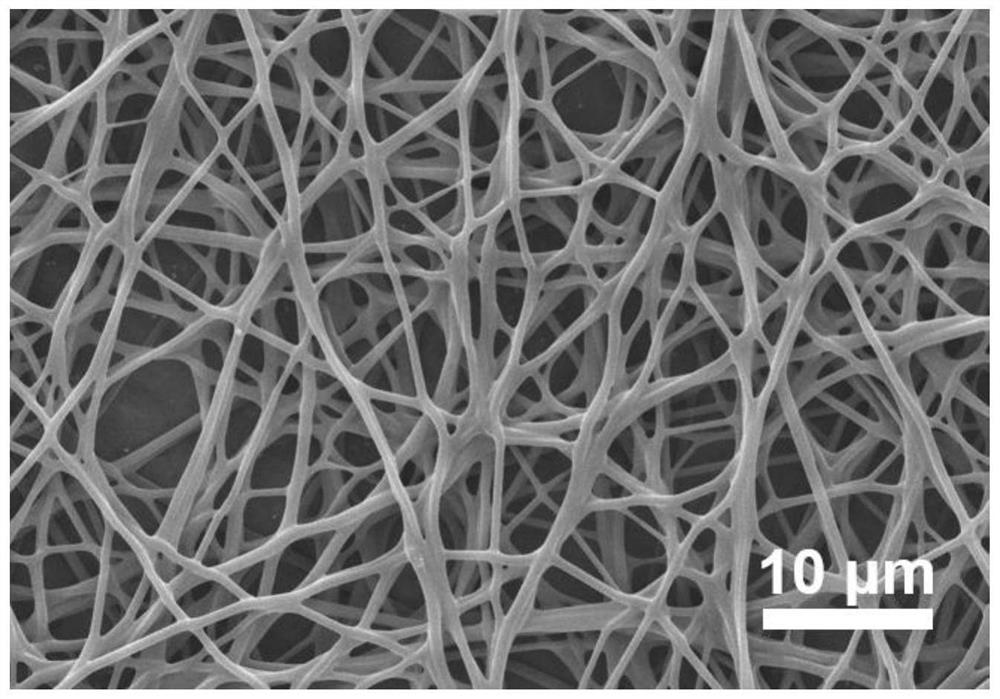
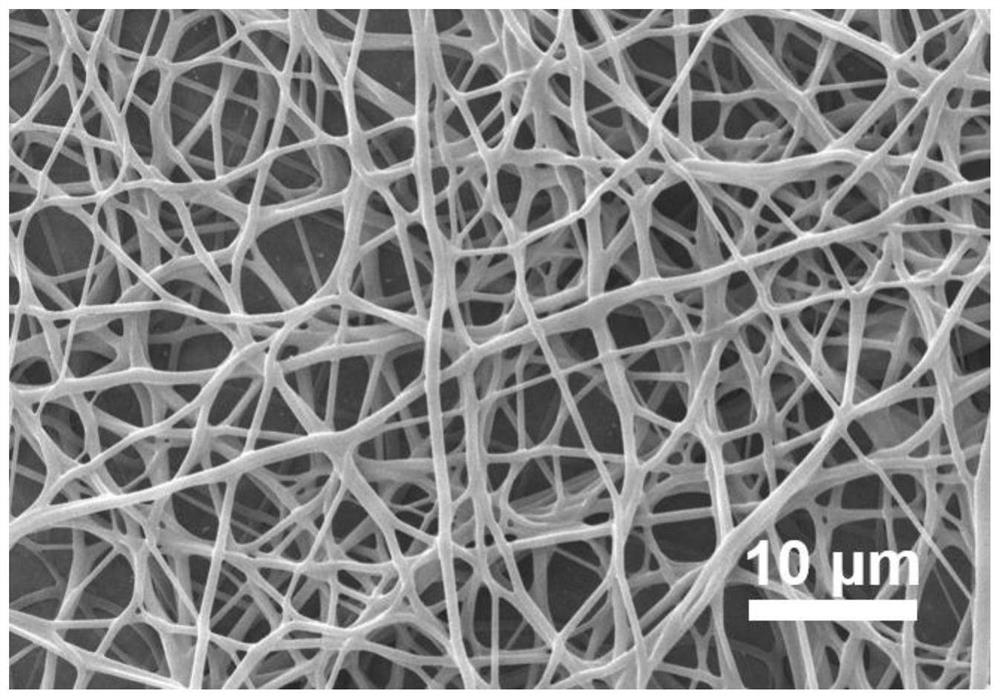
[0037] In step (3) of Example 1, "dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride" was changed to "tetradecyltrimethylammonium chloride", and the rest were the same as in Example 1 to obtain a nanofibrous membrane. The prepared submicron fiber membrane (recorded as 14) is used for scanning electron microscope, and its test result is as follows figure 2 As shown in , it can be seen that the fiber diameter is relatively thick and has a network structure.
Embodiment 3
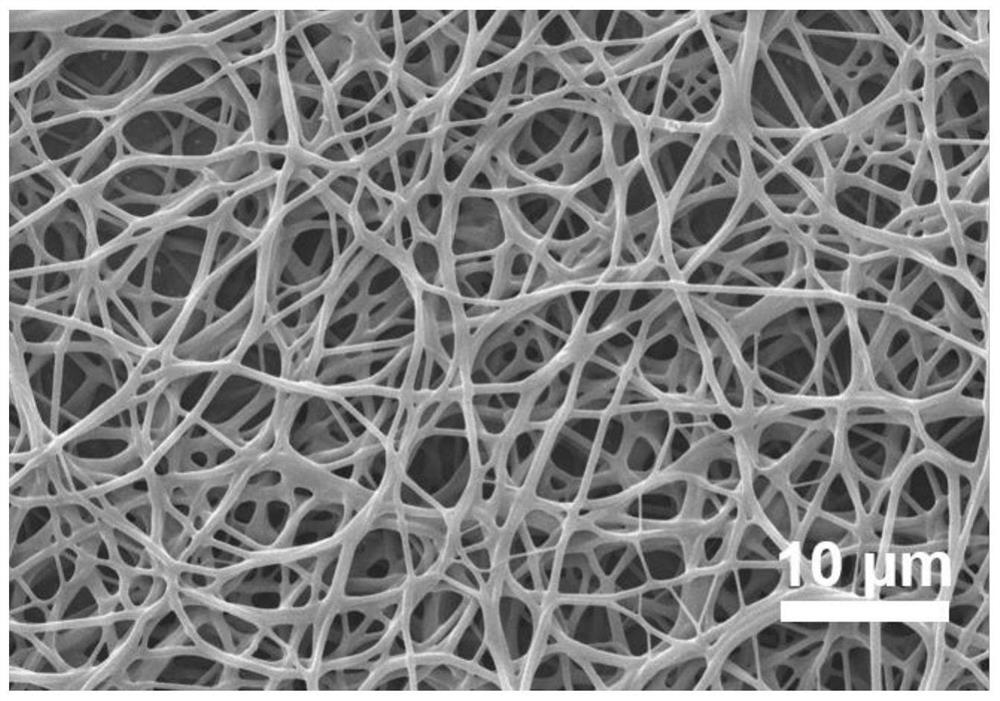
[0039] In step (3) of Example 1, "dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride" was changed to "hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride", and the rest were the same as in Example 1 to obtain a nanofibrous membrane. The prepared submicron fiber membrane (recorded as 16) is used for scanning electron microscopy, and its test results are as follows: image 3 As shown in , it can be seen that the fiber diameter is relatively thick and has a network structure. Antibacterial effects of electrospun nanofibers against Escherichia coli (E.coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S.aureus) as Figure 4 As shown, it can be seen that the bacteria on the blank sample and the PAN sample culture dish multiply in large numbers, and there is no antibacterial performance. Sample 16 has good antibacterial performance no matter it is against Escherichia coli or Staphylococcus aureus, the antibacterial rate against Escherichia coli reaches 98%, and the antibacterial rate against Staphylococcus aureus reaches 99%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com