A ti(c,n)-based cermet material and its carbon balance control method
A ceramic material and cermet technology, which is applied in the field of Ti-based cermet material and its carbon balance control, can solve the problems of unoptimistic production conditions, high cost of imported tools, increased workpiece processing cost, etc., and achieve simple, easy and precise control of the sintering process. , The effect of improving density and high mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
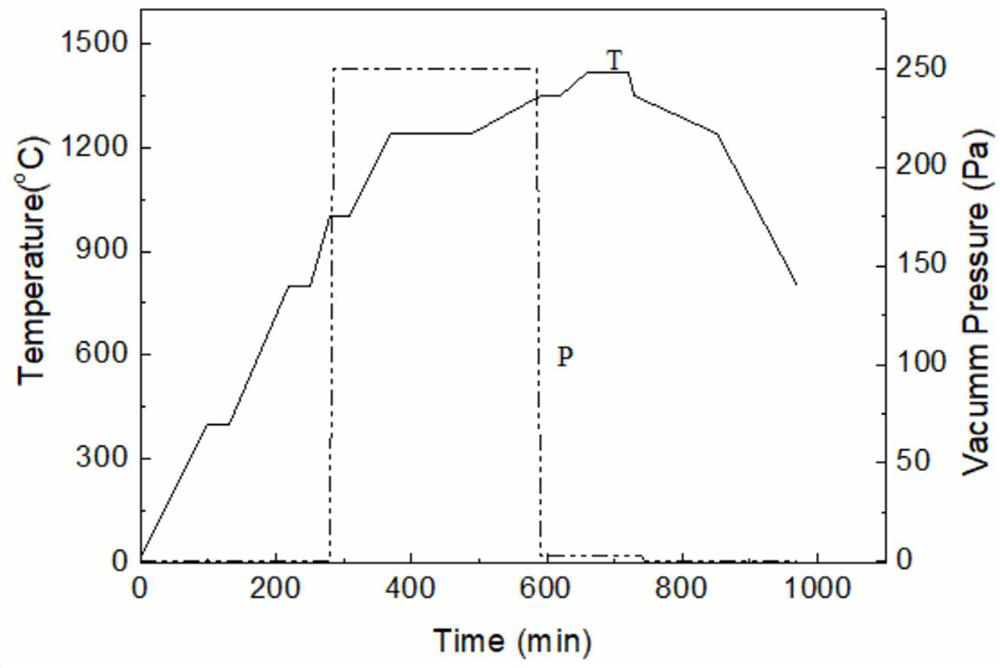
[0038] The first is the preparation of the mixture: using Ti(C,N) powder, (Ti,Re)(C,N) powder, WC powder, Cr 3 C 2 Powder, Ni powder, Co powder, Re powder, graphite powder and other raw materials. 11.5, N: a mixture of 4.6. Use absolute ethanol as the ball milling medium, the amount of absolute ethanol is 0.7:1 ratio of alcohol to material, YG8 cemented carbide balls are used as grinding balls, and the ball to material ratio is 7:1; the materials are mixed on a planetary ball mill at a speed of 200r / min, time 36h, oven dry at 80°C after obtaining the mixture. The mixed powder is compressed under a certain pressure (160Mpa). The compact is placed in a vacuum carbon tube furnace for vacuum sintering. The schematic diagram of the sintering process is shown in figure 2 shown. The vacuum degree in the furnace below 1000°C is 4.0×10 -2 Pa; above 1000°C, the staged sintering process is adopted, methane gas is introduced, the methane pressure in the furnace is 250Pa at 1000-13...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The composition combination, mixing method, preparation process and sintering route of Example 1 were adopted. In the sintering process of Example 2, adjust the methane pressure in the furnace during the solid-phase sintering stage at 1000 to 1350 ° C, and the methane atmosphere pressure is reduced to 200 Pa; the methane atmosphere pressure in the liquid-phase sintering stage is the same as that in Example 1; ℃ / min is increased to a cooling rate of 1.3 ℃ / min, and the vacuum degree is still the same as in Example 1.
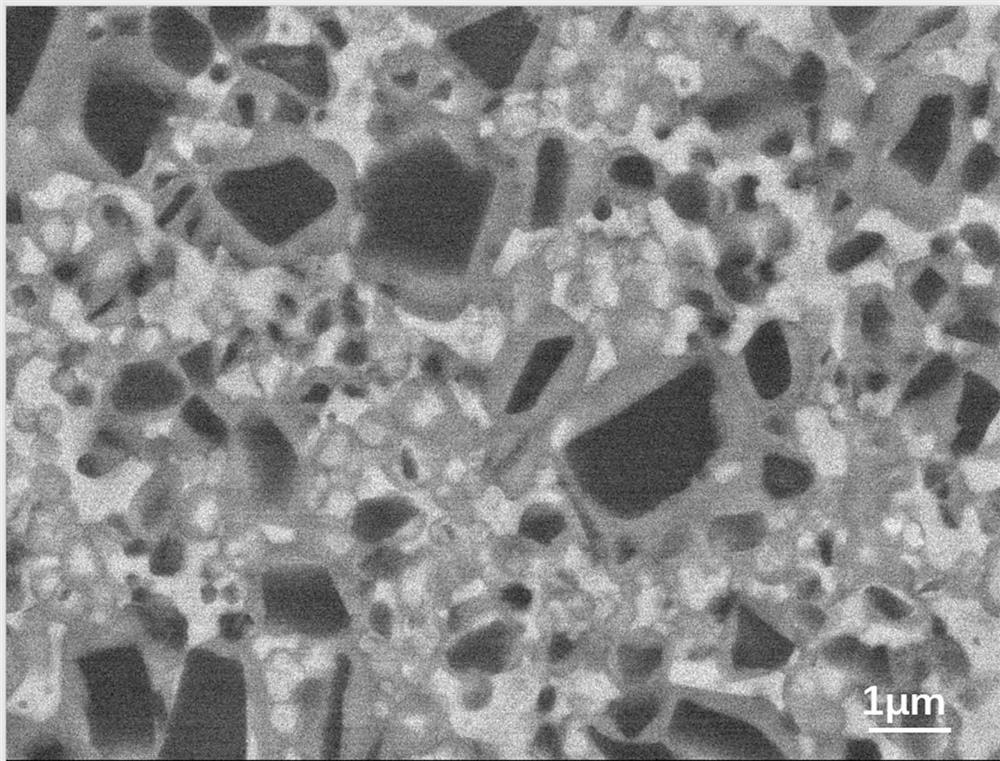
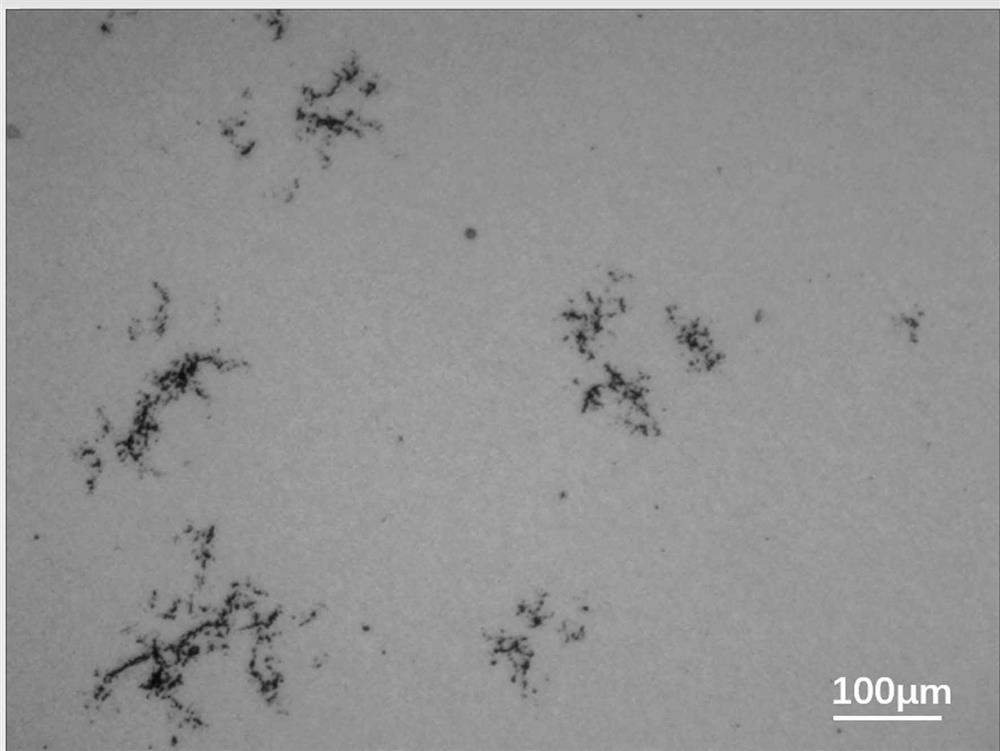
[0048] Figure 5 The metallographic structure of the sintered body is given, and the structure is dense and free of defects. Figure 6 The SEM structure of the sintered body is given, which further confirms that the structure of the sintered body is compact, and no graphite phase and other phases are found. Figure 7 Shown is the XRD pattern of the sintered body, which shows that the structure of the sintered body is a two-phase structure, the hard phase ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Changing the composition ratio of raw materials, the mass parts of the prepared cermet composition are Ti: 48.7, Ni: 20.5, Co: 4.3, W: 8.9, C: 10.8, N: 4.3, Cr: 0.6, Re: 1.9, mixed The material process, preparation process and sintering route are the same as in Example 1, and the methane pressure in the furnace is reduced to 70 Pa in the solid phase sintering stage at 1000-1350 °C; the methane atmosphere pressure in the liquid phase sintering stage and the cooling stage process are the same as in Example 1. After analysis, the metallographic structure and scanning structure of the sintered body have no other phase formation, which is a typical two-phase structure of cermet. The mechanical performance indicators of the sintered body are: hardness 1489HV, bending strength 1930MPa, fracture toughness K IC 8.8MPa·m 1 / 2 . Compared with Example 1, by adjusting the proportion of binder phase components in the raw material, reducing the content of the main carbide forming ele...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com