Method for preparing pore-space feature controlled lightweight high-strength porous nickel titanium memory alloys
A technology of memory alloy and porous nickel, which is applied in the field of preparation of porous nickel-titanium shape memory alloy, can solve the problems of strength and superelasticity decline, poor controllability of porosity, large randomness of sample performance, etc., and achieve high-strength mechanical properties High performance, high porosity and good controllability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Use pure titanium powder (average particle size 48 μm) and pure nickel powder (average particle size 57 μm) according to nickel:titanium atomic ratio 50.8:49.2 and mix thoroughly for 24 hours to obtain raw material powder A. Add 20wt% urea (average particle size 700 μm, maximum and minimum particle size 600 and 900 μm) to powder A, mix for 12 hours to make powder B. Powder B was pressed at 50 MPa into a cylindrical green body with a diameter of 16 mm, a length of 15 mm and a porosity of 45.76%. Put the billet into an electric heating tubular sintering furnace, heat it to 250°C under the protection of argon with a purity higher than 99.99% and keep it warm for 1 hour, in order to remove the pore-forming agent urea and activate the billet. Then it was heated to 840°C at a heating rate of 15°C / min and kept for 5 minutes. Finally, it was heated to 1000°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min and kept for 3 hours. Finally, a porous nickel-titanium shape memory alloy with high poro...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Use pure titanium powder (average particle size 48 μm) and pure nickel powder (average particle size 57 μm) according to nickel:titanium atomic ratio 51:49 and mix thoroughly for 24 hours to obtain raw material powder A. Add 30wt% urea (average particle size 350 μm, maximum and minimum particle size is 300 and 450 μm respectively) in powder A, make powder B after mixing 12 hours, under 200MPa, powder B is pressed into diameter 16 millimeters, length 18 mm, a cylindrical green body with a porosity of 61.59%. The billet is put into a tube-type sintering furnace, heated to 300°C under the protection of argon with a purity higher than 99.99%, and kept for 1 hour. Then it was heated to 820°C at a heating rate of 30°C / min and kept for 10 minutes. Finally, it was heated to 950° C. at a heating rate of 20° C. / min and kept for 3 hours. Finally, a porous nickel-titanium shape memory alloy with uniform distribution of pores was synthesized.
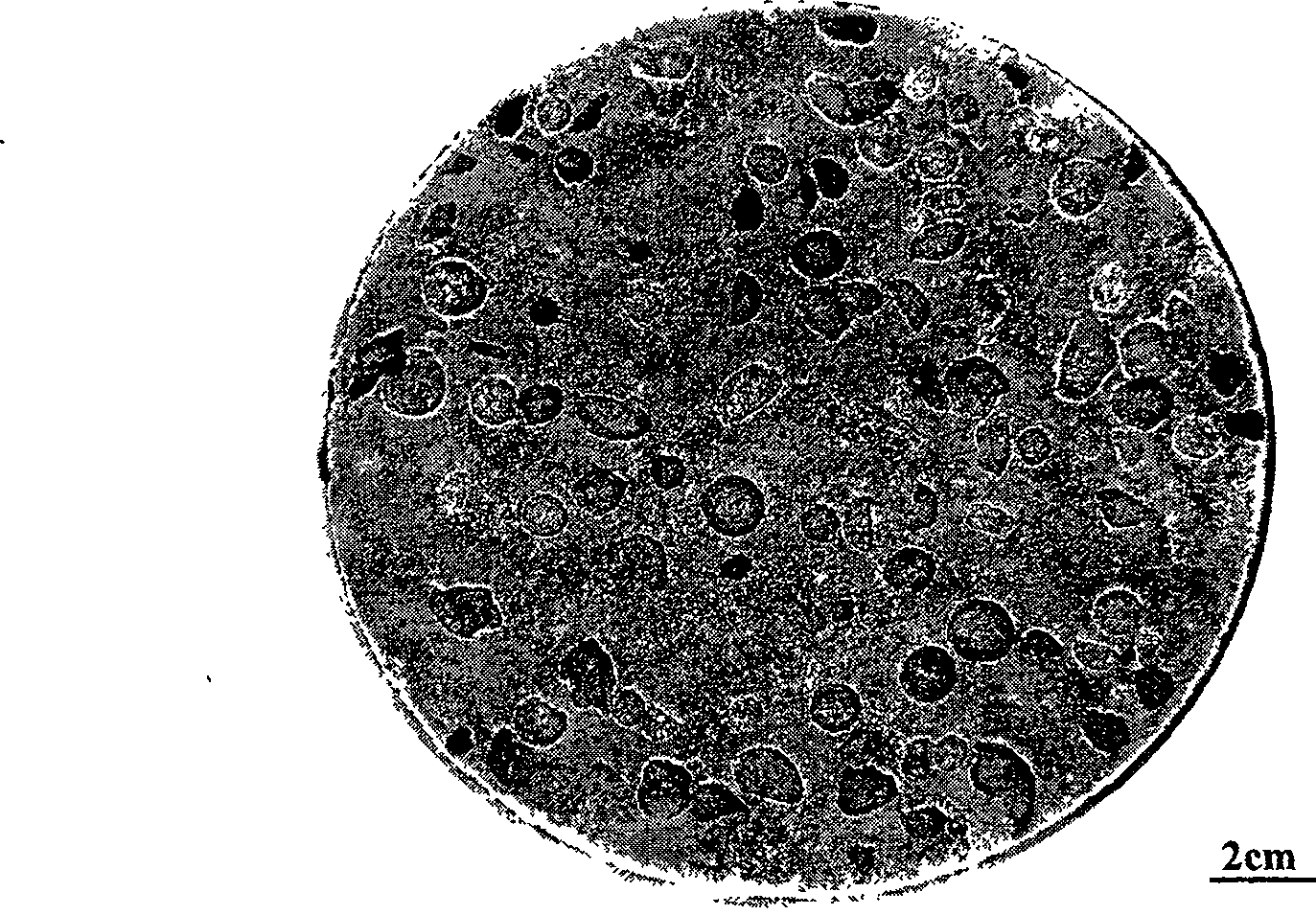
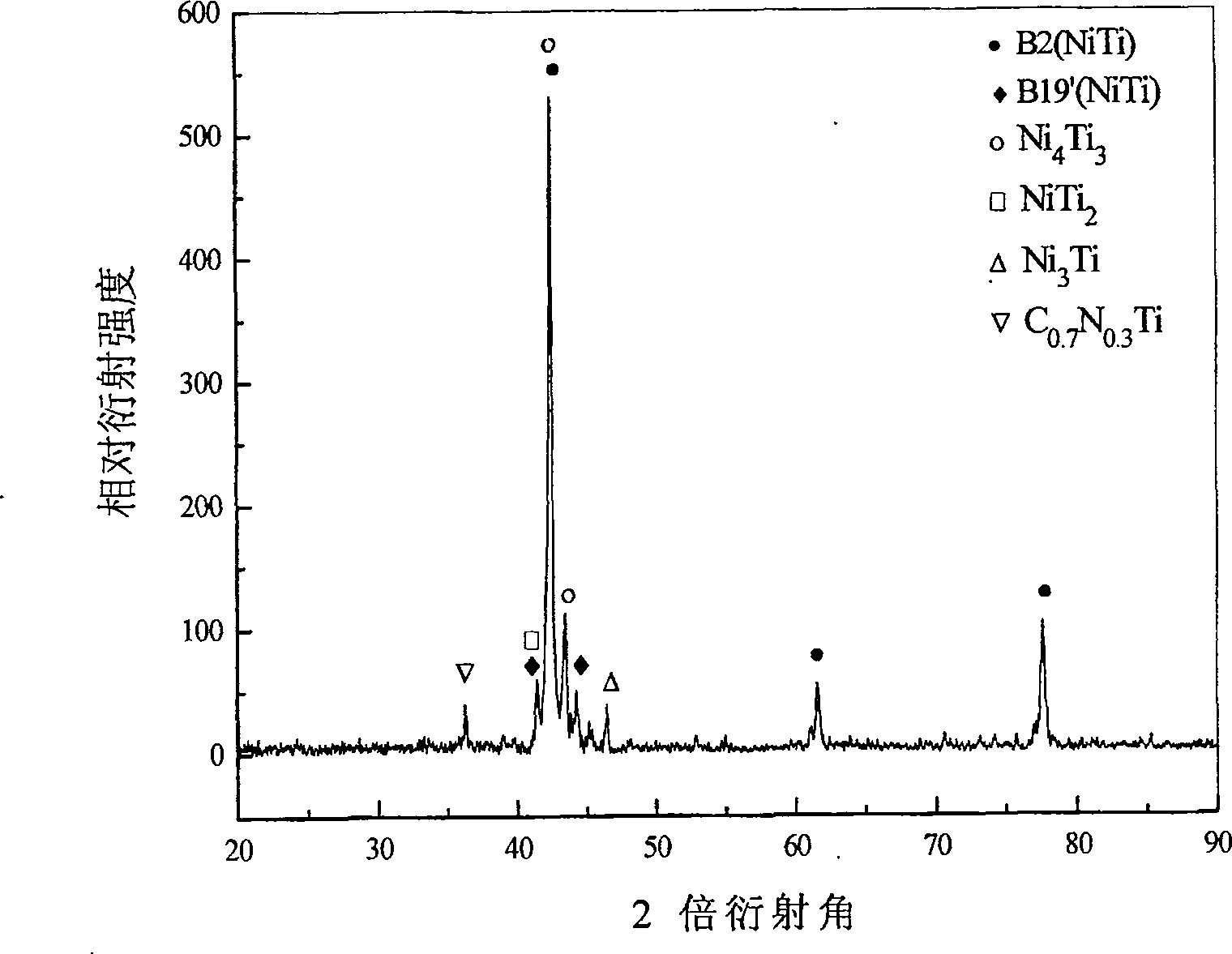
[0036] figure 2 It is a micrograp...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Use pure titanium powder (average particle size 48 μm) and pure nickel powder (average particle size 57 μm) according to the atomic ratio of nickel and titanium 50:50 and mix thoroughly for 24 hours to obtain raw material powder A. Add 10wt% urea (average particle size 500 μm, maximum and minimum particle size 450 and 600 μm) to powder A, mix for 12 hours to make powder B. Powder B was pressed into a cylindrical green body with a diameter of 16 mm, a length of 20 mm and a porosity of 35.02% at 100 MPa. The billet is put into an electric heating tubular sintering furnace, heated to 200°C under the protection of argon with a purity higher than 99.99%, and kept for 2 hours. Then, after heating to 860° C. at a heating rate of 10° C. / min, keep the temperature for 5 minutes. Then heat it up to 1150°C at a heating rate of 15°C / min and keep it warm for 1 hour.
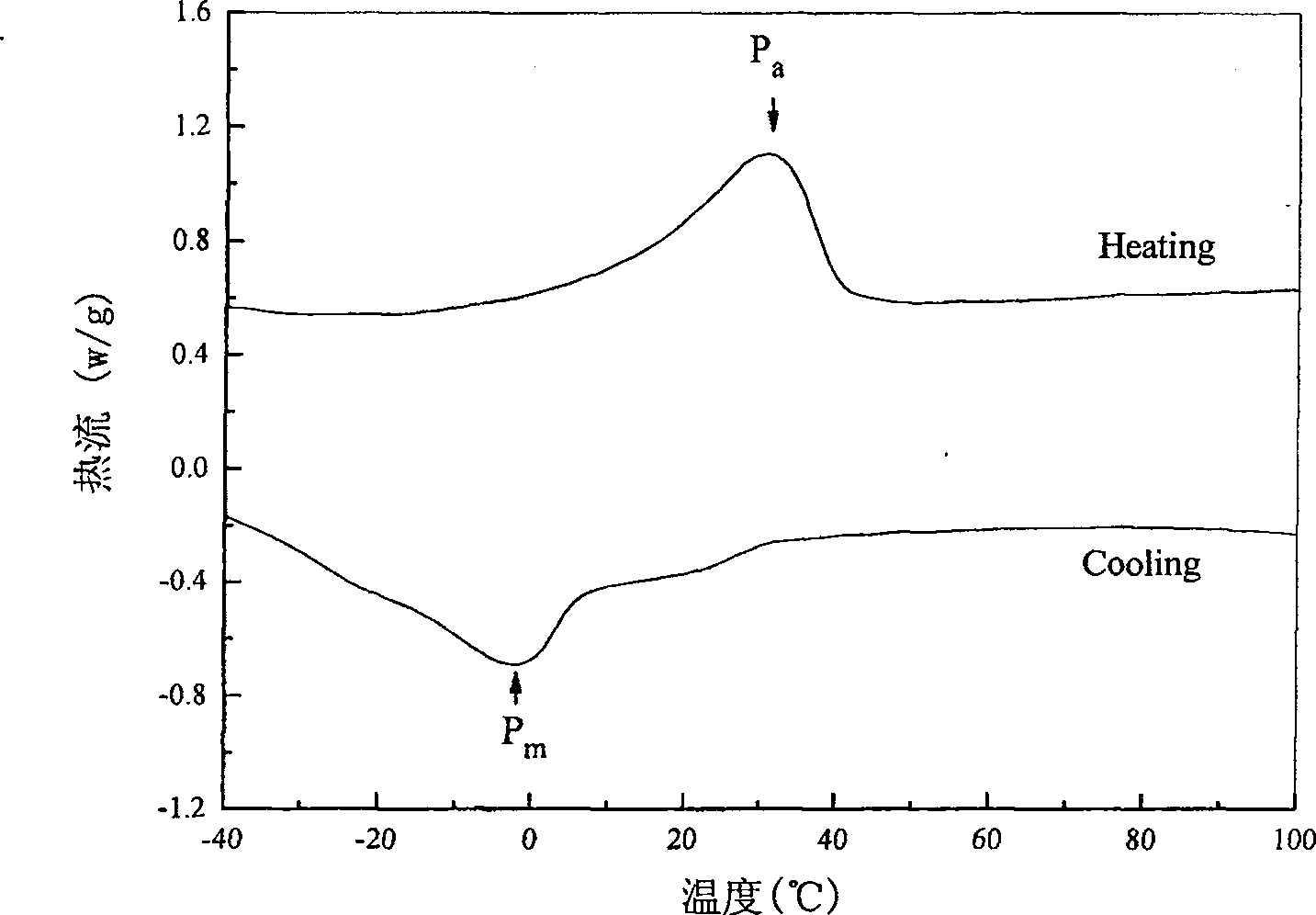
[0039] Figure 3-1 is the DSC curve of the prepared sample, P m Represents martensitic transformation, P r Repre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com