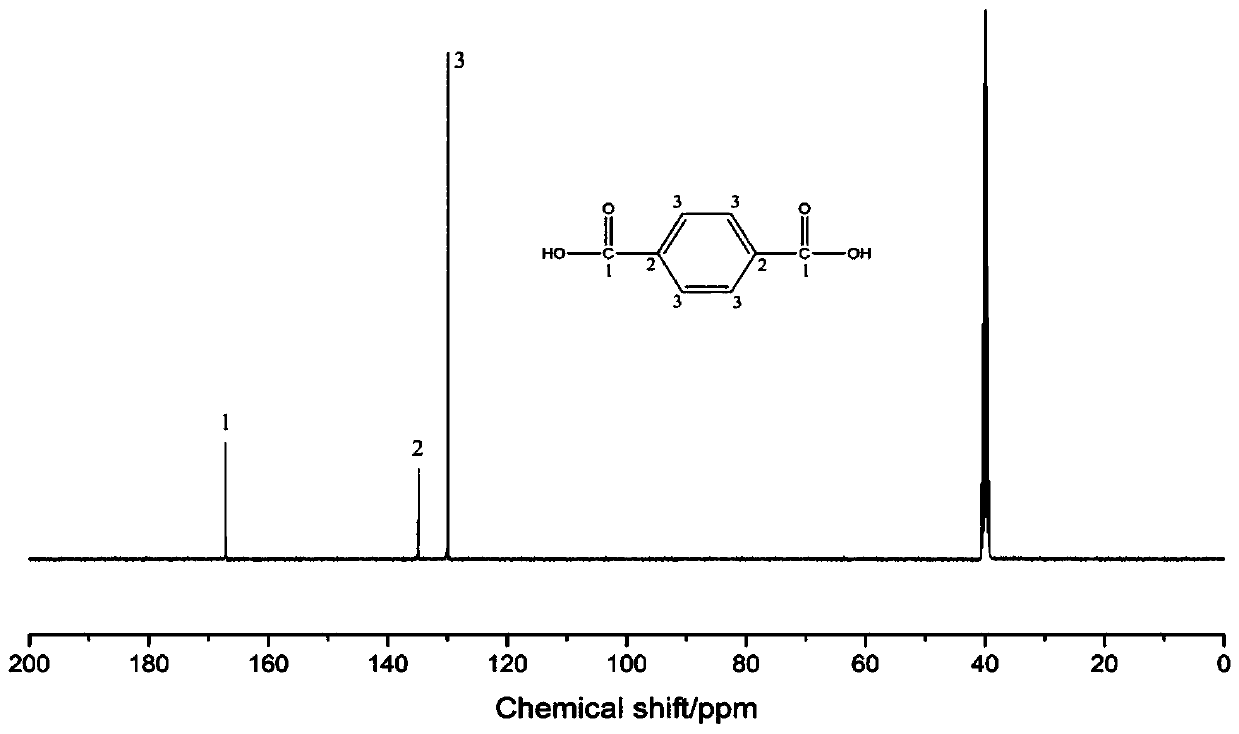
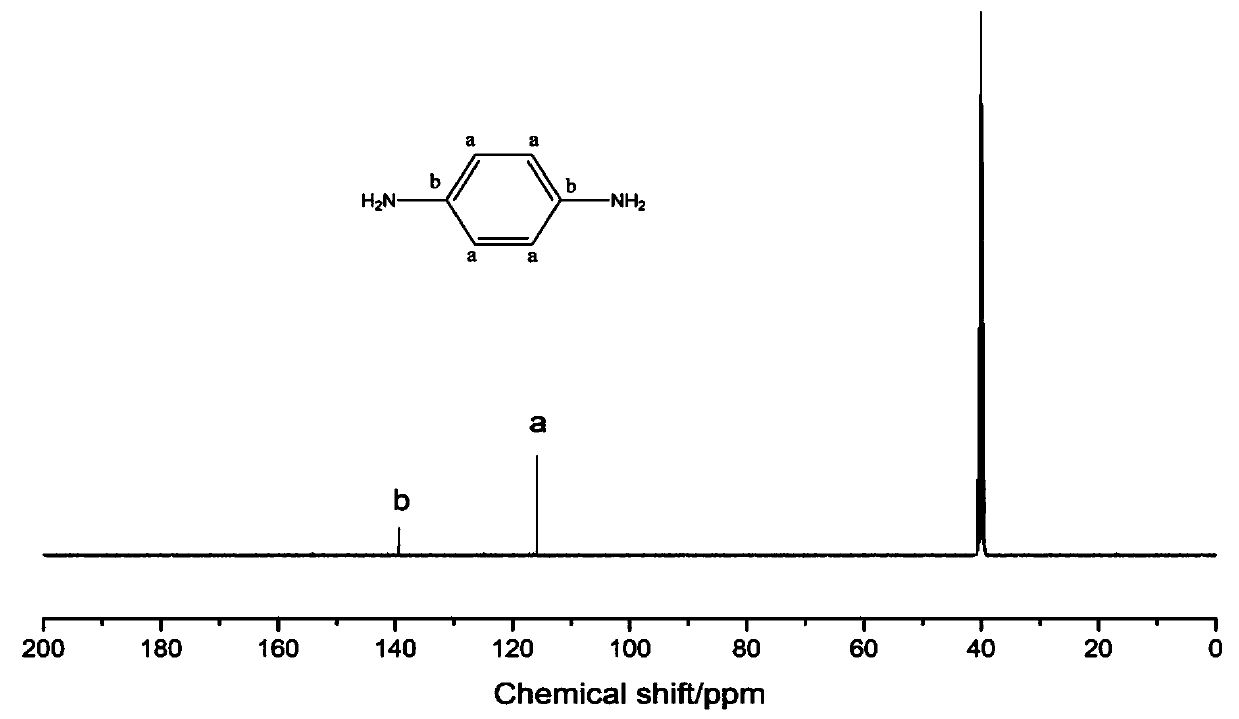
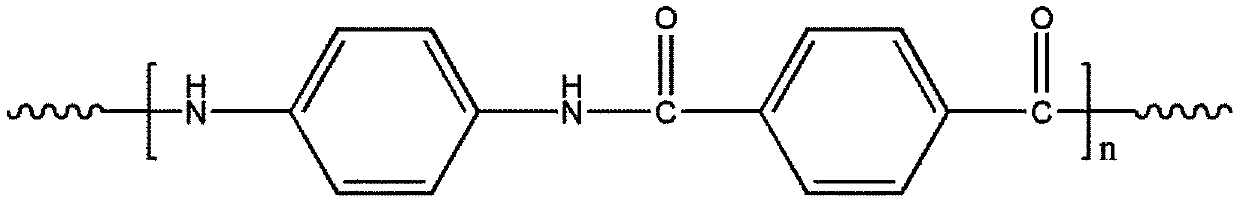
Method for preparing terephthalic acid and p-phenylenediamine by degrading p-aramid fibers
A technology of terephthalic acid and p-phenylenediamine, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, amide preparation, carboxylate preparation, etc., to achieve the effects of controllable degradation and mild reaction process conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] In this embodiment, a method for degrading para-aramid fibers to prepare terephthalic acid and p-phenylenediamine comprises the following steps:
[0028] Step 1: Prepare reaction system I by mixing aluminum chloride and formic acid with catalyst mass fraction of 10%, mix para-aramid fiber and reaction system I at a mass ratio of 1:1 and add to the reactor, seal and put into homogeneous reaction The device was heated to 280°C and reacted for 36h. Cool to room temperature after the reaction, add deionized water to wash, filter to remove aluminum chloride and formic acid, and the reaction products are terephthalic acid and terephthalic acid derivatives. Aqueous potassium hydroxide solution is added to dissolve the potassium salt of terephthalic acid, and the solution of terephthalic diamide acyl derivative and potassium terephthalic acid is separated by filtration. Add hydrochloric acid to the potassium terephthalic acid solution to precipitate terephthalic acid, wash, fi...
Embodiment 2
[0032] In this embodiment, a method for degrading para-aramid fibers to prepare terephthalic acid and p-phenylenediamine comprises the following steps:
[0033] Step 1: Prepare reaction system Ⅰ by ferric chloride and acetic acid at 1% catalyst mass fraction, mix para-aramid fiber and reaction system Ⅰ at a mass ratio of 1:50 and add to the reactor, seal and put into homogeneous reaction The device was heated to 180°C and reacted for 1h. Cool to room temperature after the reaction, add deionized water to wash, filter to remove ferric chloride and acetic acid, and the reaction products are terephthalic acid and terephthalic acid derivatives. Aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was added to dissolve the sodium salt of terephthalic acid, and the solution of terephthalic diamide acyl derivative and sodium terephthalic acid was obtained by separating by filtration. Add hydrochloric acid to the sodium terephthalic acid solution to precipitate terephthalic acid, wash, filter and dry t...
Embodiment 3
[0037] In this embodiment, a method for degrading para-aramid fibers to prepare terephthalic acid and p-phenylenediamine comprises the following steps:
[0038] Step 1: Prepare reaction system I by preparing copper sulfate and propionic acid with a catalyst mass fraction of 30%, mix para-aramid fiber and reaction system I at a mass ratio of 1:100 and add to the reactor, seal it and put it into a homogeneous reaction The device was heated to 100°C and reacted for 72h. Cool to room temperature after the reaction, add deionized water to wash, filter to remove copper sulfate and propionic acid, and the reaction products are terephthalic acid and terephthalic acid derivatives. Lithium hydroxide aqueous solution was added to dissolve the lithium salt of terephthalic acid, and the solution of terephthalic diamide acyl derivative and lithium terephthalate was separated by filtration. Add hydrochloric acid to the lithium terephthalate salt solution to precipitate terephthalic acid, wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com