Intelligent nanoparticles based on double-selenium-bond polymer, and preparation method and application of intelligent nanoparticle
A technology of polymers and nanoparticles, applied in the direction of medical preparations, drug combinations, and pharmaceutical formulations of non-active ingredients, which can solve problems such as unusable and inconsistent clinical applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
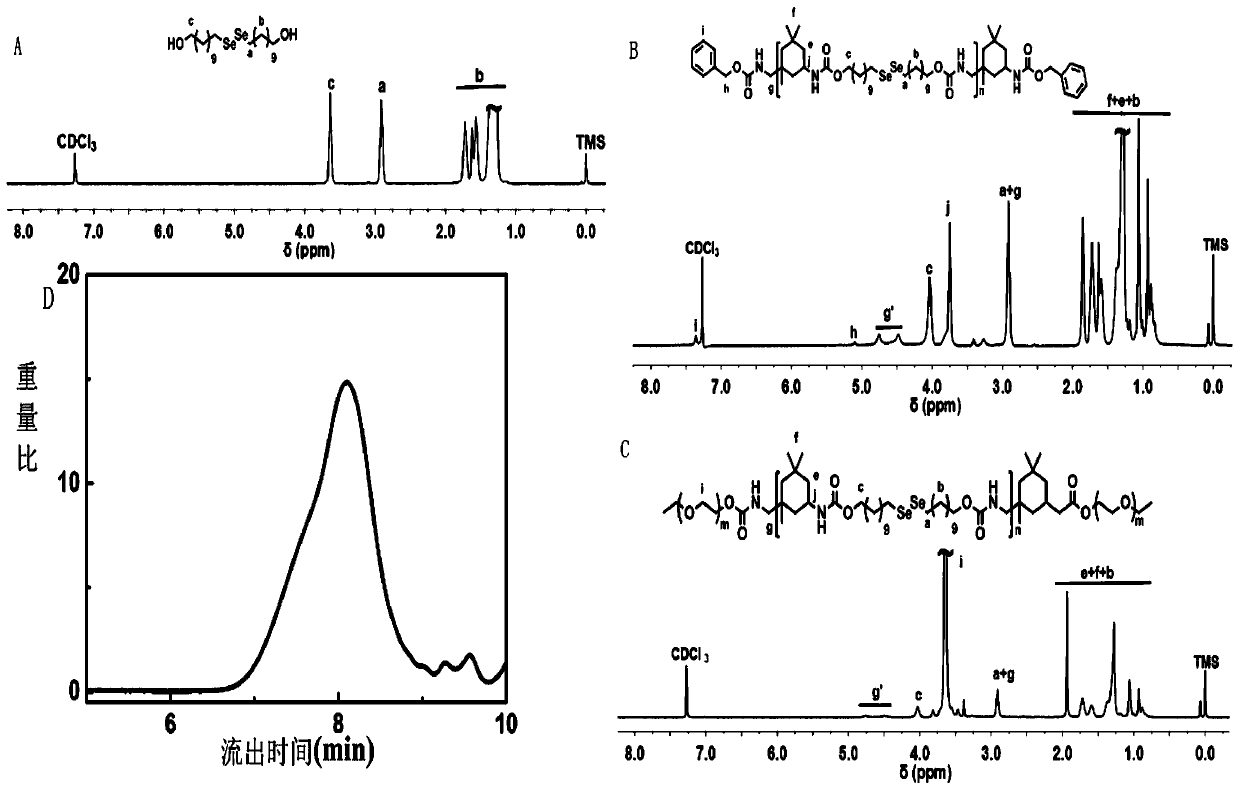
[0046] Add 1.0 g (12.6 mmol) of sodium borohydride dissolved in 10 ml of deionized water slowly and dropwise into 15 mL of deionized water containing 1.0 g (26.4 mmol) of selenium powder under stirring at room temperature, and react for 10 minutes , followed by adding 1.0 g (26.4 mmol) of selenium powder, stirring for 15 minutes, then adding 6.33 g (25.2 mmol) of bromidecanol dissolved in 25 ml of THF, and reacting in an oil bath at 50°C for 24 hours; The residue of the reaction was extracted three times with dichloromethane, dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate for 24 hours, filtered to remove sodium sulfate, and purified by column chromatography (volume ratio of 4:1 dichloromethane / ethyl acetate as eluent) The product, a yellow powder (yield 61%), is a small molecular monomer of di-selenium. 1 H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl 3 , δ)(ppm): 3.63 (4H, t, HOC H 2 ), 2.90 (4H, t, SeSeC H 2 ) 1.72-1.28(36H, m, HOCH 2 (C H 2 ) 9 CH 2 SeSe); LC-MS: theoretical molecular weight 500.53, ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Add 1.0 mg DOX·HCl, 0.1 ml TEA and 10 mg Se-polymer into 2 mL DMF, stir for 2 h, then add 10 mL deionized water dropwise within 5 hours under stirring, and dialyze with deionized water after the addition (MWCO 3500 Da) for 24 hours, and then centrifuged with an ultrafiltration centrifuge tube (MWCO 10000 Da) to obtain drug-loaded nanoparticles (D-NPs) containing diselenium bonds. In order to measure DOX loading (DLC) and drug loading efficiency (DLE), D-NPs were dried by freeze dryer and dissolved in DMSO, and measured by UV-vis spectrometer. It was found that the DOX loading of the above D-NPs (DLC ) and drug loading efficiency (DLE) values were calculated to be 8.69% and 41.78%, respectively.
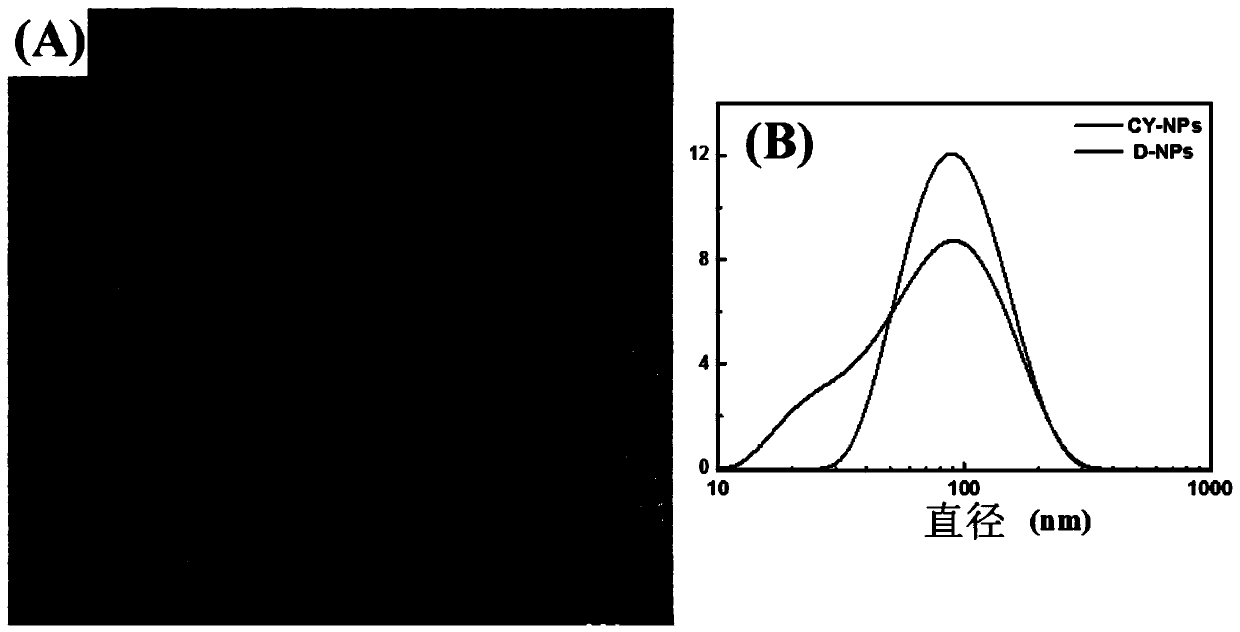
[0054] Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) characterization analysis such as figure 2 Shown in A, the successful fabrication of the designed DOX-loaded dual-Se nanoparticles (D-NPs) was demonstrated. According to the dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurement, D-NPs hav...
Embodiment 3
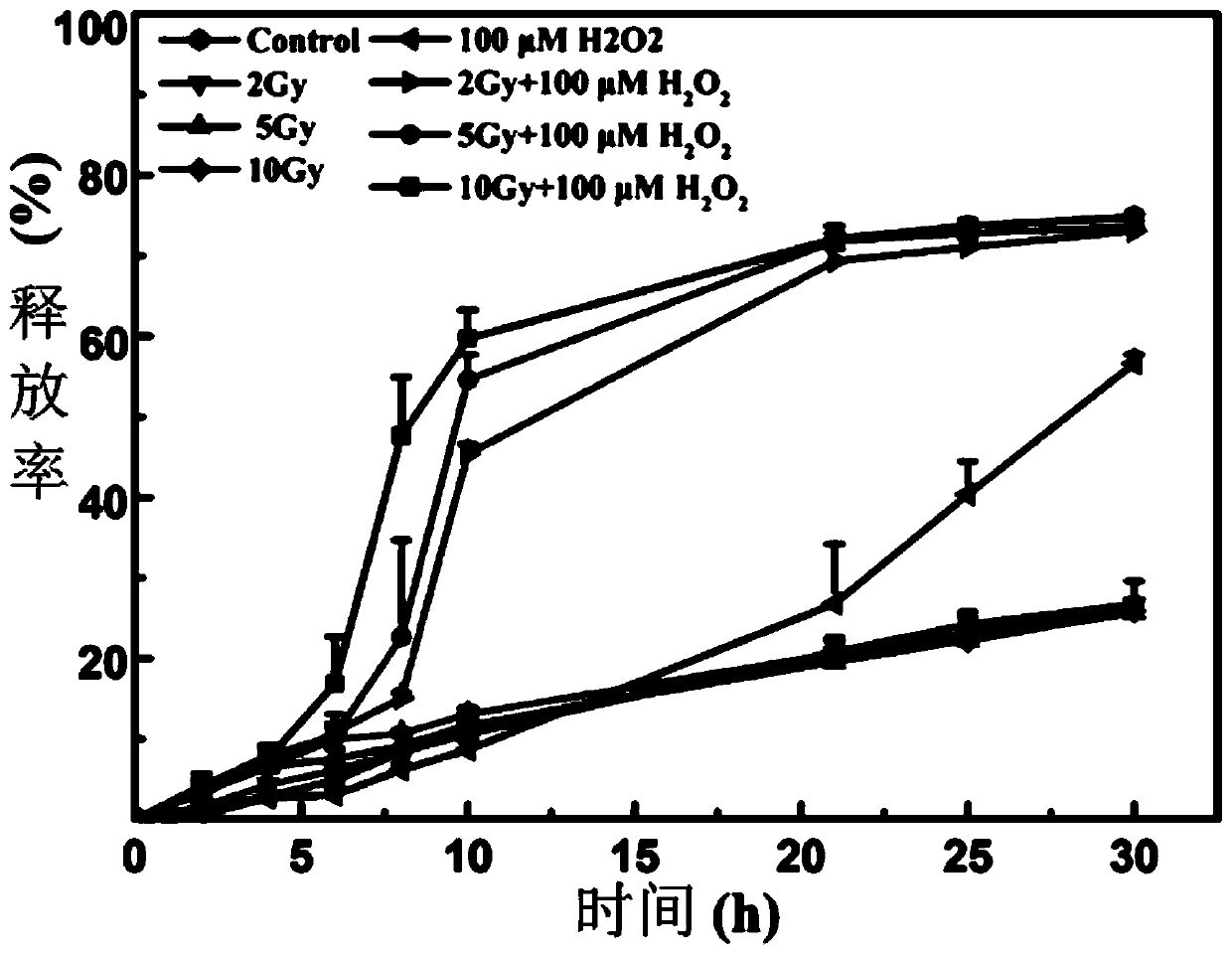
[0060] Nile red (NR) was loaded as a model compound to study drug release in vitro because of its 2 o 2 And high stability under X-ray conditions. image 3 In order to release NR from Nile Red-loaded nanoparticles (NR-NPs) in vitro under different conditions, the data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, n=3, specifically the PBS control group, simple X-ray irradiation group (2Gy, 5Gy and 10Gy), single H 2 o 2 Treatment group (100 μM), X-ray and H 2 o 2 Synergistic group (2Gy X-ray, 5Gy X-ray, 10Gy X-ray use 100μM H 2 o 2 co-treatment); the X-ray exposure dose used here is comparable in clinical practice, set H 2 o 2 The concentration (100 μM) matched the ROS level in the real tumor microenvironment; a fluorescence spectrophotometer, excited at 543 nm, was performed in the wavelength range of 500 to 700 nm to determine the content of NR. Interestingly, in all three groups irradiated with X-rays alone at different doses, the drug release behavior was not signifi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dispersity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com